|
|
Links |
|
Links |
|
|
|
Syllabus, Online Course |
|
|
|
|
Resources |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Social Injustice | ||
|
|
What is the difference btwn sex & gender? | ||
|
|
Intro to Feminism | ||
|
|
A Global Perspective on Gender | ||
|
|
Intro to Race & Ethnicity | ||
|
|
Racial & Ethnic Demographics | ||
|
|
Social Injustice Based on Social Differentiation | ||
|
|
Majority / Minority Patterns of Interaction: | ||
|
|
Causes of Contemporary Racial/Ethnic Inequality | ||
|
|
Causes of Sexism: | ||
|
|
Gender Socialization by the Social Structures ( AOSs ) | ||
|
|
Traditional Gender Roles | ||
|
|
"The Rules" | ||
|
|
Gender Socialization at Work | ||
|
|
Effects of Sexism | ||
| Theoretical Issues | |||
|
|
Functionalism on Gender | ||
|
|
Conflict Theory on Gender | ||
|
|
Defeating racism | ||
|
|
Defeating sexism | ||
|
|
Affirmative Action | ||
|
|
Affirmative Action Backlash | ||
|
|
Socio Historical Analysis of Gender Relations: | ||
|
|
Gender in Hunter Gatherer Societies | ||
|
|
Gender in Pre Empire Era: Morgan: Development of the Patriarchal Family | ||
|
|
Industrial Age: 1st Wave Feminism | ||
|
|
Industrial Age: Suffragettes | ||
|
|
Post Industrial Society: "The New Woman & the New Man" | ||
|
|
Socio Historical Analysis of Race Relations: | ||
|
|
Race in Hunter Gatherer societies | ||
|
|
Race in the Pre Empire Era | ||
|
|
Race in the Middle Ages | ||
|
|
Race in the Early Industrial Age | ||
|
|
Race in the Industrial Age | ||
|
|
Race under Global Capitalism |
|
|
Links |
|
Links |
|
| Many people use the terms sex & gender interchangeably, however, social scientists consider the two terms to have different meanings | |||
| SEX | |||
|
|
Sex is the biological categorization of male, female, "other" |
|
|
| Sex refers to the physical characteristics that make a person male or female | |||
|
|
Less than 1 % of the population has major physical characteristics of both male & female | ||
|
|
Much of the population has minor physical characteristics of both males & females such as seen in the TV show "He's a Lady" | ||
| GENDER | |||
|
|
Gender is the social category of male, female, other |
|
|
|
|
Gender socially learned traits associated w/, & expected of men or women | ||
|
|
Gender refers to the personal traits & social positions that members of a society attach to being female & male | ||
| Gender refers to a sense of being male or female or having the recognizable traits of one's sex | |||
| Biologically, men & women differ in limited ways, but culture can define the two sexes in dramatically different ways | |||
| Social indicators of gender have changed over time:
Long/short hair Skirts/pants What are some other social indicators? |
|||
| Biological indicators of sex have changed as, for example, women are now over 1 inch taller than 30 yrs. ago | |||
| It is important not to think of social differences btwn the sexes exclusively in biological terms | |||
| THE SOCIAL SCIENCES, GENDER, & SEX | |||
| Sociology of gender is the study of socially constructed female & male roles, relations, & identities | |||
| Feminist theory is the study of woman centered patterning of human experience |
|
||
|
|
Today there is a growing sociology of gender on masculinity |
|
|
| Characteristics & behavior generally associated w/ being a male are called masculine | |||
| Characteristics & behavior generally associated w/ being a female are called feminine | |||
| The development of sexuality is influenced by two major forces related to gender: gender identity & gender role | |||
| Gender identity is a personal sense that "I am a male" or "I am a female" | |||
| Gender identity develops partly from biological influences, such as body shape & genitals, & partly from cultural influences, including clothing & hairstyle | |||
| Gender role refers to a society's expectations for males & females, including values, attitudes, & behavior | |||
| Individuals develop these expectations w/ the influence of parents, friends, & teachers, as well as television, motion pictures, & other sources | |||
|
|
SEX & THE BODY | ||
| Primary sex characteristics refer to the organs used for reproduction, namely the genitals | |||
| Secondary sex characteristics are bodily differences, apart from the genitals, that distinguish biologically mature females & males | |||
| The term inter sexual people refers to people whose bodies (including genitals) have both female & male characteristics | |||
| An older term for inter sexual people is hermaphrodite | |||
| Transsexuals are people who feel they are one sex even though biologically they are the other |
|
Links |
|
Links |
|
| - Project: Feminists R' Us |
|
||
|
|
- Project: Song: "I Am Woman" & Social Theory |
|
|
| - Song: "I Am Woman" by Helen Reddy 3:16 |
|
||
| FEMINISM IS A SOCIAL MOVEMENT & IDEOLOGY SUPPORTING EQUALITY BTWN MEN & WOMEN | |||
| Feminism is the advocacy of social equality for men & women, in opposition to patriarchy & sexism | |||
| A primary belief of feminists is that an equal share of resources/benefits should go to each according to abilities | |||
| A small % of women ( less than 10 % ) will admit to being feminist, while a large % of women ( over 90 % ) actually subscribe to it's tenants |
|
||
| Nearly as many men as women are feminists | |||
| FEMINIST THEORISTS ARE A CENTRAL PART OF FEMINISM, IT IS
CHARACTERISTIC OF IT'S MORE EXTREME BRANCH,
FEMINIST PRAGMATISTS MAKE UP THE OTHER MORE MAINSTREAM BRANCH |
|||
| Feminist theory is the study of woman centered patterning of
human experience
Much of social theory, history, philosophy, etc., has excluded women & women's ideas Feminism reinterprets patriarchal theory & history Because of feminist theory, there is a growing literature on masculinity |
|
||
| Feminist doctrine suggests that women are systematically disadvantaged in modern society & in response to this, advocates equal opportunities for men & women | |||
| Feminist sociologists have argued that conventional sociologists have neglected the significance of women in all areas of the subject | |||
| For example, many studies of social stratification have defined a family's class position based on the wages of the male "head of household" & this ignores the fact that women make economic contributions to their families from work both inside & outside the home | |||
| Typical studies of strat often assume that women have equal access to the wages their husbands earn | |||
| Masculinist theory is the study of the development of non patriarchal
theory
Some social theorists hold that all theory, except for feminist theory, is masculinist Much social theory is patriarchal in that women & other groups are omitted |
|
||
| THE FEMINIST REINTERPRETATION IS WOMEN'S REEXAMINATION OF THE WORLD BASED ON GENDER |
|
||
| - Marx's reinterpretation reinterpreted the world based on class struggle |
|
||
| - The deconstructionists reinterpreted the world based on removing the bias of rationalism |
|
||
| - Deconstruction is the examination or pulling apart of traditional views, showing its gaps, flaws, etc. | |||
| - Part of any reinterpretation is deconstruction which is the examination or pulling apart of traditional views, showing its gaps, flaws, etc. | |||
| Feminists' reinterpretation of the world follows the Marxists' reinterpretation | |||
| Marx said that one's world view (explanation of the world) is shaped by their position in that world | |||
| Marxists & Weberians reinterpreted the world based on economics/status/power | |||
| Women have reinterpreted the world based on gender | |||
| This is to say that women & men see things differently & that women are reintegrating women's thoughts into theory & practice | |||
|
|
