Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Union
Activities: What do Unions Do? Why Join a Union?
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
- Project: What
Do You Think Unions Do? |
Link
|
| |
- Supplement: Why Join
a Union? |
Link
|
| |
The labor movement & unions seek to organize workers to take advantage
of their "strength in numbers" |
|
|
|
The labor movement uses the power of the strength in numbers to seek
a greater share of society's resources for labor movement members,
workers, & other selected group w/ which they have allied |
|
|
|
Workers form unions to redress grievances in the workplace such
as inadequate or unfair wages, work that is too rapidly paced, unfair retention
& promotion practices, & exclusion from decision making |
|
| |
When workers first have problems in the workplace they tend to blame
themselves, then they discuss the problems only w/ a few trusted
coworkers, & thus workers may been seen as going through THREE
stages |
|
| |
Workers deal w/ problems in the stages of individualism, work
group support, & collective action |
|
| |
Workers deal w/ workplace problems in stage one by being individualistic,
apathetic, withdrawn, & by quitting |
|
| |
In the second stage of addressing workplace problems workers
go to the informal work group in the hopes it will provide a medium
for airing complaints in collective terms |
|
| |
In the second stage of addressing workplace problems workers may also
rely on family, community or ethnic group ties |
|
| |
Solutions in the second stage of addressing workplace problems tend
to remain largely personal |
|
| |
In addressing workplace problems, some specific events may stimulate
the transition from the second stage of work group support to organized
collective action |
|
| |
The transition to collective action frequently requires leadership
from one or more outspoken workers |
|
| |
Collective action will occur only if workers are committed enough to
their jobs to forgo the option of leaving & if a significant core
of workers sufficiently overcomes fears of mgt reprisal to start organizing
coworkers |
|
| |
The third stage of addressing workplace problems is some form
of collective action which may include forming a union, forming a workers'
committee to represent workers to mgt & address problems, going outside
the workplace to some other org such as a govt. agency, etc. |
|
| |
What Do Unions Do? |
|
| |
Unions have SEVEN major functions, including: |
|
| |
a. addressing the needs of the union membership &
other workers |
|
| |
b. organizing & rallying workers to join a union |
|
| |
c. negotiating via collective bargaining over wages, hours,
benefits, workplace rules, etc. |
|
| |
d. implementing contracts by overseeing the workplace
to ensure compliance w/ contracts & govt rules, regs, laws, etc. |
|
| |
e. addressing grievances; where the union perceives workers
are treated "illegally," the union will be an advocate for them |
|
| |
f. lobbying the govt & bringing
court cases
to shape the law of the land to address workers' needs |
|
| |
g. participate in politics through participation in the
formation of public policy in light of workers' needs |
|
| |
Unions collectivize bargaining power & attempt to create
monopoly power |
|
| |
Unions give workers voice power |
|
| |
Unions organize workers, campaign to win representation, conduct
elections, & negotiate for wages & benefits for the members |
|
| |
Unions negotiate contracts: aka engage in collective bargaining
for:
wages
fringe benefits
hours
working conditions
grievance settlements
union security (right of one union to represent workers) |
|
| |
Unions organize strikes & other disputes |
|
| |
Unions lobby |
|
| |
Unions implement apprenticeship programs |
|
| |
Other union activities in running hiring halls & education of union
members & the public |
|
| |
Which Side Are You On?' Why Organize? |
|
| |
Workers join unions because of perceived "injustices" & because
their expectations are not met in workplace |
|
| |
Perceived net worth from union (benefits - cost = worth) FIGURE
1 - 2 |
|
| |
List benefits & costs of unions |
|
| |
Workers are voting for an indirect voice through representation |
|
| |
For a union to represent a group of wkrs, the majority of workers must
choose the union |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Union
Membership
|
|
External
Links
|
|
|
Union demographics |
|
| |
Today, there are approximately 20 million US Union members |
|
| |
Gender make-up of Union Membership in the US is approximately 65 %
male & 37 % female |
|
| |
21.3 % of working males are union members |
|
| |
14.8 % of working women are union members |
|
| |
Two of the 95 unions in AFL CIO have female president & women in
other leadership positions have similar numbers |
|
| |
At the local level, women have a greater role than at the national
level, but not proportional to men's number |
|
| |
Women are not generally involved in bargaining & grievance settlement |
|
| |
The racial demographics of the Labor Movement approximates the racial
demographics of the working population they represent |
|
| |
Thus, the Labor Movement is nearly racially representative of the overall
population, but is somewhat voluntarily concentrated by race because races
& ethnic groups are occupationally concentrated |
|
|
Link
|
The Table on Union Membership shows
that participation in the Labor Movement grew until the 1950s, declined
slowly until the 1980s then rapidly declined & has recently stabilized |
|
| |
Unions peaked in power from 1945 to 1955 when union membership percentages
were the highest |
|
|
Link
|
The Table on
Who
Belongs to Unions? shows that union membership varies somewhat by various
factors including industry, occupation, region, age, gender, race, education,
& work status |
|
| |
Workers in transportation, govt., manufacturing, mining, & construction
are more likely to be union members than workers in trade & services |
|
| |
Manual workers are more likely to be unions than are professionals,
service, clerical, or farm workers |
|
| |
Workers in the Midwest, Northeast, & West are more likely to be
union than are workers in the South |
|
| |
Because of more commitment to their jobs, older workers are more likely
to be union |
|
| |
Men are more likely to be union than women, but women are being organized
at a faster rate |
|
| |
In relation to union membership, Blacks, Hispanics, Asians, et al are
more likely to be union than are Whites |
|
| |
In reference to education, the largest segment of the unionized population
has a high school diploma |
|
| |
Full time workers are more likely to be union that part time workers |
|
|
Link
|
The Table on the 25 Largest Labor Unions
in the US shows that in general, big unions are going, but the reason
the percentage of the workforce is declining is because the unions grow
at a slower rate than the workforce |
|
| |
Unions are no longer confined to blue collar jobs in the manufacturing
sector |
|
| |
In recent yrs., the white collar, professional, & service sectors
are important growth sectors for the labor movement |
|
| |
The Individual & the Local |
|
| |
The union security clause in the collective bargaining agreement
requires |
|
| |
- members to join the union |
|
| |
- nonmembers to pay an agency fee for representation |
|
| |
In right to work states, the nonmembers pay nothing |
|
| |
In some jobs (e.g. construction, maritime), unions the take lead
in skill training & entry to employment |
|
| |
Joining & Socialization |
|
| |
We are socialized on the job by mgt., workers, the union, customers |
|
| |
A union often exempts new workers from joining the union for a probationary
period |
|
| |
W/ a union shop, workers join immediately, & pay an initiation
fee |
|
| |
The steward introduces worker to union, union role, etc. |
|
Table on US Union Membership 1930 -
2000 |
|
Year
|
Total Wkrs
in millions
|
Union
in millions
|
% in Unions
|
% Change
|
|
1930
|
29.4
|
3.4
|
12%
|
|
|
1935
|
27.1
|
3.6
|
13%
|
+ 1 %
|
|
1940
|
32.4
|
8.7
|
27%
|
+ 14 %
|
|
1945
|
40.4
|
14.3
|
36%
|
+ 9 %
|
|
1950
|
45.2
|
14.3
|
32%
|
- 4 %
|
|
1955
|
50.7
|
16.8
|
33%
|
+ 1 %
|
|
1960
|
54.2
|
17.0
|
31%
|
- 2 %
|
|
1965
|
60.8
|
17.3
|
28%
|
- 3 %
|
|
1970
|
70.9
|
19.4
|
27%
|
+ 1 %
|
|
1975
|
76.9
|
19.6
|
25%
|
- 2 %
|
|
1980
|
87.5
|
20.1
|
23%
|
- 2 %
|
|
1985
|
94.5
|
17.0
|
18%
|
- 5 %
|
|
1988
|
101.4
|
17.0
|
17%
|
- 1 %
|
|
1990
|
102.4
|
16.8
|
17%
|
NC
|
|
1998
|
116.7
|
16.2
|
14%
|
- 3 %
|
|
1999
|
|
16.2
|
|
|
|
2000
|
|
|
15.4
|
|
| The Table on Union Membership shows
that participation in the Labor Movement grew until the 1950s, declined
slowly until the 1980s then rapidly declined & has recently stabilized |
| Red denotes the high
in union membership in absolute numbers & in percentage, respectively.
Note that unions peaked in power from 1945 to 1955 when union membership
percentages were the highest |
Table on Who Belongs to Unions?
HS0206
|
| Criterion |
% Represented in 1993
|
% Represented in 1999
|
|
Industry
|
|
|
| Manufacturing & mining |
21 %
|
17
|
| Mining |
|
13
|
| Construction |
21
|
13
|
| Transportation |
33
|
27
|
| Trade |
7
|
6
|
| Service industries |
7
|
7
|
| Govt. |
43
|
42
|
|
Occupation
|
|
|
| Professional |
18
|
15
|
| Service occupations |
16
|
14
|
| Clerical |
12
|
10
|
| Manual |
27
|
23
|
| Farm |
6
|
5
|
|
Region
|
|
|
| Northeast |
20
|
|
| Midwest |
21
|
|
| South |
12
|
|
| West |
19
|
|
|
Age
|
|
|
| 16 - 24 yrs. |
7
|
6
|
| 25 - 64 yrs. |
18
|
18
|
|
Gender
|
|
|
| Men |
21
|
17
|
| Women |
15
|
13
|
|
Race
|
|
|
| Minority |
22
|
|
| Hispanic |
|
13
|
| Black |
|
22
|
| White |
17
|
15
|
|
Education
|
|
|
| Less than high school |
17
|
|
| High school or more |
19
|
|
|
Work Status: Hours
|
|
|
| Full time |
20
|
18
|
| Part time |
9
|
8
|
|
Total
|
18
|
|
| Table 6.1 Who Belongs to Unions?
shows that union membership varies somewhat by various factors including
industry, occupation, region, age, gender, race, education, & work
status |
| US Dept. of Commerce, Bureau of the Census,
1993e, 1999; Statistical Abstracts of the US, 1993, 2000; Washington, DC,
US Govt. GPO, p.436 |
Table on the 25 Largest Labor Unions
in the US
HS0206
|
| Labor Organization |
Members in Thousands, 1993
|
Members in Thousands, 1999
|
| NEA |
2,001
|
2,001
|
| Teamsters |
1,379
|
1,271
|
| AFSCME |
1,191
|
1,236
|
| SEIU |
881
|
1,081
|
| Food & Commercial Workers |
997
|
989
|
| UAW |
840
|
766
|
| AFT |
573
|
694
|
| IBEW |
730
|
655
|
| CWA |
492
|
504
|
| Steelworkers |
459
|
499
|
| IAM |
534
|
431
|
| Carpenters |
494
|
324
|
| Laborers |
406
|
298
|
| Operating Engineers |
330
|
294
|
| Postal Workers |
228
|
279
|
| Paperworkers Intl Union |
202
|
226
|
| Hotel & Restaurant Employees |
269
|
225
|
| Plumbing & Pipe Fitting |
220
|
220
|
| Letter Carriers |
210
|
210
|
| Am. Fed. of Govt. Employees |
151
|
170
|
| Firefighters |
151
|
156
|
| Electronic, Electrical, & Tech Wkrs. |
160
|
128
|
| ILGWU |
143
|
|
| Transit Workers |
|
98
|
| Bakery, Confectionery & Tobacco Wkrs. |
|
95
|
| Clothing & Textile Wkrs. |
154
|
|
| UMW |
240
|
81
|
| Table 6.2 The 25 Largest Labor
Unions in the US shows that in general, big unions are going, but
the reason the percentage of the workforce is declining is because the
unions grow at a slower rate than the workforce |
| US Dept. of Commerce, Bureau of the Census,
1993e, Statistical Abstracts of the US, 1993, Washington, DC, US Govt.