Part of any reinterpretation is deconstruction, which is the examination or pulling apart of traditional views, showing its gaps, flaws, etc. | ||
| Deconstruction uses a variety of post-modern methods utilizing literature, philosophy, history, etc. | |||
| THE FEMINIST PRINCIPLES SEEK TO END THE OPPRESSION OF WOMEN & ESTB EQUALITY BTWN THE SEXES | |||
| There are common principles of feminist theory: |
|
||
| 1. Women & the experiences of women are a key starting point for social theory & understand the world |
|
||
| 2. Adding feminist insights to traditional theory complements/competes it |
|
||
| 3. Feminist theory must be innovative/radical because major changes are needed |
|
||
| 4. Men oppress, either directly or structurally |
|
||
| - Violence against women both in the home & on the street is all too common | |||
| - The commercialization of sexuality exploits women, & today, men | |||
| - The gender wage gap & the glass ceiling are significant & tenacious | |||
| 5. Feminism seeks to end sexual violence | |||
| 6. Feminist theory has a goal which is equality btwn the sexes |
|
||
| - A primary belief of feminists is that an equal share of resources/benefits should go to each according to abilities | |||
| 7. Feminism seeks to eliminate gender stratification | |||
| 8. Feminist theory seeks to produce a better world for women, & thus for all |
|
||
| 9. Feminist theory must be interdisciplinary |
|
||
| 10. Feminism seeks to expand human choice for all | |||
| 11. Feminism promotes sexual freedom | |||
|
|
FEMINISM SEEKS TO MODIFY TRADITIONAL WOMEN'S ROLES TO GIVE THEM EQUALITY & POWER | ||
| Traditional gender roles: To a greater or lesser extent, we each exhibit, or can relate to traditional gender roles | |||
| Gender socialization: Socialization is highly gender oriented & it is done primarily through the social structures | |||
| The feminist sociology of knowledge accents the importance of recognizing silenced knowledge & ways of knowing | |||
| The stratification of gender in status, power, & income was non-existent in hunter gatherer society, was the greatest in the patriarchal societies of feudalism & early industrialism, & now appears to be declining in industrial & post-industrial societies | |||
| While in common usage, there is little distinction made btwn sex & gender, in the social sciences the former indicates the biological category of female or male while the latter indicates the social traits of female or male commonly attributed to a particular sex | |||
|
|
The solutions to sexism lie in both individual & societal level initiatives | ||
| PATRIARCHY IS A FORM OF SOCIAL ORGANIZATION IN WHICH MALES DOMINATE FEMALES | |||
| Matriarchy is a form of social organization in which females dominate males | |||
| The Matriarchy form OF society has never been documented in human history | |||
| Patriarchy is not inevitable because modern technology has eliminated most of the historic justifications for it | |||
| THE TYPES OF FEMINISM OF FEMINISN INCLUD LIBERAL, SOCIALIST, RADICAL, & OTHERS | |||
| Although feminists agree on the importance of gender equality, they disagree on how to achieve it | |||
| Liberal feminism is rooted in classic liberal thinking that individuals should be free to develop their own talents & pursue their own interests. | |||
| Socialist feminism regards capitalism as increasing patriarchy by concentrating power in the hands of a small number of men | |||
| Radical feminism finds liberal feminism inadequate, believing that gender equality will be achieved only through the elimination of gender itself. | |||
| OPPOSITION TO FEMINISM WAS CREATED BY THE BACKLASH OF MEN & WOMEN OPPOSING STRONG, FREE WOMEN | |||
| Opposition is primarily directed at the socialist & radical forms of feminism, while support for liberal feminism is widespread | |||
| There is a trend toward greater gender equality |
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
|
|
Supplement: Females in World Legislatures |
|
|||
| THE ISRAELI KIBBUTZ |
|
||||
| In Israel, collective Jewish settlements are called kibbutzim |
|
||||
| Members of kibbutzim consider gender irrelevant to most of everyday life |
|
||||
| MARGARET MEAD'S RESEARCH ON GENDER |
|
||||
| Anthropologist Margaret Mead carried out groundbreaking research on gender, determining that gender varies across cultures |
|
||||
| Among the Arapesh, both sexes would be described by Americans as feminine |
|
||||
| Among the Mundugumor, both sexes would be described by Americans as masculine |
|
||||
| Among the Tchambuli, by American standards, gender roles are reversed | |||||
| Critics charge that Mead oversimplified the implications of gender | |||||
| GERORGE MURDOCK'S RESEARCH | |||||
| George Murdock surveyed over 200 societies & found substantial but not complete agreement concerning which tasks are feminine or masculine | |||||
| The wide variation in task demonstrates that what is considered to be female or male is mostly a creation of society | |||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
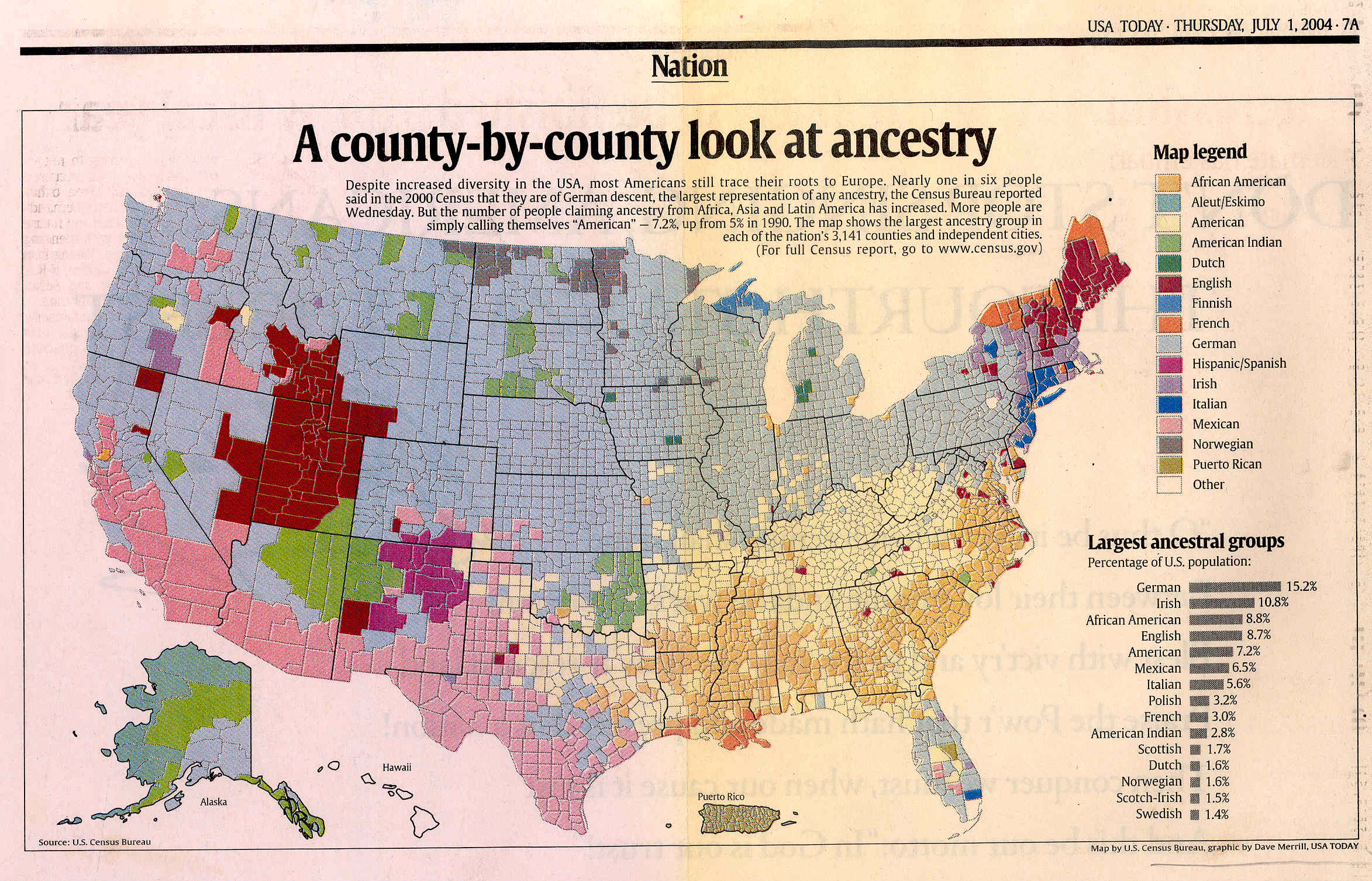
The Pie Chart on the 2000 Census Data on Race in the US
The Pie Chart on the 2000 Census Data
on Race in the US shows that we are made of of 63% whites, 13% blacks,
13 % Hispanics, 4 % Asians, & others
|
|
Pie Chart on the Demographics of US Hispanics, 2002
|
 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
| Social scientists describe interaction btwn majority & minority members of a society in terms of the several models, including: pluralism, assimilation, segregation, genocide |
|
||||
| PLURALISM |
|
||||
| Pluralism is a state in which racial & ethnic minorities are distinct but have social parity |
|
||||
| The US is pluralistic to the extent that all people have equal standing under the law, but it also has non pluralistic characteristics |
|
||||
| ASSIMILATION |
|
||||
| The term assimilation to describe the process by which minorities gradually adopt patterns of the dominant category of people |
|
||||
| The degree of assimilation in the US varies by the category of people by race, ethnicity, religion, nationality, etc. |
|
||||
| Assimilation in the US has occurred more rapidly for grps defined by ethnicity than race |
|
||||
| For racial traits to diminish over generations requires miscegenation, biological reproduction by partners of different racial categories |
|
||||
| SEGREGATION |
|
||||
|
|
Segregation is the physical & social separation of categories of people |
|
|||
|
|
Segregation may be voluntary, but it is usually imposed |
|
|||
| Segregation by race & ethnicity was legal in the US until the Civil War & then many laws were passed to keep segregation legal | |||||
| The Civil Rights Mvmt of the 1950s & 60s began to break down segregation laws & norms & this process of desegregation continues today | |||||
|
|
GENOCIDE |
|
|||
|
|
Genocide is the systematic killing of one category of people by another |
|
|||
|
|
Genocide has been used throughout history but was made illegal after WW 2 |
|
|||
|
|
Despite the illegality of genocide, it still occurs today w/ one of the major genocides of the 2000s taking place in Darfur, a region of Sudan in NE Africa |
|
|||
|
|
ETHNIC CLEANSING |
|
|||
|
|
Ethnic cleansing is the process of removal of a people from an area by either forced relocation or genocide |
|
|||
|
|
Like segregation, ethnic cleansing can be voluntary or involuntary, but is usually involuntary |
|
|||
|
|
Ethnic cleansing has occurred recently in the Balkan region (the former Yugoslavia), & may be occurring in the late 2000s in Iraq |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Links |
|
Links |
|
| - Project: Which Traditional Gender Roles Shall We Keep? |
|
||
| I
DO NOT approve of these roles!