GPO, p. 435. Court Gifford, ed., Directory of US Labor Orgs.
Washington, DC, Bureau of National Affairs |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
Time
Period
|
|
Outline on a Historical
Overview of the Labor Movement
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
|
Introduction: Marx
1818 -1883
Wealth could only be created by labor
Another class: owners: monied
aristocracy
10 % own 90 % of the wealth, & thus also have more power
In a democracy, unions are necessary to help balance this power
1999 in US: richest 17 mm have same amount of wealth as poorest
100 mm
Most of the Labor Movement want this inequality leveled out to a certain
extent |
|
| |
|
Summary: Before unions, workers had almost no voice
in determining wages, hours, working conditions, etc.
Since the shift from agricultural econ to the industrial
economy, there was a consistent surplus of labor
Workers always recognized that collective power was greater
than individual power
From the very beginning, those in power regarded unions/ guilds / prof
assoc as immoral /illegal etc.
The US the courts viewed unions as illegal until the late 1800s, &
it wasn't until the early 1900s that actual union legality was established |
|
| |
10 K
BC
|
Early Worker Associations formed estbing the
Labor Movements prior in the Pre Empire Era circa
10 K BC - 500 AD |
|
| |
|
Early Worker Associations, circa 1500 BC, were closed groups
of profl assocs which arose as a collective response to exploitation |
|
| |
|
The qualities of the early professional associations influenced the
modern Labor Movement |
|
| |
500
|
Guilds were common in the Labor Movement in
the Middle Ages
circa 500 - 1300 |
|
| |
|
Craft Guilds developed during the Medieval Era, circa 400 -
1600 |
|
| |
|
Craft unions & guilds spread from Rome to Europe, & eventually
to the US |
|
| |
|
Guilds evolved into other types of labor associations |
|
| |
1300
|
The Labor Movement during the early industrial
revolution began its move from craft guild to labor unions
circa 1300 - 1700 |
|
| |
|
The Industrial Revolution created the decapitalization of Labor |
|
| |
|
Labor Parties first developed in Europe |
|
| |
|
Craft unions came to US via European immigrants |
|
| |
|
There were many early US Labor Movement actions |
|
| |
1700
|
The Labor Movement during the Industrial Age
gained power & legitimacy circa
1700 - present |
|
| |
|
Illegality to Legality
In the early 1800s, unions were illegal & forced to exist as secret
societies
In the mid 1800s, unions became legal, but strikes were still illegal |
|
| |
|
During the industrial age, many unions were born, some have gone out
of existence
NLU 1866 - 1872
KOL 1869 - 1899
AFL 1869 - 1955
IWW 1905 |
|
| |
|
During the industrial age, court cases were very important for the
Labor Movement |
|
| |
|
There were many historic strikes, & other forms of labor unrest
during this era
Molly Maguires
1865
Haymarket Square Riot 1886
Homestead Strike
1892
Pullman Strike
1894
Danbury Hatters Boycott 1906 |
|
| |
|
During the indl age, some noteworthy legislation was passed, but legislation
legalizing Labor Movement as we know it today does not occur until the
next era |
|
| |
1910
|
The Labor Movement & Global Capitalism,
as global capitalism developed, Labor lost power |
|
| |
|
During the era of global cap, the Labor Movement gained full legitimacy
in the form of all the rights & obligations it possesses today |
|
| |
|
During the era of global cap, more important unions were born including
the
CIO 1935 - 1955
AFL CIO merged in 1955 |
|
| |
|
During the era of global cap, there were many historic strikes, &
other forms of labor unrest, especially the
Triangle Fire
1911
Ludlow Massacre
1914 |
|
|
|
|
During the era of global cap, the cornerstone labor relations legislation
was passed, legalizing the Labor Mvmt as we know it today |
|
| |
|
Business Unionism, aka "The Great Labor Compromise," allowed
the Labor Mvmt to gain legitimacy but limited Labor's options |
|
| |
1970
|
The Labor Movement During the Post Industrial
Age lost much influence & struggled to
reinvent itself |
|
| |
|
During the post indl era, public employees unions came to the fore
front |
|
| |
|
Labor law in the 1970s addressed the issues of public sector wkrs |
|
| |
|
During this era, the Labor Movement experienced its greatest decline
& also began its resurgence |
|
| |
2000
|
The Future of the Labor Movement |
|
| |
|
The Future of the Labor Mvmt is fraught w/ many challenges related
to changes in the economy, govt support, etc., but the assets of the Labor
movement, such as a committed leadership & membership, will find opportunities
in new sectors of the economy & in unorganized workers |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Race
& the Labor Movement
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
Well after WW 2, some labor unions, esp. in the building trades, keep
out minorities or restricted them to lower paying jobs, or jobs in specific
neighborhoods |
|
| |
Minorities participate equally in Locals, but are often under represented
in officer positions |
|
| |
One major reason for the continuing segregation in unions is that firms
have the right to hire who they want |
|
| |
Segregated union patterns generally follow segregated workplace patterns |
|
| |
Occupational segregation is widespread |
|
| |
Occupation segregation is greatest btwn the genders in that there are
men's jobs & there are women's jobs |
|
| |
There are some occupations that are segregated by race or ethnicity:
farm workers are often Hispanic; uranium miners are often Native American |
|
| |
Unions have traditionally favored civil rights, but have not been able
to enforce them in the workplace |
|
| |
Civil rights in the workplace is considered to be a mgt. prerogative |
|
| |
Unions now have policy of no discrimination in the union, but union
leaders at the national level do not necessarily reflect the demographics
of the members |
|
| |
Except for minority dominated unions, there are no minority national
union presidents |
|
| |
The racial demographics of the Labor Movement approximates the racial
demographics of the working population they represent |
|
|
|
Thus, the Labor Movement is nearly racially representative of the overall
population, but is somewhat voluntarily concentrated by race because races
& ethnic groups are occupationally concentrated |
|
|
|
Racism, discrimination, & specifically keeping minorities out of,
or restricting them in the building trades & other occupations continued
into the late 60s, i.e. until the Civil Rights Mvmt was powerful |
|
| |
The trades of plumbing, electrician, sheet metal workers, & more
discriminated against minorities until the Civil Rights Mvmt, & the
legislation that resulted, forced change |
|
| |
By the late 60s many unions & trades had substantial percentages
of Blacks & other minorities |
|
| |
The AFL CIO, the lead & umbrella labor org in the US, had become
a strong supporter of the Civil Rights Mvmt |
|
| |
The AFL CIO was a lead player in getting the equal employment opportunity
section, Title VII, included in the Civil Rights Act of 1994 (Marshall
& Briggs, 1989) |
|
| |
Today, Blacks are more likely to be union members than Whites (DeFreitas,
1993) & they have secured many leadership positions (Cornfield, 1989) |
|
| |
During the 60s, the Labor & Civil Rights Mvmts often worked together
on policies beneficial to both |
|
| |
On Feb 12, 1968, Black sanitation wkrs struck in Memphis, TN w/ the
active support of the local Black community, the AFL CIO, & civil rights
orgs such as the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) |
|
| |
Martin Luther King spoke at labor / civil rights rallies in Memphis
3 times & was assassinated there on April 4, 1968 during his 3rd visit
in support of the strike |
|
| |
The union practice of basing layoffs (or advancement) on the basis
of seniority has the quality of institutional racism in that it has the
unintended consequence of laying off new hires, who are often minorities |
|
| |
The courts have weakened a purely seniority based layoff system, allowing
race to be considered as a factor in addition to seniority |
|
| |
Asian Am are the only minority group significantly less represented
in the Labor Mvmt today than their percentage of the population would indicate |
|
| |
Labor organizers are trying to increase Asian participation in unions
by organizing garment wkrs, hotel & restaurant wkrs, & medical
wkrs (Chen, 1993) |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Women
in the Labor Movement
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
Women have been active in the Labor Mvmt since its inception |
|
| |
Women's representation in officer positions is nearly proportional
to their membership |
|
| |
As the Women's Movement grew in the 1960s & 70s, the AFL CIO became
strongly influenced by it |
|
| |
The AFL CIO was a strong supporter of the ERA |
|
| |
During the 1970s, a group of female trade unionists formed the Coalition
of Labor Union Women (CLUW) |
|
| |
See Also: CLUW www.CLUW.org |
Link
|
| |
CLUW addresses many issue important to women in the workplace including
the elimination of the restriction of women from occupations because of
irrelevant tactics such as height or weight, the need for pregnancy &
maternity leave, childcare programs, sexual harassment, pay equity, &
more |
|
| |
While women have always met resistance in the workplace from some men,
other men have supported women in the workplace |
|
| |
In 1979, 1400 members of the Int'l Wookworkers of America (IWA) successfully
struck over the unfair firing of a female worker at a plywood plant |
|
| |
The female worker at the plywood plant was fired because of
her discrimination suit against the company resulting from her restriction
from preferred jobs & shifts |
|
| |
The Labor Mvmt has aggressively organized in heavily female occupations
& industries |
|
| |
Female membership in unions is growing rapidly as male membership continues
to decline |
|
| |
Women's wages in unionized jobs are higher than in nonunion
jobs & the disparity btwn men & women's wages is significantly
less |
|
| |
Labor recognizes that the concerns of women often do not receive
commensurate attention as compared to more traditional issues |
|
| |
The Communications Workers of America (CWA) local at Indiana University
consists primarily of women & is concerned w/ salary equity, job security,
health insurance, pensions, parking, childcare, & eldercare most of
which are traditional union issues |
|
| |
Except for women dominated unions, there are no women national union
presidents |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Women &
Minorities in the Labor Movement
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
Minorities participate equally in locals, but are often under
represented in officer positions |
|
| |
One major reason for the continuing segregation in unions is that firms
have the right to hire who they want |
|
| |
Segregated union patterns generally follow segregated workplace
patterns |
|
| |
Occupational segregation is widespread |
|
| |
Occupation segregation is greatest btwn the genders in that there are
"men's jobs" & there are "women's jobs" |
|
| |
There are many occupations that are segregated by race or ethnicity
such as farm workers are Hispanic, uranium miners are Native American,
& more |
|
| |
Unions have traditionally favored civil rights, but have not
been able to enforce them in the workplace |
|
| |
Civil rights in the workplace are considered to be a mgt prerogative |
|
| |
Unions now have policy of no discrimination in the union, but
union leaders at the national level do not necessarily reflect the demographics
of the members |
|
| |
Except for minority dominated unions, there are no minority national
union presidents |
|
|
|
The racial demographics of the Labor Movement approximates the
racial demographics of the working population they represent, except that
minorities are slightly more likely to be in a union |
|
|
|
Thus, the Labor Movement is nearly racially representative of the overall
population, but is somewhat voluntarily concentrated by race because races
& ethnic groups are occupationally concentrated |
|
| |
| Mother Jones, i.e. Mary Harris Jones (1830-1930) was an important
labor leader who was inspirational & a powerful organizer |
 |
|
|
| |
In 1881, the Knights of Labor appointed a special committee to promote
the interests of women |
|
| |
In 1899, the Women's International Union Labor League was formed |
|
| |
The AFL tried to persuade women to take action against corrupt business
mgt in the early 1900s |
|
| |
In 1903, the National Women's Trade Union League was formed |
|
| |
Women were forced, or allowed, to work in time of war, esp WW 2 |
|
| |
For women & minorities, wartime fostered:
- greater freedom
- a greater opportunity to prove themselves
- an opportunity to learn about, & join, unions
- more power |
 |
|
|
| |
Unions that were created during WW 2 include the:
- Sewing Women's Protective Benevolent Union
- Working Women's Relief Association |
|
| |
Today, important women's issues in the workplace include:
- sexual discrimination
- occupational sex socialization
- occupational gender segregation
- hiring patterns
- comparable worth
- sexual harassment
- feminization of poverty
- affirmative action |
|
| |
Today, important civil rights issues in the workplace include:
- hiring patterns
- comparable worth
- affirmative action
- institutional discrimination |
|
| |
|
|
| |
Women were instrumental in the struggle of the Pitson Strike
of 1989 |
|
|
|
SEE Term Papers for additional info |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Public
Sector Unions
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
Public sector unions are those which represent workers in fed,
state, city, or county govt or public employees |
|
| |
Two of the biggest public sectors unions are the Service Employees
International Union (SEIU), the American Federation of State, County,
and Municipal Employees (AFSCME), but public sector employees are
represented by other unions such as the Clerical Workers at Indiana University
who are represented by the Communication Workers of America (CWA) |
|
| |
Many public sector employees such as teachers, police, & firefighters
cannot form unions because it is illegal for them to strike; therefore,
they often form associations such as the National Education Association
(NEA) who conduct collective bargaining & other union functions for
their employees |
|
| |
See Also: Unions |
|
| |
By the 1970s, public sector unions were growing very fast |
|
| |
In the 1960s, less than one third of fed employees belonged to labor
organizations, but by 2000 almost two thirds were union members |
|
| |
From the 1960s to the 2000s, union membership among state, county,
& local employees increased from one to five million bringing the unionization
rate among eligible govt employees above 40%, higher than any private sector
industry |
|
| |
A majority of states now utilize final & binding arbitration
for some or all state employees |
|
| |
Arbitration allows collective bargaining in the public sector
WITHOUT
the use of strikes that might disrupt public services |
|
| |
While it is illegal for many public employees to strike, when
collective bargaining breaks down, they often conduct "sick outs" or work
slowdowns |
|
| |
Not all states have laws recognizing state workers' rights to join
unions & negotiate their conditions of employment |
|
|
There are FOUR types of nonfederal public sector labor orgs,
including:
1. all public sector unions
2. mixed public & private sector unions
3. state & local associations
4. unions & associations representing uniformed
protective services |
|
|
|
Examples of all public sector unions include the Intl Assoc of Fire
Fighters (IAFF) & the Fraternal Order of Police (FOP) |
|
| |
Examples of major mixed sector unions include the Service Employees
Intl Union (SEIU) & the Teamsters |
|
| |
The Am Fed of State, County & Municipal Employees, (AFSCME)
represents state & local unit wkrs |
|
| |
The Am Fed of Govt Employees (AFGE) represents fed wkrs |
|
| |
Postal service wkrs are represented by several national unions,
such as the Am Postal Wkrs Union (APWU) & the National Assoc of Letter
Carriers (NALC), but some postal unions have recently merged w/ larger
primarily private sector unions |
|
| |
Because early on public wkrs did not have any unionization rights,
many public sector bargaining units:
- began as profl assoc
- were involved in estbing standards
- were involved in estbing occupational licensing
requirements
- lobbied for improved funding & facilities
- began as civil service assocs
- were involved in meeting & conferring w/ mgt |
|
| |
Some unions, like Ca State Employees Assoc (CSEA) are large
enough o exercise pol influence through large blocks of voters |
|
| |
Assocs are most prevalent where laws forbid bargaining, but where legislative
lobbying representing numerical strength is imp |
|
| |
Prof assoc are usually organized on occupational bases &
have begun to bargain in response to unions who demand bargaining rather
than the meet & confer tactic |
|
| |
Most nat unions, such as the Nat Ed Assoc (NEA) bargain
at state & local levels organize along a fed model |
|
|
|
Because laws vary by state & even district, most bargaining by
the NEA is done at local school board levels |
|
| |
Other state level services primarily involve lobbying & negotiating
assistance |
|
| |
Public sector locals seldom need approval from the nat un for contract
ratification & strikes |
|
| |
Membership in public sector unions increased in the 90s & 00s,
while private sector union declined |
|
| |
About 40% of public sector wkrs are union members |
|
| |
Mgt resistance to unionization is lower in the public
sector |
|
| |
Future unionization in the pub sect depends on the amt of growth
of services in the pub sec, which declined in the Clinton admin but have
grown at unprecedented rates during the Bush Jr Admin |
|
| |
While privatization has slowed the growth of the public sector,
much reduction of fed level services has transferred to the state level,
& the general trend is toward growth |
|
| |
Duty to bargain laws have the greatest effect in increasing pub sect
unionization |
|
| |
Pub sect un have a strong interest in promoting soci programs, ed,
municipal services, & uniformed protection because it increases
employment & because these wkrs understand the efficacy of such growth |
|
| |
Pub sect un have success by linking bargaining issues /w the broader
concerns of the public, such as smaller class sized & their relationship
to ed outcomes, or the fact that the greatest asset to public safety is
more police on the streets, or the type of welfare system that is needed
to break the welfare cycle, or the effectiveness & ineffectiveness
of proper & improper regulation of industry |
|
| |
Active support of candidates at the state & local level is a powerful
tool for public sect un |
|
| |
Pub sect unions support those candidates who are sympathetic to pub
sect un interests, which is also helpful during negotiations |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
A professional is an organizational actor who, because of their
occupation, based on advanced education, is generally afforded high status
& authority |
blank
|
| |
Traditionally, the professions included only doctors, lawyers, accountants,
& professors |
|
| |
Today, the types of professionals has grown to include dentists, computer
programmers, & other white-collar occupations |
|
| |
In relation to professionals, a new category of workers has emerged
who are called semi-professionals |
|
| |
Semi-professionals include nurses, police, firefighters, legal aids,
and so on |
|
| |
For Professionals, the evaluation, reward, control, & their relationship
to their orgs is unique as compared to many other classes of workers |
|
| |
a. The evaluation of professionals by non-professionals
is problematic |
|
| |
Evaluation of professionals is done the best by professionals in the
same area of expertise |
|
| |
Often, there is no similarly trained professional available to do the
evaluation |
|
| |
Professionals are not generally trained to do evaluations |
|
| |
The evaluation of professionals by non-professionals is NOT widely
practiced |
|
| |
Problems arise in the evaluation of professionals when it is done by
a manager w/o expertise |
|
| |
The evaluation of professionas by those w/o expertise creates conflict |
|
| |
b. The control of professionals is problematic
for many orgs |
|
| |
Our society has even developed a cultural icon of the the "nutty professor" |
|
| |
Orgs attempt to exert legitimate control over professionals
through the organizational hierarchy |
|
| |
The professional is apt to resist control |
|
| |
If the org gives control over professionals to the professionals themselves,
then the org loses control & cannot be sure they are contributing to
org goals |
|
| |
The Control Dilemma is resolved by allowing professionals to control
themselves w/ fellow professionals held accountable for the unit's success |
|
| |
c. The reward system for professionals is unique
to them |
|
| |
The reward system is more complicated for professional
While professionals desire $$, etc., they are likely to want recognition
from other professionals |
|
| |
Professionals are not promoted by moving them to administration positions |
|
| |
Professionals have a dual career ladder
Professionals can advance by |
|
| |
a. The traditional method; i.e., into
an administrative position |
|
| |
b. Staying at professional work w/
an increase in pay |
|
| |
c. Publications & fame |
|
| |
d. Participation in professional associations |
|
| |
Argyris, 1969 critiques this reward system |
|
| |
d. Professionals & the orgs they work in often have
a different views of each other |
|
| |
Professionals feel as if org is intrusive, rules & regulation bound,
& unresponsive to their contributions to their field |
|
| |
The org sees professionals as hopelessly impractical, & out of
touch w/ what is important for the org |
|
| |
The professionals themselves have very widely divergent points of view |
|
| |
There is no one universal org'l or sociological truth system |
|
| |
Experts can take differing views of what is good, rational, legal,
or effective |
|
|
|
Perspectives of accountants, lawyers, research scientists, mgt. consultants
& execs often differ radically |
|
|
|
Perspectives differ so much that they are often speaking different
languages, using different vocabularies & meaning systems |
|
|
|
PROFESSIONALS; & PROFESSIONAL ASSOCIATIONS |
|
|
|
In the past, the four classic professions of doctors, lawyers, accountants,
& professors were primarily self employed |
|
|
|
Self employed professionals had near total autonomy |
|
|
|
Today, professionals increasingly find themselves in large bureaucracies
subject to the control under managers |
|
|
|
Because of the loss of autonomy, professionals are more frequently
turning to unions & professional associations to retain & even
regain some of their lost power |
|
|
|
Professionals have begun to unionize to improve their bargain position
relative to the large bureaucratic orgs in which they are increasingly
employed |
|
|
|
In the past, prof orgs focused on training, defense of members' legal
rights, conferences, intellectual sharing, & legislative lobbying |
|
|
|
Recently many prof orgs are turning to collective bargaining |
|
|
|
The National Education Assoc. (NEA) & the Am. Federation
of Teachers (AFT) have a combined membership of over 2.7 mm making
teachers the largest group of organized workers in the US |
|
|
|
See Also: The AFT |
Link
|
|
|
The largest white collar strike in the US was conducted by 23,000
engineers & technicians at Boeing over class trade union issues as
pay, benefits, & health insurance. A favorable settlement was
reached after 37 days off the job |
|
|
|
Professors & medical doctors have begun to organize or join unions |
|
|
|
In CA, many faculty are organized by the AFT |
|
| |
Nationwide, 170,000 of 400,000 full time & 300,000 part time faculty
are organized into unions |
|
| |