The following roles are considered 'traditional' in that they existed, more or less, in the past However, as you should recognize, they still exist to a great extent today This analysis does not suggest that this is the way things should be Non-traditional androgynous roles are developing Non-traditional heterogeneous roles are developing The point is, even if one is not like these roles, & knows no one who is, we can still recognize them These roles are still very much a part of our culture & thus, a part of each person |
|
||
|
|
There are SIX major types of traditional gender roles 1. Traditional Male Role 2. Traditional Female Role 3. Traditional Male Worker Role 4. Traditional Female Housewife Role 5. Men's Traditional Relations w/ Women 6. Women's Traditional Relations w/ men |
|
|
|
|
1. THE TRADITIONAL MALE ROLE IS THAT OF A CONTROLLER |
|
|
|
|
Men are
- unemotional: i.e., "emotional idiots" in that they don't talk about or understand feelings - leaders, take control, & make decisions - active, worldly, & aggressive - blunt, loud, & a bit sloppy |
|
|
|
|
2. THE TRADITIONAL FEMALE ROLE IS THAT OF A COMPANION |
|
|
|
|
Women are
- "emotional" i.e. out of control emotional, no quantitative thinking - dependent, followers, & cannot make decisions - neat, considerate, appearance is primary - pushy/ aggressive |
|
|
| Traditionally, women's status is product of what they are not what they do | |||
| Boys are sometimes so negative toward the traditional female role that even girls look down upon it as a result | |||
| In terms of income, wealth, status, power, & free time, all indications are that traditional sex roles work to the advantage of men | |||
| 3. THE TRADITIONAL MALE WORKER ROLE IS THAT OF THE LEADER OR WORKER | |||
|
|
- provide for family, & put job above all else
- provide for a wife & family - put the job & success above all else - be strong & successful |
|
|
|
|
A man's status is measured primarily by his income & occupational status |
|
|
| Men typically create an identity, their master status, via an occupation because a man w/o a job is no man, is not "marriage material" | |||
| In early American history, both men & women engaged in the production of goods to be sold, but as the industrial revolution progressed, some women were relegated to the home | |||
| There is no male equivalent word of "bitch," only words such as shark, go getter, etc. | |||
| 4. THE TRADITIONAL FEMALE WORKER ROLE IS THAT OF THE HELPER | |||
|
|
- enjoy nurturing & serving
- enjoy housework, because it is not "real work" - revel in motherhood because a women w/o children is no woman & is not "marriage material" |
|
|
| The role of housewife, which typifies the dominant role of middle class American women in the early & mid 20th C, is a rather recent invention |
|
||
| The housewife role, as it developed historically, was largely the realm of white middle class women |
|
||
| The housewife role fit well w/ the Victorian morality that reigned through much of the Industrial Revolution |
|
||
| Women experience a double standard in that an aggressive woman, in the home or at work, may be called a "bitch" | |||
|
|
Recently, social scientists have noted the shifting double standard where women become proud of their aggressiveness as seen in the bumper sticker: "I am bitch, hear me roar! adapted from the 1970s Helen Ready song: "I am woman, hear me roar!" | ||
| Time budget studies indicate that full time working mothers interact w/ their children about as much as do full time housewives, although housewives may spend more time on care related tasks |
|
||
| The housewife role, so ingrained in American society, is far from universal, is not the norm in the Russia, or in many Asian countries |
|
||
|
|
Despite all the recent changes in the roles of men & women, most boys & girls still plan on seeking jobs that have traditionally been held by persons of their sex |
|
|
| The housewife role is a product of Industrial Revolution which created the ideology of women as a frail consumers, replacing their co worker roles of prairie wife & merchant wife | |||
| The housewife role fit w/ Victorian morality that women are fragile & more moral | |||
| In early America & earlier, men & women were equal in what they produced & brought value to the home such as during the hunter gatherer society & the Little House on Prairie society of the pre industrial era | |||
| The Industrial Revolution separated family members from each other | |||
| Beginning w/ the Industrial Revolution, men went out of the home to work | |||
| Beginning w/ the Industrial Revolution, women stayed in home to have kids & keep house, but not to "work" | |||
| The Industrial Revolution created the role of the breadwinner & the family wage | |||
| Henry Ford is credited w/ coining the concept of the family wage, & institutionalizing it in modern industrial society, although the concept was in widespread use before Ford | |||
| Many industrial leaders in the US & Europe believed that it was their responsibility to develop the morals of their workers, & they generally advocated conservative, traditional family values | |||
| Beginning w/ the Industrial Revolution, men became responsible for production & women became responsible for consumption | |||
| “I'll bring home the bacon & she'll cook it up in the pan”
Paula Cole: “You'll pay all the bills, & I'll do the laundry” |
|||
|
|
5. MEN'S TRADITIONAL RELATIONS W/ WOMEN IS THAT OF THE INITIATOR |
|
|
|
|
Men's traditional relations w/ women include that they:
- are worldly - initiate relations & sex - are unemotional - are expected to be sexual & enjoy sex - are the aggressor - are expected to be sexually experienced - are active - care little for intimacy |
|
|
|
|
The double standard can be seen in that there is no male adjective of "slut" & being a gigolo is almost respectable, while being a prostitute is not | ||
| Sattel, 1989, & other sociologists found that men withhold their true feelings from their partners because to admit their feelings would make them vulnerable | |||
|
|
6. WOMEN'S TRADITIONAL RELATIONS W/ WOMEN IS THAT OF THE RECIPIENT |
|
|
|
|
Women's traditional relations w/ men include that they
- are emotional - do not initiate; they try to entice - are dependent - are expected to be a virgin - are not expected to be sexual or enjoy sex - believe intimacy is most important part of a relationship - must live w/ the double standard where female sexual experience equates w/ "sluttiness" |
|
|
|
|
The double standard can be seen in that men are expected to be sexually experienced, while women are not in that a sexually experienced woman is seen as a slut, while a sexually experienced man is just that, experienced |
|
|
| Historically there have only been culturally negative terms for a woman who was sexually active / aggressive, including such terms as whore, slut, tainted woman, fallen women, etc. | |||
| In the mid 2000 possibly the first culturally positive label is coined for a woman who is sexual or sexually aggressive | |||
| Cougar is the label given to older women who are sexually active / aggressive | |||
| As a result of the positive label of cougar for older women, younger women who are sexually active / aggressive are being called kittens or cubs | |||
|
|
"The Rules" by Fein & Schneider | ||
|
|
The concept of cultural lag holds that dysfunctional roles will fade away, but will they? | ||
| Non-traditional or new roles for men & women include the male househusband role, the female worker role, & nontraditional relations btwn women & men | |||
| Women of the Early Industrial Era | |||
| The Industrial Era | |||
| 1st Wave Feminism |
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
| - Project: Which Traditional Gender Roles Shall We Keep? |
|
||||
| "The Rules" demonstrate that traditional gender roles are still in existence | |||||
| "The Rules" & traditional gender roles demonstrate the principle of cultural lag | |||||
| 1. Be a Creature unlike any other |
|
||||
| 2. Show up to parties, dances & social events even if you do not feel like it |
|
||||
| 3. It's a fantasy relationship unless a man asks you out |
|
||||
| 4. In an office relationship do not email him back everytime he emails you unless it is business related |
|
||||
| 5. If you are in a long distance relationship, he must visit you at least three times before you visit him |
|
||||
| 6. When considering whether to use ads or other personal dating services, you should place the ad and let the men respond to you |
|
||||
| 7. If he does not call, he is not that interested. Period. |
|
||||
| 8. Close the deal-- women do not date men for more than two years |
|
||||
| 9. Buyer beware-- observe his behavior so you do not end up with Mr. Wrong |
|
||||
| 10. Keep doing The Rules even when things get tough |
|
||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
| Sexism is the belief that one sex is innately superior to the other |
|
||||