The American Association of University Professionals (AAUP)
is feeling competition form the AFT & has therefore increased its collective
bargaining in addition to traditional lobbying & professional development
activities |
|
| |
See Also: The AAUP www.aaup.org |
Link
|
| |
The Union of American Physicians & Dentists has grown to
over 50,000 in response to the pressure doctors experience from such large
health-are orgs such as HMO & corporate hospitals |
|
| |
The increasing centralization of the health-care industry in large,
for-profit orgs is expected to shift the allegiance of doctors from the
AMA
to orgs practicing traditional union strategies |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
- United Farm Workers (UFW) webpage http://www.ufw.org/ |
Link
|
| |
INTRODUCTION |
|
| |
Historically farm workers have not been organized due to legislation
which exempted them from most labor laws |
|
| |
See Also: Labor Law |
|
| |
Recently some states have passed laws increasing farm worker rights |
|
| |
CA was the first state to include farm wkrs under labor laws w/ the
passage of the Agriculture Labor Relations Act in 1975 |
|
| |
Since 1975 FL & TX have allowed farm wkrs to organize though they
have met resistance from ag corps |
|
| |
In the 1980s the United Farm Wkrs (UFW) succeeded in getting farm wkrs
in TX covered by unemployment insurance |
|
|
|
Over time the farm worker population has become increasingly male w/
80% being male today |
|
|
|
Farm workers are very young, w/ 2/3s being less than 35, & almost
one fifth are in their first year of US farm work |
|
|
|
Most adult foreign farm workers are married & have children |
|
|
|
Most foreign born farm workers w/ families live & work separately
from their spouses & children |
|
|
|
Most foreign farm workers live w/ non relatives |
|
|
|
ETHNICITY |
|
|
|
In the 1994-1995 period, 37% of farm workers were unauthorized, up
from 7% in 1989 |
|
| |
The proportion of foreign born workers rose 10% from 1989 to 1995 w/
seven in ten ag workers born outside the US |
|
|
|
Table on
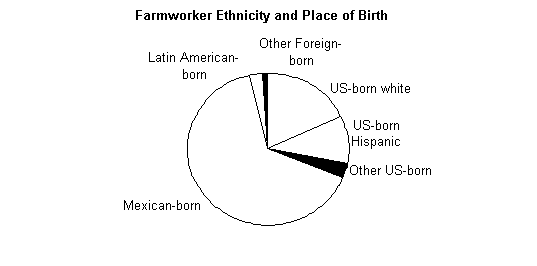 The Table on Farm worker Ethnicity & Place of Birth shows that about
1/3 are US born & about 2/3s are Mexican born
The Table on Farm worker Ethnicity & Place of Birth shows that about
1/3 are US born & about 2/3s are Mexican born |
|
| |
In 2007 over 70% are foreign born & over time the population has
become increasing foreign born |
|
|
|
Farm workers were quite young; two thirds were under the age of thirty
five |
|
|
|
The participation of women in farm work declined over the last several
years from 25% to 19%. |
|
| |
One in three US born workers was a woman whereas only one in eight
foreign born workers was a woman |
|
| |
The Immigration Reform and Control Act (IRCA) legalized a very large
group of farm workers |
|
| |
The vast majority of these workers became Legal Permanent Residents |
|
| |
Many of these newly legalized workers stayed in US agriculture and
many left for other occupations |
|
| |
INCOME |
|
| |
Farm workers had low individual earnings from farm work; the median
income from farm work was between $2,500 and $5,000. |
|
| |
Three fourths earned less than $10,000 annually |
|
| |
Most (3/5th) farm workers are poor & and the proportion is increasing
over time |
|
| |
Despite their poverty, few farm workers use social services |
|
| |
About 100,000 foreign born eligible farm worker households may be excluded
from each of the major programs such as food stamps, Medicaid & WIC
due to legislation passed by Congress in 1996 |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
External
Links
|
|
|
BARGAINING |
|
| |
Bargaining is the contract negotiations, & all that it entails
( bargaining structure, unit(s), issues, etc. ) engaged in by unions(s)
& employer(s) |
|
| |
Bargaining structure is the organizational nature of the relationship
btwn union(s) and employer(s) in contract negotiations, including a specification
of the employees and facilities covered |
|
| |
Types of bargaining structure units: A bargaining unit
is a collection of employees w/ similar interests who are represented by
a single union representative |
|
| |
Factors Impacting Bargaining: The most important factors impacting
bargaining are economic, in the form of the increased competition
that resulted from globalization & deindustrialization, and political,
in the form of an aggressive anti labor stance by mgt & the govt |
|
| |
Unionization has traditionally been fought by US firms |
|
| |
Beginning in the 1970s, firms implemented active union avoidance programs
by fighting new organizing, shifting production from unionized plants to
new greenfield operations, & reducing investment in unionized plants |
|
| |
Adversarial relationships carry over from organizing to bargaining
& implementing contracts |
|
| |
The union needs gains through bargaining to keep the membership committed
to the union |
|
| |
Unions are granted the right to exclusive representation by
the Wagner Act, therefore the union must be responsive to all bargaining
unit members |
|
| |
The law specifies that mandatory bargaining issues focus on immediate
economic issues of wages & hours, & not employer issues or union
survival issues |
|
| |
As a result of the increased competition from globalization,
mgt has sought some cooperative relationships w/ wkrs in the wkplace |
|
| |
Mgt tends to view cooperative relationships as those in which the union
has an insignificant role in decision making |
|
| |
Integrative bargaining is the bargaining over issues in which
both parties may achieve a better position than the one held previously |
|
| |
The primary role of unions is to negotiate wages & conditions at
work & to enforce the contract agreed to by mgt & labor |
|
| |
After a union wins a certification election, it negotiates a contract
w/ the employer, who is required to bargain in good faith |
|
| |
There are 150,000 contracts covering 17 mm unionized workers in the
US & over half of these workers are covered by the 2000 largest contracts |
|
| |
Labor contracts are a significant extension of the property rights
of wkrs over their jobs & over their conditions of employment |
|
| |
Col barg has resulted in union wkrs earning about 10 to 15% more than
nonunion wkrs (Wallace, Leicht & Raffalovich, 1999), not including
fringe benefits |
|
| |
Union employees receive 24% of their total compensation in fringe benefits
as compared w/ 18% for nonunion wkrs |
|
| |
Labor contracts typically reduce the gap btwn the highest & lowest
paid wkrs in a wkplace because unions are committed to improving conditions
for the lowest paid wkrs & because a small wage gap increases wkrs'
solidarity |
|
| |
Col barg agreements are open contracts that include almost anything
including wages, benefits, overtime & shift premiums, promotion &
layoff procedures, due process, grievance procedures, etc. |
|
| |
Elected officials, including the president, vice president, & the
shop steward get limited release time to deal w/ union business such as
grievances |
|
| |
See Also: The Shop Steward |
|
| |
Provisions concerning wk rules are uncommon in labor contracts
because mgrs regard the determination of wk rules as their inalienable
right |
|
| |
Some work rules are negotiated, especially in hazardous wk situations |
|
| |
Featherbedding is forbidden by law |
|
| |
Seniority clauses are used to allocate first choice of shifts, protection
from layoffs, job transfers, access to training, etc. |
|
| |
Mgrs favor promotions based on merit as opposed to seniority |
|
| |
GRIEVANCES |
|
| |
Contracts include provisions for due process & grievance procedures |
|
| |
Grievance procedures are the set of procedures for handling
wkrs' complaints about violations of their rights under the contract |
|
| |
The shop steward or other appropriate union official has the right
& duty to represent wkrs |
|
| |
If there is a grievance, the wkr, the appropriate mgrs & the shop
steward will try to resolve it |
|
| |
If it cannot be resolved this level, the shop steward will advance
the grievance, in writing, to the next highest orgl level, perhaps to the
plant mgr & the union president |
|
| |
If the steward, the plant mgr, or the union president cannot agree,
most contracts mandate final & binding arbitration by a third party
mutually agreed on by the union & mgt |
|
| |
Most arbitrators are members of the American Arbitration Assoc |
|
| |
Dealing w/ grievances is very important to the functioning & value
of the labor mvmt |
|
| |
Grievance settlement is many workers' primary experience of their union |
|
| |
Individually wkrs are powerless in relation to mgt, but w/ the union
behind them & w/ the negotiation of strong grievance procedures, the
power relationship btwn wkrs & mgt is equalized |
|
| |
The grievance procedure creates an impartial hearing if a dispute cannot
be settled by direct negotiation |
|
| |
Grievance procedures can also benefit mgt because they channel personal
disputes into more peaceful mechanisms of conflict resolution |
|
| |
EMPLOYEE INVOLVEMENT PROGRAMS |
|
| |
Because mgt has attempted to eliminate the involvement of the Labor
Mvmt in employee participation programs, labor has been slow to warm
up to such programs |
|
| |
Members often support unionization because they seek some "voice"
in their employment relationship |
|
| |
Employee involvement programs also give some form of "voice" |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Landmark
Strikes
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
A strike is any coercive measure which utilizes a refusal to work or
to continue some procedures |
|
| |
A strike is a concerted or general quitting of work by a body of employees
in order to coerce their employer or employers in some way, as when higher
wages or shorter hours are demanded, or a a reduction of wages is resisted |
|
| |
A general strike occurs when several trades strike simultaneously |
|
| |
A mass strike revolt by general population against some major
aspect of the social order |
|
| |
A sitdown strike is a strike where workers stay in their places
on the job, but stop working |
|
| |
Unskilled workers developed the sitdown strike in the 1930s |
|
| |
Sitdowns adopted by other mvmts: civil rights, antiwar, nuclear freeze,
env mvmt |
|
| |
A sitdown strike is a normal strike where workers withhold their labor
would not work for unskilled workers in this era because they were too
easily replaced |
|
| |
Sitdowns were stage against speed ups or abuses by foremen |
|
| |
Sitdowns were used to pressure a company to recognize & bargain
w/ a union |
|
| |
Sitdowns were generally short, lasting from a few minutes to a few
hours |
|
| |
But these these short sitdown strikes could disrupt production, especially
in highly coordinated mass production industries |
|
| |
The most important feature of the sitdown strike is that it prevents
workers from being replace w/ strikebreakers |
|
| |
A limited strike is a strike that is limited in some way that
is intended as a demonstration of power or a "warning shot" |
|
| |
A wildcat strike is a strike by a local or some other subset
or unionized workers that is not authorized by the union as a whole |
|
| |
Strikes & the threat of strikes are the most important method though
which unions win benefits (Wellman, 1995) |
|
| |
Strikes are infrequent & are not always successful |
|
| |
In 1998, there were 40 strikes in the US that involved over a thousand
workers |
|
| |
In 1998, a total of 387,000 workers were involved in these 40 strikes |
|
| |
In 1998, lost time due to strikes represented only 0.02% (0.0002) of
workers |
|
| |
The peak of strike activity in the postwar period occurred in 1971
when 2.5 mm workers were involved |
|
| |
Throughout the postwar period an average of less that 0.1% of work
time has been lost due to strikes amounting to less than one day per thousand
days worked by the labor force |
|
| |
More time is lost to the cold, industrial accidents & other common
causes than to strikes yet strikes are public information, & important
to mgt. because they represent a challenge to power |
|
|
|
In recent decades, workers are reluctant to strike because: |
|
|
|
- in 1980 President Reagan clearly signaled that the govt. was not
sympathetic to the Labor Mvmt when in response to a strike by the Air Traffic
Controllers, he fired them all & effectively destroyed the union |
|
| |
- strong anti labor tactics by corporations including the threat &
practice of closing entire factories & moving the jobs overseas |
|
| |
- of less public & govt. support for unions |
|
| |
The reluctance to strike has forced unions to look for alternatives
to strikes such as political lobbying & worker ownership |
|
| |
See Also: Lobbying as Labor Movement Strategy |
|
| |
See Also: Workplace Democracy |
|
| |
The direct benefits of strikes & unions are that wages &
benefits are higher & working conditions better for unionized workers
&
nonunionized workers |
|
| |
Union gains bring up wages in related plants & industries because
business must offer competitive wages & because they see commensurate
wages as an anti union strategy |
|
| |
Non unionized workers who benefit from union practices are indirect
beneficiaries & thus in the economic sense are termed "free riders" |
|
| |
See Also: Landmark Strikes: |
|
| |
The Homestead Strike, July, 1892 |
|
| |
The Pullman Strike, 1894 |
|
| |
The Anthracite Strike, |
|
| |
The Easter Strike, Ludlow, CO |
|
| |
The Flint Sitdown Strike, 1937 |
|
| |
Air Traffic Controllers Strike |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on the
Labor Movement, Politics, & the National Legislative Agenda
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
Labor parties first developed in Europe |
|
| |
In Europe, most unions attached themselves to political parties |
|
| |
Labor Parties are powerful in Europe, but non-existent in the US &
Japan |
|
| |
Labor Parties pursued improvement for the working class through
a combination of labor & political action |
|
| |
While some attempts at US Labor Parties were made, a Major US Labor
Party never developed in the US or w/ US Unions |
|
| |
Guilds grew into unions & by 1820s established political parties
in over a dozen states |
|
| |
Labor parties became important power brokers among the major political
parties |
|
| |
Labor parties never developed in the US as compared to Europe because
the Europeans had the unifying force of the remnants of feudal elite to
rally against |
|
| |
The US political system makes 3rd party movements difficult to establish |
|
| |
The US has historically, violently repressed unions |
|
| |
The Democratic Party has historically been the party that Labor has
supported |
|
| |
In the 1990's & 2000s, this coalition has become frayed for a number
of reasons |
|
| |
The Democrats have embraced causes at odds w/ the Labor Movement, including: |
|
| |
- the Civil Rights Movement |
|
| |
- the Environmental Movement |
|
| |
- the Free Trade Movement |
|
| |
In 2004, Labor cast its support primarily behind Richard Gephardt,
& to a certain extent, John Dean; however, both were defeated by John
Kerry, who was then endorsed by Labor |
|
| |
Unions exert political power through their organizational influence |
|
|
|
See Also: Power as Influence |
|
|
|
Unions register voters, especially low income & working class voters,
encourage voters to vote, allocate non cash union resources such as staff
time & volunteer efforts to the candidates who support Labor, &
lobby as an interest group for legislation favorable to workers |
|
|
|
Because unions have declined to a point where they directly represent
less than 20% of the workforce, they have had limited success in getting
favorable legislation passed |
|
| |
Labor supports legislation to liberalize picketing laws, elimination
of states' rights to outlaw union shops, national content legislation,
Labor's campaign contributions rights, etc. |
|
| |
Labor has greater success when it cooperates w/, rather than compete
w/ other groups |
|
| |
Labor has found common ground w/ other groups on public education,
antipoverty legislation, civil rights, voting rights, health insurance,
public housing, occupational safety & health, etc. |
|
|
|
Unions have been a vital component, perhaps the most important component,
in support of, & in defense of the FDR New Deal social structure |
|
|
|
LABOR'S NATIONAL LEGISLATIVE AGENDA |
|
| |
Labor unions are seeking reforms in labor law to
- streamline the process of union certification elections
- extend labor rights to new grps of wkrs such as farmers
& public sector wkrs
- liberalize picketing laws
- eliminate the right of states to outlaw union shops
- restrict firms' rights to hire permanent replacement wkrs
- reinstate the sympathy strike & secondary boycott |
|
| |
The Labor Mvmt seeks to enforce firm noninterference w/ wkrs' rights
to decide if they want to be represented by a union |
|
| |
Unions have successfully backed plant closing laws but they desire
to strengthen them because of several weaknesses including serial layoffs,
lack of scope, & more |
|
| |
In recent years, the Labor Mvmt has not made much headway on legislation
under either Republican or Democratic administrations |
|
| |
Thus the Labor Mvmt has broadened it's goals to include laws that favor
the working class & the working poor generally rather than just unions
& union members |
|
| |
The Labor Mvmt supports laws that promote full employment through
- tax incentives
- public works programs
- restricting trade w/ nations that employ convict labor
- restricting trade w/ nations that employ child labor
- restricting trade w/ nations that violate wkr rights |
|
| |
The Labor Mvmt supports more funding & innovation for education |
|
| |
The Labor Mvmt frequently pairs w/ the NAACP & other civil rights
orgs to lobby, demonstrate, fund, organize, etc. for civil rights |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on the Decline
& Resurgence of the Labor Movement
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
- Project: The Decline
& Resurgence of the Labor Movement |
Link
|
| |
- Project: Video:
Walmart:
Factors Affecting Success & Decline of the Labor Movement |
Link
|
| |
- Supplement: Walmart:
The High Price of Low Cost |
Link
|
| |
- Summary: Union membership peaked in the mid 1940s &
50s at approximately 1/3 of the workforce & has declined steadily since
the mid 1950s to about half that level today. Labor has been under
attack & in decline since the 80s. Deindustrialization &
globalization have both affected labor negatively. The political
climate has shifted away from Labor in that there is less enforcement of
Labor laws & regulations & less public support for Labor.
Labor has succeeded so much that many workers are relatively satisfied
w/ work conditions & outcomes |
|
|
Link
|
The Table on US Union Membership
shows that membership peaked in the mid 1940s & 50s at approximately
1/3 of the workforce & has declined steadily since the mid 1950s to
about half that level today |
|
| |
Union membership in the US grew during the Great Depression, the 1950s,
1960s, the early 1970s, & now, the early 2000s |
|
| |
Union membership in the US declined during the 1980s, 1990s |
|
| |
But Labor is experiencing somewhat of a resurgence in the 2000s |
|
| |
For more on union demographics & growth rates see Union Membership |
|
| |
See Also: Union Membership |
|
| |
See Also: Membership Trends |
|
| |
Strikes decline from 70s to 90s |
|
| |
In 1971 at the peak of union membership, 2.5 mm workers struck |
|
| |
In 1992, when Labor was weakened by political & economic factors,
there were only 35 strikes of 364,000 workers |
|
| |
Overall, only .1% of work time is lost to strikes |
|
| |
Strikes are unpopular in today's climate of downsizing |
|
| |
There are many factors affecting the success, the decline & resurgence
of the Labor Movement, including economic, technological, social, cultural,
demographic, political factors & international competition, company
resistance, & internal union affairs |
|
| |
a. Economic Factors affect the success of the Labor Movement |
|
| |
Deindustrialization, the movement of smokestack industries to
foreign, low wage countries, has resulted in the loss of traditional union
jobs in industry |
|
| |
Globalization, the movement of all industries (industrial, agricultural,
service, high tech, etc.), to low wage, foreign countries, has resulted
in the loss of traditional union jobs as well as jobs in new, growth areas |
|
| |
Traditional union jobs, i.e. industrial jobs, have largely disappeared |
|
| |
The decline of major "smokestack" industries, which were heavily organized,
resulted in less union members |
|
| |
Unions have failed at limiting downsizing |
|
| |
Wage inequality has continued / worsened by unions, as a result of
large
economic cycles ( Dual economy as created by the Great Labor Compromise
) |
|
| |
b. Technological Factors affect the success of the Labor
Movement |
|
| |
For all of history up to the beginning of the industrial age, there
was a labor shortage |
|
| |
Empires rose & fell based on how much labor they could gather |
|
| |
Since the industrial revolution, there has been a labor surplus
in the modernized sectors |
|
| |
Labor from the non modernized sectors used as competition for modernized
workers |
|
| |
Technology serves to increase the surplus of labor in the modernized
sector |
|
| |
Unions have adapted to the contrasting sectors w/ their surpluses &
deficits of labor w/ the traditional tactics of featherbedding & holdout |
|
| |
c. Social, cultural, & demographic factors affect
the success of the Labor Movement |
|
| |
For the Labor Mvmt, saturation denotes that all "easy" unionization
targets have been organized |
|
| |
The workforce has changed on many social, cultural, & demographic
dimensions, including:
- race
- skill
- nationality
- class |
- gender
- age
- politics
- status, etc. |
|
|
| |
Unions have been slow to adapt to social, cultural, & demographic
changes |
|
| |
Today the workforce is less homogenous, i.e. more diverse &
is therefore harder to unionize, to create a community of interests |
|
| |
As workers moving into the middle class (MC) had made it easier for
them to be easy to be free riders |
|
|
|
Unions entail costs such as dues, risk, cost of expansion, issue fragmentation,
& others |
|
|
|
MC wkrs see little benefit in incurring the costs of unionization since
they get many of the benefits of unionization as firms provide them to
prevent unionization |
|
| |
Non unionized wkrs receive the spillover benefits from unionized wkrs
in that the higher wages, benefits, safety programs, training & so
on that organized Labor has won for its workforce have become the standard
conditions for even the non unionized wkforce |
|
| |
Thus the key to organizing wkrs is to directly address practical membership
concerns of traditional & non traditional wkrs |
|
|
|
One reason the Labor Mvmt has declined is because of it's failure to
address membership concerns of traditional union workers (white,
working class, males in industry), as well as those non traditional wkrs |
|
| |
Today there are more professional orgs which address Labor issues
but fail to federate w/ unions |
|
| |
Labor has failed to organize the middle class (MC) & the upper
middle class (UMC) |
|
| |
The demographic set of the middle class & the upper middle class
has not been organized both because of demographic changes, but also because
the Great Labor Compromise / Wage Unionism are inherently flawed ( See
Below: Internal, Union Factors affecting the success of the Labor
Movement ) |
|
| |
The MC & the UMC get paid more today & so are not as hungry
as the WC |
|
| |
The MC & the UMC have false consciousness, i.e. they do
not have a world view or ideology that supports the interests of their
own class |
|
| |
False consciousness is similar to such concepts as inauthenticity in
philosophy |
|
| |
The MC & the UMC believe (wrongly) that:
- they may move up to the upper class
- what happens to others, i.e. the LC, does not really affect
them
- (wrongly) in individualism is the most noble / best
lifestyle
- the position of the LC & below is their own fault; i.e.