| Sexism underlies patriarchy & harms men, women, & the society as a whole |
|
||||
| Sexism stunts the talents & limits the ambition of women, who represent half the population |
|
||||
| Although men benefit in some respects from sexism, privilege comes at a high price, especially in terms of intimacy & trust |
|
||||
| VIOLENCE AGAINST WOMEN |
|
||||
| Family violence is still frequently directed at women |
|
||||
| Gender violence is also an issue on college & university campuses |
|
||||
| Off campus or on campus, most gender linked violence occurs in the home |
|
||||
| Violence toward women also occurs in casual relationships |
|
||||
| In global perspective, violence against women is built into other cultures in many different ways |
|
||||
| VIOLENCE AGAINST MEN |
|
||||
| If our way of life encourages violence against women, it may encourage even more violence against men |
|
||||
| Our culture tends to define masculinity in terms of aggression & violence |
|
||||
| While feminists & others track the violence of men against women to the best of their ability, male on male violence is not tracked unless it occurs such that it comes to the attn of the CJS | |||||
| SEXUAL HARASSMENT |
|
||||
| Sexual harassment refers to comments, gestures, or physical contact of a sexual nature that are deliberate, repeated, & unwelcome | |||||
| Women are more likely to be sexually harassed than are men | |||||
| Some harassment is blatant, but much of it is subtle | |||||
| Feminists define pornography as a form of sexual violence against women, arguing that it demeans women & promotes rape | |||||
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
| A functional analysis of gender suggests that traditional sex roles emerged in hunting & gathering societies where they promoted the efficient functioning of the family |
|
||||
| Each sex plays a role that complements the role played by the other, w/ men taking the instrumental part & women the expressive |
|
||||
| DURKHEIM ON GENDER | |||||
| With roots in anthropology, Durkheim was well aware that women take on very many different roles in different societies & that women's roles have changed over time | |||||
| In relation to functionalism on gender, w/ roots in anthropology, Durkheim was well aware that women's roles have changed over time | |||||
| Applying the concepts of modernization & the development of mechanical solidarity, Durkheim's theory supports feminist goals to the extent that fostering the interdependence of members & parts of society regardless of organic / traditional constraints mandates that women function to the full extent of their true capacities | |||||
| PARSONS & GENDER COMPLEMENTARITY |
|
||||
| Parsons argued that gender role complementarity helps to integrate society |
|
||||
| girls & boys are socialized into expressive & instrumental roles respectively |
|
||||
| social control reinforces gender linked behavior |
|
||||
| CRITIQUE |
|
||||
| The functionalist analysis of gender is criticized for ignoring the fact that many women have had to work outside the home out of necessity |
|
||||
| The functionalist analysis of gender ignores the personal strains & social costs produced by rigid gender roles |
|
||||
| Functionalism is often criticized for supporting the status quo, but this is more the result of the individuals such as Parsons who applied the theory w/ their own predilections, & not necessarily inherent in the theory itself |
|
||||
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
| Conflict analysis explains contemporary sex roles in terms of dominance, subordination, & sexism |
|
||||
| CONFLICT THEORY ON GENDER & OTHER CONTEMPORARY ISSUES | |||||
| While conflict analysis has it's roots in Marxism & thus class conflict based on economic exploitation, it has been usefully applied by many social theorists to gender, race & many other social problems |
|
||||
| Thus conflict theory has been generalized so that it may be usefully applied to any social conflict |
|
||||
| Some social scientist question which conflict is the conflict, i.e. is at base the most fundamental conflict: economic, race, gender, religion, etc. |
|
||||
| While the debate over the most fundamental conflict is important in some decisions, for most people & social change orgs, more important questions lie w/in the social problem / change they are dealing w/ |
|
||||
| MORGAN, ENGELS & MARX ON GENDER |
|
||||
| See Also: The Origin of the Family, Private Property & the State by Friederich Engels & Karl Marx, 1884 | |||||
|
|
See Also: Morgan on the Development of the Patriarchal Family | ||||
| Morgan, Engels & Marx believed that capitalism intensified male domination because it allowed the concentration of wealth in the hands of males, esp upper class males |
|
||||
| Patriarchy & the monogamous family began when civilization began, which began when agriculture was well established |
|
||||
| Patriarchy & the monogamous family created the first surplus of goods which could be bequeathed |
|
||||
| Men established monogamy & patriarchy so that they could control their wealth, who their heirs were, & what they would receive |
|
||||
| Before the production of a surplus, bequeathal follow female lines (matriarchy) while after the production of a surplus, bequeathal followed male lines (patriarchy) |
|
||||
| Men gained power over women by controlling agriculture, war, husbandry, & bequeathal |
|
||||
| These new relationships of patriarchy & strict monogamy created what Marx & Engels called "The historic defeat of women" |
|
||||
| CRITIQUE OF CONFLICT THEORY ON GENDER |
|
||||
| This view has been criticized for casting conventional families as morally evil & for minimizing the extent to which people live happily in families | |||||
| This view has been criticized for arguing, perhaps falsely, that capitalism stands at the root of gender stratification | |||||
| However, there is little doubt among social scientists that family structure does play an important role in patriarchy as well as other forms of social exploitation | |||||
|
|
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
| Executive Order 11375, signed by President Johnson, established Affirmative Action in 1967 |
|
||||
| The various executive orders calling for affirmative action are an attempt to compensate for past discrimination through hiring quotas, preferential consideration, or active recruitment of women or minority workers | |||||
| The aim of Affirmative Action is to prevent institutional discrimination: It is believed that non-white & females are sufficiently qualified but are less qualified than typical white males who have access to the best preparatory schools |
|
||||
| EO 11375 mandated the Federal Office of Contract Compliance to issue govt purchasing contracts only to orgs that are making efforts to remedy the effects of past discrimination |
|
||||
| EO 11375 affected much more than govt orgs because many orgs sell at least some of their products to the fed govt, & therefore they had to comply w/ Affirmative Action rules or loose all govt contracts |
|
||||
| Defense contractors, utilities, computer & electronic manufacturers, & many other businesses have been forced to develop affirmative action plans |
|
||||
| Affirmative Action plans give preference to minorities or women if the purpose of the plan is to erase "a manifest imbalance in traditionally segregated job categories" |
|
||||
| Affirmative Action plans can be instituted voluntarily by an employer or jointly by an employer & a union |
|
||||
| Affirmative Action plans can be brought about as a result of a discrimination lawsuit |
|
||||
| The majority of Affirmative Action plans are adopted by large firms w/ a white collar labor force |
|
||||
| Such plans have the potential to redistribute some desirable jobs to previously excluded female & minority workers |
|
||||
| Many plans are extremely modest & call for only minimal adjustments as necessitated by law |
|
||||
| Most small firms lack Affirmative Action plans & thus minorities & women continue to face significant limits in these sectors |
|
||||
| A study of the Sex Discrimination Act of 1975 in Britain found that its main effect was to eliminate overt discrimination in recruiting, especially in job advertisements |
|
||||
| The study also found that there was little change in the allocation of training & promotions |
|
||||
| Over half the orgs surveyed in the study had acted to minimize their compliance |
|
||||
| Thus in Britain, Affirmative Action did not eliminate discrimination, & minorities & females are not equally represented at any level in the workforce; furthermore, they are over represented at the lower levels, & under-represented at the middle levels, & extremely under-represented at the upper levels of employment |
|
||||
| Never the less, Affirmative Action has had positive consequences for some female & minority workers & has helped break down sexual & racial hiring barriers |