the MC & the UMC fail to understand the operation of the social forces
of culture & social structure |
|
| |
The MC & the UMC have a "voice" & so have less of a
need for unionization, because they:
- understand the legal & social systems, thus understand
their rights
- have some political power
- have some $$, & thus can afford a lawyer |
|
| |
d. Political Factors affect the success of the Labor Movement |
|
| |
As a result of the Great Labor Compromise, the American Labor Movement
has never had a political party |
|
| |
Thus, the American Labor Movement has always had a rocky relationship
w/ political parties |
|
| |
Labor lost of control of the NLRB through the election of sequential
Republican Presidents: Reagan in 1980 & 1984; Bush Sr. in 1988 |
|
| |
Staffing of the NLRB has one Presidential appointment, one Labor, one
mutually agreed to |
|
| |
Reagan Republican appealed to cross-over Democrats such as conservative,
white males, including many unionized members |
|
| |
Reagan Democrats caused decreased member solidarity |
|
| |
The US population in general is believed to be more politically alienated |
|
| |
The political climate has shifted to the right, worldwide (conservatives
gained power; liberals lost power) |
|
| |
Legislative acts (laws), regulatory agencies (govt agency rules), judicial
ruling (judicial precedent), and public opinion have all moved to the right |
|
| |
This has made it more difficult for unions |
|
| |
Employers have been supported in their aggressive stance against unions |
|
| |
More specialized anti organizing mgt. consultants |
|
| |
During the Bush Jr. administration (2000- 2004 ) first week
in office, he institutes new Executive Orders limiting union ability to
use union dues for political purposes |
|
| |
e. International Competition has resulted
in the decline & resurgence of the Labor Movement |
|
|
|
As a result of Deindustrialization & Globalization, competition
among workers has increased as has competition among businesses |
|
|
|
Increased job pressure as seen in high unemployment, lay-offs, &
downsizing have all made workers reluctant to join unions & to go on
strike |
|
| |
Job pressure resulted at least in part from international competition
& the movement of factories & corporations overseas for cheap labor,
low taxes, low environmental regs, & low safety & health regs |
|
| |
Because of job pressure many corporations have felt able to seeks contractual
concessions from Labor or their total elimination |
|
| |
Wage concessions peaked in the early 1980s when unemployed was above
9% & have declined since then |
|
| |
Chronically high unemployment has created a new bargaining environment
that creates an aggressive stance on the part of mgt. |
|
| |
Direct plant closings, layoffs, downsizing all replace demands for
wage concessions & put fear into the workforce |
|
| |
f. Increased Company Resistance has resulted in the decline
of the Labor Movement |
|
| |
See Also: Corporate Activity & the
Labor Movement |
|
| |
Mgt is increasingly resistant to unions, & has activity used union
busting strategies & tactics |
|
|
|
g. Internal, Union Dynamics
affect the success of the Labor Movement |
|
| |
The Labor Mvmt is not a monolithic org, rather it continues to have
deep internal schisms |
|
| |
Vrious unions had employed different strategis for articulating &
realizing wkrs' goals (Form, 1985) |
|
| |
Labor embraces a variety of divergent viewpts & needs, ranging
from those of doctors & skilled craftwkrs to clerical wkrs & janitors |
|
| |
Labor often merely reacted to circumstances both because of the conservative
nature of it's leadership, but also because of the power of corps, &
the rapid changes in the socio historical landscape |
|
| |
Unions have been attacked physically, & w/ econ & social methods
such as disinformation & propaganda |
|
| |
Unions have had to embrace innovative & risky strategies in the
past to overcome adversity, & are doing so again |
|
| |
Risky strats imply that some will fail & some will succeed &
at present, Labor is experiencing a modest, but important comeback |
|
|
|
Unions reacted to technological displacement of workers w/ traditional
strategies of "featherbedding," & hold-out |
|
|
|
Unions reacted to economic factors of downsizing, etc. w/ traditional
strategies of "featherbedding," & hold-out |
|
|
|
Unions have not accepted economic change; unions should advocate
retraining & organization of new industries |
|
|
|
Unions chose political allies based on interests other than
those of the membership, i.e., rejection of politicians who fought corruption |
|
|
|
Unions have rejected, & not embraced political allies |
|
|
|
- Minorities & the Civil Rights Movement |
|
|
|
- The Environmental Movement |
|
|
|
- The Women's Movement |
|
|
|
The Labor Movement has been less aggressive at organizing |
|
|
|
Working together has the advantage that there is less "raiding", but
it has the disadvantage that there is less competition for members |
|
|
|
Unions have been slow to change: to organize service jobs,
women, minorities, etc. |
|
|
|
Union corruption has discouraged many workers from joining a union |
|
|
|
Lack of union democracy creates a lack of internal debate &
domination by an old guard who is not always responsive to the desires
of the membership |
|
|
|
The GLC & Wage Unionism are inherently flawed |
|
|
|
Union Strategy as controlled by the old guard needs revision / updating |
|
|
|
Great Labor Compromise / Wage Unionism are inherently flawed |
|
|
|
Part of the "wage unionism deal"/ Great Labor Compromise was that Labor
would unionize only craft & industrial workers, who at that time were
Lower Class (LC) |
|
|
|
This strategy retards organization of non-traditional workers |
|
|
|
This strategy retards organization around non-traditional issues |
|
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Industrial
Economic Systems
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
The Industrial Revolution (IR) is said to have begun in England
even though industrial tendencies existed in many countries |
|
| |
The IR spread throughout Europe, North American & eventually to
the rest of the world |
|
| |
The Early Industrial Age was characterized by the use of water power,
then steam power to power machines in factories |
|
| |
The secondary sector became the most powerful & important |
|
| |
The industrial sector is the result of the development of technology
and social organization in the form of bureaucracy, the factory system,
the wage system, etc. |
|
| |
During the industrial age tradition became less influential,
& rationality, science, technology, education, etc. became more influential |
|
| |
Large scale govts based on legal rational authority replaces
the traditional authority of monarchies |
|
| |
See Also: Weber on legal rational authority, traditional authority,
charisma |
|
| |
Industrialization of the economy produced a surplus unlike the
world had ever seen |
|
| |
The industrial production of a surplus resulted in a dramatic long
term
rise in the standard of living w/in the industrialized countries,
though it also created more poor people living at a worse level
than under feudalism or other economic systems |
|
| |
Dickens noted this in the Tale of Two Cities, which begins,
"It
was the best of times and it was the worst of times..." |
|
| |
Industrialization made life harder because of the long hours, low wages,
& brutal & unsafe working conditions |
|
| |
But w/ the rise of unions, the middle class & a govt. that
regulates the functioning of big business people have better diets, more
adequate shelter, better health care, & more luxury goods |
|
| |
Because of industrialization, life expectancy has increased dramatically
& birth rates have declined dramatically |
|
| |
Industrialization has resulted in greater social equality than
feudalism |
|
| |
Industrialization has created greater equality w/in the system
in that there is a middle class, yet there remains a lower class who are
very poor |
|
|
|
Industrialization has created greater inequality btwn nations
in that the wealth is concentrated in the industrial nations while non
industrialized nations are poorer than ever |
|
|
|
See Also: Globalization |
|
| |
Inequality increased during the Early Industrial Age
because unions had not yet gained enough power to resist the exploitation
of the Robber Barons of big business |
|
| |
The wealthy have retained wealth but allowed a middle class to emerge,
which gives a historically high level of prosperity to a significant segment
of the population, & thereby avoiding revolutions that might deprive
them of their wealth |
|
| |
The rise of the middle class is accompanied by declining birth rates
& increasing democratization |
|
| |
Most social theorists believe that the rise of the middle class, declining
birth rates, & democratization are all mutually reinforcing
& that the demise of any would be seriously dysfunctional for modern
society |
|
| |
Though it is too early to be certain, the trend toward greater equality
may be reversed in the Post Industrial Age |
|
| |
See Also: Post Industrial Age |
|
| |
Major industrialized societies of the first world experience few revolutions
though many smaller, developing countries do |
|
| |
The transition from agricultural to industrial society is often
accomplished w/ the blood of revolution & war |
|
| |
Farley posits that industrialized nations to to war less often
than preindustrialized nation, but notes that industrialized nations have
fought WW 1 & 2 which killed more people than all other wars combined,
& the cold war resulted in the biggest military build-up the world
has ever seen |
|
| |
Though it is too early to be certain, it seems democracies rarely go
to war w/ democracies; however it is useful to note that pre WW 2 Germany
& Italy were democracies that became oligopolies ruled by a single
man |
|
| |
During the Cold War, the industrialized nations of the US & its
allies fought proxy wars w/ the USSR & China & their allies
in SE Asia & Africa |
|
| |
After 1989 when the Cold War ended, the industrialized nations fought
wars w/ partially industrialized nations such as Bosnia, Afghanistan, Iraq,
etc. which are largely the result of the collapse of the Cold War world
order |
|
| |
INDUSTRIAL SHIFTS |
|
| |
The shifts in the indl econ sys from the Early Indl Age to the Indl
Age to the Post Indl Age represents, one type of indl shift, one of the
overall maturing of industry |
|
| |
Shifts in the composition of industries & occupations have always
occurred, & they always have many effects throughout all the structures
of society |
|
| |
Many types of shifts occur in industry including shifts related to
major technological changes such as that inherent in the rail roads, the
automobile, & computerization |
|
| |
Indl shifts today have tended to undermine traditional union strongholds |
|
| |
Employment has declined in industries & occupation in which unions
became strong in the 1930s, such as mining & steel |
|
| |
Employment has increased white collar occupations & services industries
in which unions have historically been weak |
|
| |
The Labor Mvmt has organized aggressively in the areas of employment
growth such as restaurants, hotels, teachers, & others, just to maintain
membership at current levels |
|
| |
Organizing wkrs in the economic growth sectors has only been partially
successful in that unionization among white collar wkrs increased from
12% in 1970 to 15% by the mid 90s |
|
| |
While new organizing has increased the number of female wkrs from 10
to 12%, today well over half of new union members are female |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Global
Labor Relations
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
Labor orgs vary in:
- collective bargaining
- their involvement in political activity
- decision making w/in societies, industries, & enterprises
- the amt of globalization they experience, &, or
react or relate to |
|
| |
The organization & structure of lab mvmts & unions around the
world also differs widely |
|
| |
Major labor mvmts can be found in the European Union (EU), Australia,
Japan, East Asia, & Eastern Europe |
|
| |
The major differences btwn the No Am lab mvmt & the EU is that:
the EU lab mvmt has formed political parties in many nations |
|
| |
Around the world, plant level activities are more likely to
embrace union mgt control of the wkplace |
|
| |
Around the world, many govts have laws that are more conducive
to the lab mvmt |
|
| |
Around the world, union power resides in labor federations in
the EU & Japan |
|
| |
Work councils are most prominent in Germany & Sweden |
|
| |
Wkrs may be represented by more than one union in a wkplace,
& recognition is gained through the bargaining process |
|
| |
Trade unions continue to undergo change in Eastern Europe, i.e.
the Warsaw Pact nation which were satellites of the former Soviet Union |
|
| |
In some east Asian nation, unions are either outlawed, highly restricted
or controlled by the govt & firms |
|
| |
In the EU, bargaining issues are broadly defined because:
- bargaining structures are more centralized
- firms' associations represent many wkrs
- federations or national unions bargain w/ large firms
- there is no legislation in most EU countries differentiating
btwn mandatory & permissive issues |
|
| |
In Japan, bargaining issues are dealt w/ as are most decision, they
are made at the enterprise level |
|
| |
Most EU strikes are short, but strike incidence is higher in Australia,
New Zealand, Italy, & Finland |
|
| |
Conciliation is mandated in some countries, & arbitration
precedes contracting for wages in Australia |
|
| |
Union mgt coop is higher in the EU |
|
| |
A common mechanism for cooperation in the EU is the works council
which
is involved in any decision affecting employment |
|
| |
Effects of unions on firm performance is similar in the EU &
the US in that union wkrs are more skilled & productive but wage differences
btwn union & non union wkrs is smaller in the EU |
|
| |
INTERNATIONAL COMPETITION |
|
| |
The decline in union membership was also caused by many factors which
depressed manufacturing employment & discouraged unionization |
|
| |
High levels of unemployment in manufacturing have resulted from increased
international competition & the mvmt of US factories & corps overseas
in search for cheaper labor, lower taxes, & less stringent envl regs,
safety regs, health regs, child labor laws, etc. |
|
| |
See Also: Globalization |
|
| |
See Also: Deindustrialization |
|
| |
From 1970 to 2000, the Machinists & Aerospace Workers Union declined
from 754,000 to 431,000 |
|
| |
Unionized steelworkers declined from a peak of 1,062,000 in 1975 to
500,000 by 2000 |
|
| |
Because of low wage competition from less developed nations, Am indl
goods became less competitive on the world mkt |
|
| |
Because they can get better deals in less developed nations, many corps
have contracted concessions from labor, & even eliminated unions |
|
| |
In the 90s many auto plants in the US & Canada have closed as mkt
share has been lost to Japanese & Euro car makers & as US corps
have moved production overseas |
|
| |
Demands for wage concession reached a peak in the early 80s when unemployment
climbed above 9% & have declined since then |
|
| |
High unemployment has produced a new bargaining env that encourages
a much more aggressive stance by corps |
|
| |
Worse yet, direct plant closings & downsizings have often replace
demands for wage concessions |
|
| |
In 2006 Ford adopted a plan to close 18 plants, mostly in No Am |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Corporate
Activity & the Labor Movement
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
- Project: Union Avoidance |
Link
|
| |
- Project: Video:
Walmart:
Envl Factors affecting Union Avoidance |
Link
|
| |
- Supplement:
Video:
Walmart & the Labor Mvmt
19:36 |
Link
|
| |
Union busting is now a professionalized business consulting
service |
|
| |
There are now more “consultants” in the field of antiunion consulting
than there are union leaders |
|
| |
Businesses have improved conditions which unions traditionally fought
for: wages, hours, benefits, working conditions |
|
| |
Unfair labor practices have increased making workers more reluctant
to join unions & face up to mgt power |
|
| |
Charges of firing for union activity makes workers reluctant to join
unions |
|
| |
Mgt opposition to unionism, including legal & illegal labor
campaign tactics, a major determinant of NLRB election results, makes
it more difficult for unions to win elections |
|
| |
Paid spies, sophisticated antiunion consultants are used by corps.