|
||||
| Affirmative Action legislation has encouraged the creation of decentralized state, county, municipal & org Affirmative Action plans | |||||
| Many firms have focused on placing minorities & women in highly visible positions to implement affirmative action | |||||
| The wages of Black college grads have risen faster than those of White college grads, but are still behind | |||||
| The wages of Black high school grads have fallen even further behind White high school grads | |||||
| Thus, Affirmative Action has helped created a Black middle class, but has done little to help the large Black underclass, & has barely broken "the glass ceiling" of upper level jobs | |||||
| Inequality in wages by race has been exasperated by the concentration of Blacks & Hispanics in regions & urban areas w/ high unemployment | |||||
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
| As a matter of fact, social movements usually generate an opposition social movement |
|
||||
| At the beginning of a social movement, the status quo forces attempt to stem the institutionalization of the new social relationships | |||||
| If the new social movement can prevail, it becomes an accepted feature of society, & the status quo opposition must contend w/ defeat | |||||
| As the social movement becomes institutionalized & accepted in society, it may either become complacent & weak, it may over reach its original goals & therefore lose supporters, it may be so successful that it is no longer needed, or it may be so successful that it re energizes its opposition | |||||
| Because of the social tendency to create counter movements, it was inevitable that at some point a white backlash would occur against Affirmative Action & Civil Rights |
|
||||
| Supporters of affirmative action claim that it is so successful that it re energized its opposition while opponents of affirmative action claim that it has overstepped its bounds & it is no longer needed, thus re energizing its opposition |
|
||||
| Affirmative action has sparked resistance from Whites & men who believe they are being deprived of opportunities because of increased opportunities for minorities & women | |||||
| 30 years of affirmative action has not eradicated the inequalities resulting from 300 yr.. of legal restrictions on Blacks in America & thousands of years of gender based inequality | |||||
| The increasing economic stress in the developed world has made all people less sympathetic to the problems of minorities & women | |||||
| It is well known that all forms of discrimination increase during economic, political, etc. hard times | |||||
|
|
See Also: The Causes of Discrimination | ||||
| A backlash against civil rights has come in the form of an attack on affirmative action, Title IX, & support for school vouchers | |||||
| In the 1980s, the Berkeley Medical School is sued over Affirmative Action on the premise that it is admitting under qualified minorities in lieu of more qualified Whites | |||||
| A White male lost the Berkeley Medical School case, but his cause energized affirmative action opponents | |||||
| In the 1990s, affirmative action opposition coalesced & Clinton attempted to balance the opposition & the supporters w/ the policy of "Mend it, don't end it" | |||||
| While some maintain that affirmative action was essentially ended under Clinton, other believe it was kept alive; regardless, affirmative action is much less practiced today | |||||
| In 2002, the Supreme Court rules that the University of Michigan may not use affirmative action admittance procedures but can seek to maintain a diverse student body, in essence offering a split decision | |||||
| Affirmative action supporters makes FOUR points |
|
||||
| a. The "playing field" is not level
New cases of race discrimination in workplace are reported everyday Minorities face discrimination in education which translates into discrimination at work |
|
||||
| b. Affirmative action is fair because hiring is an inexact science & it's difficult to choose the "most qualified" person |
|
||||
| Affirmative action supporters make the point that hiring is an inexact science & it's difficult to choose the "most qualified" person & it is in these cases where quotas can be used | |||||
| c. Affirmative action does work as evidenced by the fact that we are gaining a non-white Middle Class & that women's wages are increasing as a percentage of men's wages |
|
||||
| d. Affirmative action is possibly the weakest form
of restitution
In the US, because whites have benefited from centuries of racism & men have benefited from centuries patriarchy, there is a debt owed |
|
||||
| Affirmative action is applied only to orgs doing govt contracts & thus has little effect on smaller firms |
|
||||
| Under affirmative action rules, orgs w/ govt contracts must develop plans to rectify "manifest imbalances" in race or gender inequities in the workplace |
|
||||
| Affirmative action can be voluntary or court ordered & quotas were possible but infrequent, & they are not legal today |
|
||||
| Overall the effect of affirmative action has been minimal because orgs minimized their compliance |
|
||||
| Affirmative action & other factors have created a Black middle class, but affirmative action has not had a great effect overall | |||||
| Affirmative Action Opposition made THREE points |
|
||||
| a. For the opponents of affirmative action because the playing field is now level, affirmative action is no longer needed |
|
||||
| b. For the opponents of affirmative action, affirmative action is unfair to Blacks & Whites because it allows the hiring of under qualified people & does not allow the hiring of most qualified person |
|
||||
| c. For the opponents of affirmative action, affirmative action does not work because it does not serve to help minorities |
|
||||
| The opposition to affirmative action can be seen in the beliefs of some sub-cultures of the White population that every employed Black they encounter owes his or her job to federal pressure rather than to personal qualification & efforts (Jencks, 1985) |
|
||||
| The fate of civil rights in general & affirmative action in particular depends to a significant extent on the political climate in the next decade | |||||
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
| INTRODUCTION: Note in this historic overview that sexism & patriarchy do not develop until "civilization" begins, circa 13,000 to 4,000 BC. Thus humans have spent 99+% of existence in non-sexist society. Thus, those who say that male domination is "natural" are mistaken | |||||
|
|
1. GEOLOGIC ERA
5 bb - 5 mm |
Socio Biology | Earth formation
- early primates |
||
|
|
2. PRE HUMAN ERA
5 mm - 1.5 mm |
"The sex contract" | Early primates | ||
|
|
3. HUNTER
GATHERER SOCIETY 1.5 mm - 10 K BC |
During the Hunter Gatherer Era, there was gender equality in
that there was little or no patriarchy or sexism
Gender & Racial Equality has existed for over 99 % of human existence |
Early humans: 99 % of
human existence has occurred in hunter gatherer society |
||
|
|
4. PRE EMPIRE ERA
10 K BC - 3 K BC |
Patriarchy & sexism began | "The historic defeat of women." | ||
| Morgan: The Origin of Patriarchy | |||||
| Marx & Engels: The
Origin of the Family, Private Property
& the State |
|||||
|
|
5. EARLY EMPIRES
3 K BC - 200 BC |
Women in the Ancient World | Women & others as chattel
Some Women have power |
||
|
|
6. ROMAN ERA
200 BC - 500 AD |
Women in the Roman Era | Some Women attain power | ||
|
|
7. MIDDLE AGES
500 - 1300 |
Women in the Middle Ages
( Modern form of Racism begin ) |
Romantic love develops | ||
|
|
8. EARLY
INDUSTRIAL AGE 1300 - 1700 |
Mutual & reward:
- marriage develops - romance develops - sexuality becomes more widespread - companionship develops ... as patriarchy recedes |
- Pre Enlightenment era
- Frontier Women - Women work in factories - Housewife role of develops |
||
|
|
9. INDUSTRIAL AGE
1700- present |
First Wave Feminism develops | Enlightenment thinkers
Beginning of end of patriarchy Wollstonecraft, Martineau, Taylor |
||
| Suffragette movement develops | In 1920, US Women win the vote w/ the 19th Amendment | ||||
| Depression & WW II Era Women | Women return to work outside the home | ||||
|
|
10. GLOBAL
CAPITALISM 1910 - present |
Second Wave Feminism develops | Some Women experience true equality | ||
|
|
11. POST
INDUSTRIAL SOCIETY 1970 - |
The New Woman:
3rd Wave Feminism develops |
Many Women experience equality in the West | ||
|
Links |
|
Links |
IS09f
|
|
| - Project: Patriarchy, Matriarchy, & Equality in H-G Society & Today |
|
|
||
| THERE WAS A VERY HIGH LEVEL OF GENDER DIFFERENTIATION, BUT LITTLE GENDER DISCRIMINATION / PATRIARCHY |
FB MC TF \/ |
|||
| During the Hunter Gatherer Era, humanity lived in 100's of thousands of mostly isolated tribes | ||||
| Hunter Gatherer Societies, aka primitive communalism, have the major feature of | ||||
| Living by hunting & gathering
Only minimal agriculture, which developed at the end of this era Semi nomadism No accumulation of wealth Status achievement in "traditional" roles |
|
|||
| Most roles in Hunter Gatherer Society are ascribed, though increased status often served as a reward for achievement | ||||
| There was gender based division of labor in Hunter Gatherer Society | ||||
| In H-G society women & men had different, but essentially equal roles | ||||
| The major female roles in H-G Society include gatherer, herder, mother, sometimes leader (matrilineal), homemaker, medicine woman / religious leader (shaman, etc.), home defense | ||||
| WOMEN RAISED BABIES TO GIRLS & BOYS, & GIRLS TO WOMEN, BUT MEN RAISED BOYS TO MEN | ||||
| Many tribes used a matrilineal methods of tracing descent | ||||
| The major male roles in H-G society include hunter, sometimes leader, explorer, warrior, medicine man / religious leader (shaman, etc.), home defense | ||||
| Men raised boys to men | ||||
| Women brought in 70 % of the food, but the 30 % that men brought in by hunting was critical |
|
|||
| Men & women had equal status, power & privileges in Hunter Gatherer Society & because 99 % of human existence has occurred in Hunter Gatherer Society, therefore patriarchy, sexism, men controlling women IS NOT "natural" | ||||
| The roles of leader, doctor, shaman, defender are all male roles today, but they were definitely filled by both genders in Hunter Gatherer Society |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Links |
|
Links |
|
|
|
FIRST WAVE FEMINISTS WERE ACTIVE BEFORE & DURING THE ENLIGHTENMENT ERA ESTBING SOME OF THE FIRST RATIONALE FOR WOMEN'S RIGHTS |
|
|
| First wave feminism began during the Enlightenment | |||
| The women of the Enlightenment created a theoretical & practical basis for equal rights for women | |||
| First wave feminists repudiated sexist notions about women | |||
| First wave feminists advocated equal education & laid the foundation for the women's movement for the next few centuries | |||
| The Enlightenment, circa 1689 - 1789, was the awakening of modern ideas on freedom, science, religion, and early feminist thought, etc., aka the Age of Reason, & was one factor in the Fr Revolution of 1789 | |||
| See Also: The Enlightenment: | |||
|
|
LEADING FIRST WAVE FEMINISTS, E.G. WOLLSTONECRAFT, MARTINEAU, ET AL, ESTBED A STRONG SOC MVMT & RATIONAL FOR SUFFRAGE & EQUAL ED |
|
|
| Leading thinkers of first wave feminism include Wollstonecraft, Macauley, Martineau, Taylor, Tubman, Rousseau, et al | |||
| Mary Wollstonecraft, 1759 - 1797, in The Vindication of the Rights of Women, which was a response to Edmund Burke, held that women should have equal education | |||
| The Vindication of the Rights of Women an important book in the Enlightenment & for US Constitution | |||
| Catherine Macauley | |||
| Harriet Martineau, 1802 - 1876, fought for women's education | |||
| Harriet Taylor Mill, 1807 - 1858, was forced to live behind her husband, John Stuart Mill, but was the intellectual leader | |||
| John Stuart Mill, 1807 - 1873, was an important utilitarian philosopher | |||
| Harriet Tubman, 1820 - 1913, was a fugitive slave, underground railroad conductor, Union scout, & an Entrepreneur who founded two hospitals | |||
| Other Enlightenment ideas on women: | |||
| Rousseau wrote Emile & Sophy, in which he advocated sexist ideas though he is considered to be a progressive political philosopher |
|
|
|
Links |
|
Links |
||||
| Summary: Racism does not develop until significantly after "civilization" begins and racism, in it's modern form, does not develop until the early Middle Ages; thus humans have spent 99+ % of existence in non racist, societies & less than 1,000 yrs. of history w/ racism | ||||||
| 1. Geologic era | 5 bb BP -
5 mm BP |
Earth formation
- early primates |
Race &
Socio-Biology |
|||
| 2. Pre human evolution | 5 mm BP -
1.5 mm BP |
Old Stone Age
Early primates |
Races emerge | |||
|
|
3. Race relations in H-G society | 1.5 mm BP -
10k BC |
Mid Stone Age
Early humans |
Racial equality: 99 % of
human existence has
occurred in hunter gatherer society Racism has existed for less than 1 % of human existence |
||
|
|
4. Race relations in Pre empire era | 10K BC -
3k BC |
New Stone Age
Civilization dawns 1st ag & villages |
Slavery begins, based on punishment or conquest but not based on race ( Patriarchy & sexism begins ) | ||
|
|
5. Race relations in Early Empires Era | 3K BC -
200 BC |
Bronze Age
Egypt, Greece, China, etc. |
Slavery is common, but based on punishment or conquest, not race | ||
|
|
6. Race relations in Roman Era | 200 BC -
500 AD |
Rome rules W
China, India E |
Slavery is common, but based on punishment/conquest, not race | ||
|
|
7. Race relations in the Middle Ages | 500 AD -
1300 |
Fall of Rome to the Enlightenment | The Modern form of ideological Racism began & is justified by religion. During the Middle Ages Christian ideology justifies racism, & both are used to justify imperialism | ||
| Racism, as we know it today, began during the Middle Ages
Slavery & Racism before the Middle Ages may be thought of as Conquest Slavery, whereas after the Middle Ages it may be thought of at Ideological Slavery Thus, racism has existed for less than 1 % of human existence |
||||||
|
|
8. Race in the Early industrial age | 1300 -
1700 |
Renaissance
Reformation Enlightenment |
Modern international slave system begins. As society nears the industrial revolution, much of racism became based on Social Darwinism as well as Christianity | ||
|
|
9. Race in the Industrial age | 1700 -
present |
Am & Fr Rev's | Slavery & racism begin to decline and Tubman, Douglas are important leaders | ||
|
|
10. Race under Era of Global Capitalism | 1910 -
present |
WW1
WW2 |
1950s & 60s Civil Rights Movement began & had it's greatest
success
MLK, Malcom X, Jackson, et al |
||
|
|
11. Race in Post Industrial Society | 1970 -
present |
Service econ
Info econ |
- a non-white middle class forms
- the use of affirmative action declines |
||
|
Links |
|
Links |
|
| Race relations in hunter gatherer (HG) society had no ideology (world view or understanding) of racial differentiation | |||
| People were not racist in that they were just as likely to fear or welcome people of any color, religion, etc. | |||
| HG tribes were so differentiated & isolated that all were encountered w/ caution & in light of their own ideology: warrior, pastoral, harvester, etc. | |||
| Tribes could wander for decades btwn encounters w/ other peoples | |||
| In the HG era, conflicts were not based on race because there were very few conflicts, because there was no surplus to be gained, population was low & the technology of hand to hand combat prevented any overwhelming advantages | |||
| During the HG era, social differences ( including race) btwn tribes were often welcomed | |||
| Because of inbreeding, isolation, etc., tribes often welcomed encounters w/ other tribes | |||
| Isolation & inbreeding was recognized as a problem by HG people and therefore, people often welcomed, celebrated w/, & intermarried w/ other tribes & races | |||
| During the HG Era, & later, people would arrange marriages & other trades in order to "bring in fresh blood," which today we recognize as diversifying the gene pool | |||
| Because humanity has spent 99 % of its existence in HG society & because race was not an issue in HG society, for over 99 % of human existence, race relations were harmonious, thus, racial conflict IS NOT "natural" | |||
| There was no slavery during the HG era | |||
| As population, "turf" pressure, & agricultural development increased, hostility btwn tribes increased | |||
| But discrimination & conflict was not based on race, but opportunity & conquest as seen in the adage: "An enemy of my enemy is my friend," & this was true regardless of race | |||
| Land, power, etc., were more important than race & this relationship did not change from a conquest orientation to an ideological orientation until the Middle Ages |
|
Links |
|
Links |
|
| - Project: The Difference in Race Relations Today & in the Pre Empire Era |
|
||
| Slavery begins along w/ "history" or "civilization" & agriculture | |||
| History, civilization, slavery, etc. begins w/ early, barely known civilizations that preceded the Egyptians, Sumerians & other early civilizations | |||
| In the pre empire era, tribal societies are just forming into sedentary societies & it takes another 6 K yrs before Egyptians, etc. buy into it all | |||
| Advances in human society & technology allowed "surpluses" to be created | |||
| One person could produce more than they needed to consume | |||
| Therefore, one person could hire or enslave another to work for them & profit from it | |||
| Thus slavery is an economic relationship | |||
| But, like in the hunter gatherer era, slavery was not based on race | |||
| In the pre empire era, slavery was based on conquest | |||
| The outcomes of conquest might include anything such as ...