to discover & eliminate pro union workers |
|
| |
75% of employers who experience union organizing hire antiunion consultants
(Levitt, 1993) |
|
| |
In the 1980s, businesses spent over $100 mm annually for antiunion
activity |
|
|
|
There are FIVE major environmental factors that affect union
avoidance |
|
| |
a. Locating the business in a nonunion region |
|
| |
b. Locating the business in a non urban region |
|
| |
c. Establishing the business in small plants |
|
| |
d. A high % of women in the workforce |
|
| |
e. A high % of professionals in the workforce |
|
| |
Union avoidance can be enhanced through a human relations program that
creates a culture of anti unionism |
|
| |
Union avoidance can be enhanced through a human relations program that
creates a culture of reluctance to engage in industrial conflict |
|
| |
Substantive policies of a human relations policy often include: |
|
| |
a. employment security |
|
| |
b. a policy of promotion from w/in |
|
| |
c. influential & proactive personnel dept. |
|
| |
d. satisfactory compensation & benefit programs |
|
| |
e. effective feedback mechanisms including communications
programs & complaint procedures |
|
| |
f. careful selection, development, & evaluation of
managers |
|
| |
In order to implement a strong human Relations programs, firms must
be: |
|
| |
a. profitable |
|
| |
b. growing |
|
| |
c. undiversified |
|
| |
d. active founders |
|
| |
e. & the best HR programs occur in light industrial
manufacturing or service companies |
|
| |
Corps believe that a corporate strategy of union avoidance is successful
by establishing trust, cooperation, confidence, & enhancing human values,
working together, ultimately resulting in the efficient & effective
long run functioning of the firm |
|
| |
A corporate strategy of union avoidance has FOURTEEN effects of: |
|
| |
1. creating a more flexible organization |
|
| |
2. no strikes |
|
| |
3. lower turnover & absenteeism |
|
| |
4. reducing 3rd party interference |
|
| |
5. more responsive & committed employees |
|
| |
6 employees' believing the firm is committed to security
& equity |
|
| |
7. positive employee attitudes |
|
| |
8. high morale |
|
| |
9. open & direct communications |
|
| |
10. the majority of the employees not wanting to join
the union |
|
| |
11. an absence of adverse relationships btwn employees
& mgt. |
|
| |
12. creating the perception that the firm is a desirable
place to work, which results in the number of applicants exceeding the
number of openings |
|
| |
13. creating higher productivity |
|
| |
14. creating strong mgt employee relationships |
|
| |
Workers' Voice: Giving the workers a voice creates a lower
employee turnover rate |
|
| |
Unions know that their efforts create voice for the workers, which
has the effect of a lower employee turnover rate |
|
| |
Voice, which deals w/ immediate issues, is generally created by grievance
procedures |
|
| |
Voice, which deals w/ long run issues, is generally created through
negotiations |
|
| |
Grievance procedures, whether developed through a union, or
independent of it, increase employee satisfaction |
|
| |
Many firms have developed a strong grievance system that mgrs take
seriously |
|
| |
Most grievance systems have a no reprisal policy |
|
| |
IBM mgrs. have direct, anonymous access to hi level mgt. on complaints |
|
| |
Most grievance systems require that remedial action be communicated
back to the grievant |
|
| |
Many grievance systems have a worker review board that impartially
resolves grievances |
|
| |
Many grievance systems have peer review panels to oversee grievances |
|
| |
Many grievance systems have attitude surveys to stay in touch w/ employees'
issues |
|
| |
To understand grievance systems it is necessary to understand justice
systems |
|
| |
There are THREE types of justice systems |
|
| |
A distributive justice system ensures that punishment is proportionate
to the issue at hand |
|
| |
A procedural justice system ensures that methods are just by
focusing on, for example, representation, appeal, etc. |
|
| |
An interactional justice system ensures that all parties have
all the info they need to achieve justice, esp in relation to resolution |
|
| |
Other innovations that enhance human relations include vertical staff
meetings & employee involvement committees |
|
| |
The non unionized workplace often exhibits particular qualities
or structures which evolved in unionized wkplace such as: |
|
| |
a. a high level of info for workers about productivity,
etc. |
|
| |
b. discussions of quality & productivity |
|
| |
c. employee involvement methods |
|
| |
d. autonomous work teams |
|
| |
e. a formal complaint systems |
|
| |
f. a reduced number of job classifications |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on the
Growth Areas for the Labor Movement
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
Despite the development of deindustrialization, globalization, the
service econ, & the resistance of corps, the Labor Mvmt has experienced
growth |
|
| |
A recent spurt in growth in the overall membership numbers of the Labor
Mvmt preceding a few decades of decline actually serves to hide the actual
numbers of new members in unions |
|
| |
Because the traditional econ sector of mfr has experienced such a steep
decline, unions had to aggressively organize just to slow their membership
loss |
|
| |
The Am Federation of State, County, & Municipal Employee (AFSCME)
is one of the fastest growing unions |
|
| |
See Also: AFSCME's website at www.afscme.org |
Link
|
| |
The Am Federation of Teachers (AFT) more than quadrupled its membership
in the last 3 decades from 165 K to 694 K members |
|
| |
In 2000, the 2 of 3 largest unions in the US, AFSCME & the United
Food & Commercial Wkrs, each w/ more than 1 mm members, represented
white collar & service wkrs |
|
| |
Wkrs in large public institutions such as hospitals & schools have
been organized aggressively |
|
| |
Public sectors unions have helped keep the Labor Mvmt afloat in the
last 3 decades |
|
| |
42% of public sector wkrs are unionized compared to only 15% in the
private sector |
|
| |
One reason that more public sector wkrs are unionized is that in the
public sector, mgrs are more restricted from intimidating wkrs as compared
to the private sector through firing & because public sector mgrs must
answer to the pubic for any poor human relations in the wkplace |
|
| |
In the private sector, stockholders are much less likely to punish
mgrs for poor or intimidating human relations in the wkplace compared to
the voting public, who will punish public mgrs |
|
| |
Union membership has grown among clerical wkrs in the insurance industry |
|
| |
Clerical wkrs have unionized because of the increasing size & anonymity
of those corps & because of office automation which has weakened job
security |
|
| |
Service wkrs, including hospital & hotel wkrs & janitors are
also a growth are for Labor organizing |
|
| |
The expansion of organizing in the service sector is a revival of serving
the poorest segments of society |
|
| |
A nationwide group called "Justice for Janitors" has made gains organizing
janitors by using 60s style sitdowns & demonstrations to pressure building
owners into negotiating |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Employee
Involvement Programs: Opportunities & Threats
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
Employee involvement (EI) committees are known as QCs, QWLs, Circles,
ECs, or Committees |
|
| |
Employer / employee committees, often called quality circles,
are formed so that workers can make recommendations to mgt. about
hiring, personnel assignments, hours, terms & conditions of work, &
other similar issues |
|
| |
The issues that are dealt w/ in EI are frequently the same issues that
are the subject of collective bargaining in unionized workplaces |
|
| |
The Taft Hartley Act forbids the dominance of a Labor or union
orgs by an employer, thus outlawing "business unions" |
|
| |
The Electromation court judgment narrows an employer's ability to broadly
ask employees to consider employment issues |
|
| |
The involvement of workers in non mandatory bargaining issues
is unlikely to lead to charges of employer domination, even though this
is one of the gray areas where some workers may feel pressure, but
are unable to prove it |
|
|
|
Unions should be aware that QCs & other EI programs can weaken
union influence in the org, & therefore, control of the org |
|
|
|
Wkrs will identify increasingly w/ the firm if the union doesn't support
opportunities for interest employees to be involved |
|
| |
Communication activities in EI programs are often similar to
collecting data w/ a survey & using this data as a representation
of wkr attitudes |
|
| |
Some EI programs are vested w/ supervisory tasks |
|
| |
General Foods established work groups & the groups made their own
work assignments, created & operated training programs,
& made recommendations on staffing |
|
| |
The employee involvement program groups in the Gen Foods org was found,
in a court case, not to be an employer dominated labor org |
|
| |
Productivity studies find that giving workers more control of work
increases
productivity |
|
| |
Today, there are greater competitive pressures because of |
|
| |
- deindustrialization (conversion of old, heavy industry to
new light industry & information age-- & to services) |
|
| |
- globalization, global competition, & the movement of multinational
firms to foreign lands |
|
| |
Because of the competitive pressures of deindustrialization & globalization,
many firms are attempting to design more efficient work relationships &
quality circles are one design for increasing efficiency |
|
| |
EI programs include FOUR components, including: |
|
| |
1. improving the wkplace climate |
|
| |
2. generating commitment in both mgt & wkrs |
|
| |
3. implementing change |
|
|
|
4. creating benefit for both mgt & wkrs through increased
productivity, higher product quality, etc. |
|
| |
In planned programs, climate & commitment lead to change |
|
| |
In evolved programs, the climate leads to change which leads
in turn to commitment |
|
| |
In induced programs, change leads to appropriate climate &
commitment |
|
| |
Union willingness to become involved in QWL programs is related to
the progressiveness of the firm & increase foreign competition |
|
| |
Increased involvement in traditional wkplace decisions is related to
deregulation, changing demographics, & support by a parent national
union |
|
| |
Cooperation in strat dec mking is often increases as a result
of foreign competition & decreases as a result of domestic competition
because unions often represent wkrs in competitive domestic industries
& therefore are less willing to pit one firm against another |
|
| |
In an EI program w/ GM & the UAW, grievances, discipline, absenteeism,
number of local contract demands, & negotiating time were reduced |
|
| |
EI programs result in higher product quality & reduced grievance
rates |
|
| |
Product quality & productivity decreased when labor mgt conflict
increased |
|
| |
EI programs are associated w/ reduced absenteeism, accidents, grievances,
& quits |
|
| |
EI programs lead to greater loyalty to the union, rather than undermining
commitment |
|
| |
The effectiveness of the grievance procedures is a stronger predictor
of attitudes to the union than EI participation |
|
| |
EI is associated w/ improved job satisfaction & enhanced commo
skills |
|
| |
EI programs increase "orgl citizenship" both through participation
& changing job characteristics that require more task sharing |
|
|
|
Union antagonism toward EI does not influence employee attitudes, but
it does reduce participation |
|
| |
THE LEGALITY OF COOPERATION PLANS |
|
| |
Among unionized firms, cooperation plans meet the requirements of the
labor acts because they are jointly agreed to by unions & mgt |
|
| |
Firms & nonunion firms estb joint mgt employee committees to deal
w/ production & employment issue |
|
| |