- mass murder - genocide - partial to full enslavement - paying tribute - enslaving low as well as high level workers - pillaging - simply conquering & moving on |
|||
| In any system of exploitation, there is always an ideology ( world view or set of ideas ) that supports it | |||
| It is through the ideological system that the economic exploitation or relationship is disguised, often as one of race, religion or nationalism | |||
| It is the ideology of conquest that supports slavery in the pre empire era, not racism per se ( i.e. genetic or developmental inferiority ) that is the justification of slavery | |||
| An ideology of modern, genetic based racism does not occur until the Middle Ages | |||
| The ideology of the Pre Empire Era was that the victors have the right to rule the vanquished, but there are still strong individuals w/in a defeated society | |||
| The ideology of the Pre Empire Era was, "I conquered, I may exploit you." accompanied w/ a respect for the enemy | |||
| The next period, the Early Empire Era, witnesses the continuation of slavery based on conquest, not race |
|
Links |
|
Links |
|
|
|
CONQUEST BASED SLAVERY TRANSFORMS TO SLAVERY BASED ON IDEOLOGY RESULTING IN MORE SLAVERY & MORE OPPRESSIVE SLAVERY |
|
|
|
|
Introduction: Race relations in the Middle Ages transformed from the relatively "tolerant" ideology & relations prevalent since the HG Era into modern forms of racist ideology & global slave trade |
|
|
|
|
The previous era, the Era of the Roman Empire ( 200 BC to 500 AD ) was characterized by relatively tolerant race relations | ||
| Previous to the mid ages, slavery was based on who was conquered, regardless of race & thus slavery was decoupled from race resulting in the many early racially tolerant societies | |||
| Conquest based slavery was less widespread than the slavery which develops in the mid ages because it was limited to times of war/conquest, which admittedly were common, but not as common as the global slave trade which developed in the mid ages | |||
| Conquest based slavery was less oppressive that the ideological slavery of the mid ages & the modern eras because many conquered people were still able to buy or work their way out of slavery & | |||
| Under conquest based slavery, the enslaved was not considered inferior; in fact it was recognized that some slaves had very important skills as when a teacher or craftsperson was conquered & enslaved | |||
| IDEOLOGICALLY BASED GLOBAL SLAVE TRADE DEHUMANIZES & EXPLOITS SLAVES TO A GREATER EXTENT THAN CONQUEST BASED SLAVERY BECAUSE EMPIRES NEED TO JUSTIFY GREATER CONQUEST & GENOCIDE | |||
| As the Age of Exploration begins & thus global capitalism begins, international trade begins, the modern form of slave trade begins | |||
| The origins of modern versions of racism & global slave trade begin w/ Age of Exploration in the Middle Ages | |||
| During the Middle Ages, people / slaves become a commodity | |||
| The emerging European Powers utilized an ideological justification of slavery / discrimination, especially religious, racist, & conquest / imperialist ideologies | |||
| The ideological justification of racism/slavery begins circa 1000 AD | |||
| Circa 1000 AD ideological racism emerges along w/ slave trade using both Biblical & imperialistic justification of colonization & the slave trade begins as a global social institution | |||
| Thus, modern relations of tension / conflict among the races has existed for less than 1000 years | |||
| Religion & racism interact w/ the result being the ideology that "primitives" may be converted & have their souls saved | |||
| There is little mention of race in the Bible, yet religions' interaction w/ other social structures has often resulted in the call to evangelize/convert a particular group of people | |||
| Papal determinations were made & if a people were found to have a soul, the Church would sanction conversion | |||
| During the middle ages, if a people were found to not have a soul, the Church would sanction enslavement or genocide | |||
| The next era, the Early Industrial Age ( 500 to 1300 ), has little change in the nature of race relations, but there is huge & tragic growth in the global slave trade |
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
| Beginning in the 1500s, the genocide of Native Americans occurs which has many similarities to the genocide of peoples throughout Age of Exploration |
|
||||
| Throughout the Age of Exploration, the international slave trade continues, and grows to become a large scale phenomenon |
|
||||
| In 1607, the first slaves were brought to the U.S. | |||||
| In 1688, the earliest protest formally voiced in colonial America was the Germantown Mennonite Resolution Against Slavery |
|
||||
| In 1776, the final version as accepted by Congress of the Declaration of Independence: omitted this paragraph written by Jefferson: "He has waged cruel war against human nature, violating its most sacred rights of life and liberty in the persons of a distant people who never offended him, captivating and carrying them into slavery in another hemisphere, or to incur miserable death in their transportation thither..." |
|
||||
| In 1787, the US Constitution provides for the extension of slavery for a 20 year period & contains the "three fifths compromise" |
|
||||
| In 1791, the Bill of Rights was intended to protect particular rights of all people |
|
||||
| In 1799, Washington's Last Will & Testament frees his slaves & reflects concern for the financial welfare & education of former slaves |
|
||||
| Europe eliminates slavery, but the young US continues to enact compromises that allow it to continue into the 1800s eventually erupting in the Civil War & the end of slavery | |||||
| The next period, the Industrial Age, witnesses the advent of Social Darwinism, & the beginning of the decline of the modern slave systems | |||||
|
Links |
|
Links |
|
| In the 1800s, Social Darwinism replaces religious / exploration conquest ideology as the major ideology supporting slavery, racism, exploitation, etc. | |||
| Social Darwinism offers false scientific justification for discrimination, genocide, & colonization | |||
| In 1863, President Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation declared the slaves "forever free" | |||
| In 1869, the 15th Amendment was passed and ratified in 1870, giving Black Men the right to vote (Women get the vote in 1920) | |||
| In the 1860s, President Johnson institutes Jim Crow laws creating American Apartheid against the vision of the late President Lincoln | |||
| The KKK forms & institutes a war of terror against Blacks, & later, other groups, through lynchings, assault & other tactics of intimidation | |||
| Employers utilize split labor market tactics to pit workers of one race against workers of another race | |||
| Split labor market tactics are used to keep wages low, prevent workers from seeing their common experience of exploitation, & thus prevent unionization | |||
| Frederick Douglass ( 1817 - 1895 ) was an eloquent abolitionist who lived as a slave until he escaped to freedom at age 21, where upon he was appointed to the position of US Marshal for Washington DC, & he was also a newspaper editor, public speaker, & diplomat | |||
| Harriet Tubman was a black abolitionist who was a leader in the Underground Railroad | |||
| Sojourner Truth | |||
| WEB Du Bois ( 1868 - 1963 ) was a Professor who educated the US on race & analyzed the migration of Blacks to North & developed an early understanding of the split labor market theory | |||
| Du Bois taught history, sociology, & political science & was one of the founders of the NAACP & editor of its "Crisis Magazine" | |||
| In 1871 in Los Angeles, mobs attacked Chinese over the issue of jobs | |||
| A brief history of early, significant Civil Rights Events: | |||
| In 1807, the Act to Prohibit the Importation of Slaves passes Congress | |||
| In 1819-21, the Missouri Compromise is struck | |||
| In 1827 the Inaugural Edition of Freedom's Journal, the first
African American Newspaper in the US, is published
Freedom's Journal is owned & edited by Samuel Cornish & John B Russwurm |
|||
| In 1831 The Liberator, the most Famous Abolitionist Newspaper in the US, was founded by Lloyd Garrison who was white | |||
| In 1847 The Abolitionist operates under the direction of Frederick Douglas | |||
| 1850 The Compromise of 1850 contained the Fugitive Slave Act | |||
| In 1852 Frederick Douglass gives his famous Independence Day Address entitled "What to the Slaves is the Fourth of July?" | |||
| In 1854 the Kansas Nebraska Act is passed | |||
| In 1863 the Emancipation Proclamation is given | |||
| In 1865 the Freedmen's Bureau provided basic health & educational services for freed men | |||
| In 1865 the 13th Amendment abolishes slavery | |||
| In 1866 the Civil Rights Act is designed to protect freed men from the Black Codes, Jim Crow Laws & other repressive legislation | |||
| In 1868 the 14th Amendment defined US Citizenship for ex slaves | |||
| In 1870 the 15th Amendment established the right to vote for ex slaves | |||
| In 1875 the Civil Rights Act prohibited racial discrimination in public accommodation | |||
| In 1895 Booker T Washington gives his famous "Atlanta Compromise" speech | |||
| The next period, the Global Capitalism Era, witnesses the dismantling of American Apartheid, & the beginning to the end of discrimination |
|
Links |
|
Links |
|||
| - Supplement: Senate Committee Approves Sweeping Immigration Bill, Kingsport Times, News, March 28, 2006, p 3A |
|
||||
| Summary: The period of Global Capitalism witnesses the dismantling of American Apartheid, & the beginning of the end of discrimination | |||||
| In the Age of Global Capitalism, there is less physical violence based on racism today than in the past | |||||
| Racist mobs attack Blacks, Asians, etc. for economic reasons, justified by racist ideologies based on Social Darwinism & religious beliefs | |||||
| Many racial attacks & harassments are coordinated or incited by the KKK & related orgs | |||||
| 1908-21 mobs attack blacks in dozens of US cities | |||||
| In 1922, Marcus Garvey gives the Universal Negro Improvement Association Speech in NYC, & this organization becomes the Negro Nationalist Movement | |||||
| From 1937-1945 the Holocaust took place in Europe | |||||
| The economic base of Nazism necessitated the Holocaust, & was justified by the racist ideology of Aryan superiority | |||||
| The US knew about the Holocaust but chose to look the other way because of American Anti Semitism, lack of public political will, & a reluctance to enter WW 2 | |||||
| An analysis of the early discrimination in unions shows that early in their development, many American unions, but not all, were discriminatory / racist | |||||
| The UMWA was not discriminatory | |||||
| Unions also discriminated against women & other groups because many early US unions were dominated by a WASP patriarchy | |||||
| The UMWA had accepted many ethnicities & races of miners from its inception | |||||
| Liberal & Radical Union leaders had been assassinated & deported by the govt. | |||||
| Since the late 1800s, lured by industrialists, Blacks traveled North & had been & used as scabs & strikebreakers | |||||
| The Internal Colonialism Theory & the Split Labor Market Theory explain much of the racism that festered in the late 1800s & early 1900s | |||||
|
|
See Also: The Causes of Racism / Social Differentiation | ||||
| Dr. Ralph Bunche (1903-1971), an African American mediator & UN diplomat, was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for his role in fostering an armistice btwn warring Arabs & Israelis | |||||
| In 1960, Wilma Rudoph made history when she became the 1st African American woman to win three Olympic gold medals in track & field. She was known as "the fastest woman in the world" | |||||
| In the 1950s & 60s, the Civil Rights Movement uses non-violent methods in 200 cities to advance its cause | |||||
| In 1957, the Civil Rights Act was passed | |||||
| In 1957, the Southern Christian Leadership Conference, w/ ML King as president, was formed | |||||
| In 1963, the Letter from a Birmingham Jail w/ the Birmingham Manifesto heralded King's legacy to African Americans | |||||
| In 1963, WEB Du Bois dies at age 95 in Ghana | |||||
| In 1964, the another Civil Rights Act passed & these two laws are the first comprehensive federal civil rights legislation of the 20th century | |||||
| The Civil Rights Act makes it illegal to discriminate on basis of race, color, religion, sex, national origin, & established the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission ( EEOC ) | |||||
| The Disabilities Act is passed decades later, but even today it is still legal to discriminate on sexual orientation though some institutions have rules against it | |||||
| In 1968, ML King is assassinated | |||||
|
|
See Also: Affirmative Action, 1967 | ||||
| Executive Order 11375, signed by President Johnson, established Affirmative Action | |||||
|
|
See Also: Affirmative Action Backlash | ||||
|
|
In 1983 President Reagan signed the bill that established January 20 as a federal holiday in honor of ML King |
|
|||
|
|
It took many years for Congress to decide to celebrate ML King Day, but a few states had declared a state holiday |
|
|||
| Unions & race today: | |||||
| In 1960, the AFL CIO supports civil rights, & begins integration in unions | |||||
| Nearly all unions have successfully integrated today | |||||
| Blacks & Hispanics in America are more likely to be union members than whites | |||||
|
|
The glass ceilings still exist in some unions as a result of institutional discrimination |
|
|||
|
|
Significant Impacts of race in modern era include that in: |
|
|||
| - the 1960s there were race riots in US cities | |||||
| - 1968 when MLK is assassinated, over 100 communities erupt in violence | |||||
| - 1973 US Steel pays $31 mm to women & minorities for past discrimination | |||||
| - 1973 the first interracial kiss occurs on national TV on Star Trek btwn Cpt Kirk & Lt Orrura (but the kiss is the result of both being under the control of an 'alien force') | |||||
| - 1980 in Miami, when the police beat a black business man to death for a traffic violation, riots occurs in Miami & other cities resulting in 18 deaths & $200 mm in property damage | |||||
| - Ford pays $ 21 mm to minorities for workplace discrimination | |||||
| - 1988 Jesse Jackson finished 2nd in the Democratic Primary despite the fact that many people would not vote for him solely because of race | |||||
| - Armenians & Azerbaijanis engage in ethnic warfare | |||||
| - 1989 Miami cops shoot a black boy resulting in waves of riots & police attacks | |||||
| - 1992 the Rodney King beating & subsequent trial, acquittal, riots, federal trial & convictions of officers occur | |||||
| - 1994 the OJ Simpson trial takes place dividing the nation & creating an unheard of national conversation on race & justice | |||||
| - 1995 Church burnings become so frequent that they gain national attention | |||||
| - 1996 Texaco agrees to pay $1.5 b for discrimination primarily against blacks who aspire to own Texaco franchises | |||||
| - the CIA crack scandal blows over | |||||
| - 1991-93 an ethnic war in Yugoslavia btwn Serbs, Croats & Slovenians who are Muslim & Christian threatens to envelop all of Southern Europe culminating in a successful UN peacekeeping action | |||||
| - 1999 NYC cops shoot an off duty black cop | |||||
| - 2005 youth riots which are ethnically based erupt in France as a result of the frustration of the underclass | |||||
|
|
"Race & ethnic" conflicts around the world are often based on 'economic' conflicts as seen in: |
|
|||
|
|
- S. Africa where Dutch Whites opposed Mandella's ANC & Budulazies Inkaataa Freedom Party & the issues were both land reform & civil rights |
|
|||
| - Northern Ireland where Irish Catholics are oppressed by British Protestants which & the issues were political econ control of N Ireland | |||||
| - Israel where Jews, Palestinians, other Arabs, & Christians all oppose each other over land & political econ control w/in that land | |||||
|
|
In the US, there is less physical violence based on racism today than in the past, though there is more institutional racism |
|
|||
| The next period, the Post Industrial Age, witnesses the major form of discrimination being institutional discrimination | |||||
The End
|