Joint mgt employee committees may violate labor law unless the process
& the subject of their work is closely regulated |
|
| |
The Taft Hartley Act (THA) forbids firms from creating & operating
employer dominated labor orgs |
|
| |
Discussion of employment issue or proposals by committees for taking
action on areas related to wages, hours, terms, & conditions of wk
which intrude into the mandatory bargaining issues specified in the act |
|
| |
The NLRB was faced w/ ruling on the legality of an employer sponsored
committee in the Electromation case |
|
| |
In the Electromation case the NLRB asked when does a mgt wkr committee
lose its protection as a communication device & become a labor org,
i.e. a business union? |
|
| |
In the Electromation case the NLRB asked what employer conduct is interference
or domination of mgt wkr committees? |
|
| |
In the Electromation case the firm had set up five volunteer committees
to look at absenteeism, pay bonuses, etc. |
|
| |
The firm initiated the committees, drafted their goals, & had mgt
reps to facilitate |
|
| |
The NLRB rules that the Electromation wkr mgt committee was a employer
dominated labor organization |
|
|
|
While it is difficult to determine what is a legal wkr mgt committee
in a nonunion setting, such committees are still going ahead in many firms |
|
| |
HIGH PERFORMANCE WORK ORGS (HPWOs) |
|
| |
High performance wk orgs are firms that have adopted many EI &
other wk practice innovations that increase wkr participation in or control
of the the wkplace |
|
| |
Research indicates that firms need to implement a coherent set of practices
in order to enhance orgl performance |
|
| |
A study of minimills found that plants that implemented a combination
of problem solving teams, flexible job assignments, training for multiple
jobs, guaranteed employment security, & flexible pay plans were more
productive & profitable than firms that implemented smaller combinations
of these |
|
| |
Operating up time & added value were proportionally greater as
more EI programs were added |
|
| |
Wkrs are proportionally more satisfied w/ work as more EI programs
are added |
|
| |
WORKPLACE RESTRUCTURING |
|
| |
Because of globalization in the form of increased foreign competition,
a great deal of wkplace restructuring has taken place over the past 20
yrs |
|
| |
This has been the orgl env in which EI programs have been born in US
Labor mgt relations |
|
| |
Restructuring increases the intensity of wk, reduces the number of
wkrs in mfr jobs, reduces mid mgt, & has outsourced many jobs |
|
| |
Wkplace restructuring & firm performance improve when the local
union has horz & vert commo network ties & internal political vitality |
|
| |
Firms that implemented substantial EI programs during the early 90s
had higher layoffs & no net increase in pay |
|
| |
Restructuring, overall, has been negative for wkrs, & had mixed
results for the firms themselves as seen in smaller sales gains & smaller
export gains |
|
| |
EI programs have neither increased job security nor pay except where
the org's revenues were growing |
|
| |
Unions have also not made gains where EI programs were implemented |
|
| |
THE DIFFUSION & INSTITUTIONALIZATION OF CHANGE |
|
| |
An imp issue for labor & mgt is how successful changes get diffused
both w/in an org, as well as among orgs & become commonplace, the norm,
i.e. institutionalized |
|
| |
EI needs a stable env to grow, & yet it is apparent that EI in
the US has grown in the era of globalization, deindustrialization, downsizing,
sourcing, restructuring, etc. |
|
| |
In any EI program, the union needs to avoid or isolate collective bargaining
shocks & mgt needs to avoid strategic shocks |
|
| |
Layoffs create problems for teams because wkrs use competitive seniority
rights to bump in & out |
|
| |
Changes are aided by implementing them in new facilities w/ new wkrs
& then diffusion of successful changes can them move to estbed setting |
|
| |
Unions can assist change best when they have a role in strat dec mking
such as plant locations |
|
| |
They may provided needed concessions & wk rule changes to make
existing facilities economically viable |
|
| |
Training in new tech, increased job security, ensuring the viability
of the firm, & satisfying wk processes are imp issues to wkrs &
unions which EI programs can address |
|
| |
Labor should recognize that gainsharing & innovative participation
are a logical pieces of successful labor mgt relations in today's wkplace |
|
| |
The ability to institutionalize change depends on high levels of trust
& commitment by union leaders, union members, wkrs, supervisors, plant
mgrs, & corp execs |
|
| |
Each of these orgl actors has different interests, a different status
quo to protect, a different perception of EI programs, & a different
role to play in advancing EI & a stronger wkplace |
|
| |
Estbing trust is not easy in the era of globalization, but it can be
done, & it will improve the wkplace for all actors |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Union
Democracy
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
LOCAL UNION DEMOCRACY |
|
| |
Local union democracy has a quality similar to municipal politics |
|
| |
Elections generate moderate to low interest |
|
| |
In union elections, incumbents are usually reelected unless a critical
issue is at hand/mishandled |
|
| |
Union locals have regular business meetings which are open to
all members |
|
| |
Business meetings often have low attendance: equates w/
relative satisfaction |
|
| |
A contentious workplace may lead to suppression of dissent w/in union
in order to maintain a united front |
|
| |
FUNCTIONAL DEMOCRACY |
|
| |
Functional democracy denotes that although an org may not have regular
elections & other features of a democratic system, democracy is maintained
through some democratic structures, but more importantly through a value
commitment to democracy |
|
| |
W/ reference to democracy, unions typically do not typically have a
party system |
|
| |
Unions must apply the contract equally to all workers as required by
the Taft Hartley Act of 1947 |
|
| |
Union elections are every 3 yrs as required by the Landrum Griffin
Act of 1959 |
|
| |
With reference to democracy, workers generally want representation
not participation |
|
| |
Members do have the right to become involved & to offer alternative
priorities or candidates |
|
| |
Union locals may be less democratic than municipal politics, but union
members are probably less diverse & thus more satisfied w/ less democracy |
|
| |
MEASURING UNION DEMOCRACY: |
|
| |
Union democracy can be measured by measuring the degree of control
members have over SIX types of major decisions related to:
a. contracts
b. contract administration
c. service to members
d. union administration
e. political activities
f. communities |
|
| |
There are FIVE types of control members have which can be used to measure
the level of democracy, including:
a. complete control
b. limited control
c. consultation control
d. veto control
e. or no control |
|
| |
DEMOCRACY IN PRACTICE |
|
| |
National unions are required by law to hold a convention at least every
5 yrs |
|
| |
Unions which elect executive board on geographic basis are less responsive
to factions |
|
| |
At large elections results in leadership responsive to factions |
|
| |
Most leaders come up through the ranks |
|
| |
Less democratic appearing unions manage to exist because of a general
consensus of ideas |
|
| |
EXAMPLES |
|
| |
Unions support democracy through the general support of programs that
give people an effective voice in govt, community, region, & society
in general |
|
| |
The CA Federation of Teachers developed a set of lesson plans for teaching
about the role of trade unions in resolving wkplace conflicts |
|
| |
A large majority of people approve of unions, & the union image
has increased since 1980 |
|
| |
Unions are taking active roles in other social mvmts & NGOs such
as the United Way, NAACP, NOW, Greenpeace, & more |
|
| |
Unions support the increase of internal democracy in both unions &
corps |
|
| |
A study of the International Typographical Union (ITU) revealed a strong
& dynamic role of internal political parties in unions as long ago
as the 1950s (Lipset, et al., 1956) |
|
| |
The Teamsters, who was connected to organized crime, has developed
an internal group called the Teamsters for a Democratic Union (TDU) |
|
| |
The TDU has over 9,000 members in 35 chapters, publishes its own newspaper,
runs an opposition slate of candidates at conventions, & holds 30 local
elected offices (Friedman, 1982) |
|
| |
In the UAW, the New Directions Movement has fostered an internal debate
over increasing union & corp democracy |
|
| |
Organizing campaigns using greater member participation are laying
the groundwork for greater internal democracy in new & emerging unions |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
An Overview of Organizing
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
- Video: Norma Rae |
Link
|
|
|
- Project: Organizing
Tactics |
Link
|
| |
Organizing wkrs is the process of bringing wage earners together into
a union |
|
| |
In some cases, the wkrs themselves form a union to increase their bargaining
power |
|
| |
In other cases, an existing union decides to organize the employees
of a particular plant or industry |
|
| |
The union sends men & women called organizers to persuade wkrs
to join |
|
|
|
Unions have the right to exclusive representation |
|
|
|
Like the American Congress & Presidency, unions have a winner take
all policy |
|
| |
Unions do not want to share the privilege of representing the wkrs
with any other grp |
|
| |
Most unions insist on being the sole representative of a particular
group of employees |
|
| |
The practice of being the sole representative for wkrs is called the
principle of exclusive jurisdiction |
|
| |
The National Labor Relations Board conducts secret ballot elections
at firms to determine which union wkrs want, if any |
|
|
|
Under the law, only one union may represent a bargaining unit |
|
|
|
In the Parliamentary System, in Europe & many other nations, in
a district, parties receive candidates in proportion to their share
of the vote |
|
|
|
They then must build a coalition to elect the Prime Minister, which
is equivalent to the American Presidency |
|
| |
Unions have several
reasons for organizing, including that: |
|
| |
a. it is easier to get wage benefits if more workers are
organized because this increases monopoly power of Labor |
|
| |
b. organizing increases financial resources available
to the union |
|
| |
c. organizing is a means to increasing union effectiveness
& power |
|
| |
Campaigns to organize
begin at the local or national level |
|
| |
National level campaigns target specific firms & send professional
organizers |
|
| |
Organizers sometimes apply for jobs at the firm they are trying to
organize |
|
| |
Most organizers attempts begin at the local level when some worker
voices interest |
|
| |
The Labor Movement was conservative & cautious in the 1980s &
1990s because of declining membership, the corporate anti union strategy,
an unfriendly political environment, & a difficult economic environment |
|
| |
The Labor Movement has become bolder & more innovative in the 2000s
because it determined that failure to "join the battle" was not a safe
haven |
|
| |
ORGANIZING STRATEGIES: THE CORPORATE CAMPAIGN & THE INSIDE
GAME |
|
| |
Two new Labor organizing & bargaining strategies are now in practice,
including the corporate campaign & the inside game |
|
| |
The corporate campaign expands union activity outside the workplace
by targeting a corporation's network w/ traditional organizing & bargaining
tactics such as distributing literature linking the target corp. w/ wage
cuts, unsafe work practices, layoffs, shutdowns, discrimination, sexual
harassment, or whatever issue the workers have w/ the corp. |
|
| |
In a corporate campaign, the union may address the financial backers
of the corp., consumers, & the public |
|
| |
Some unions have closed accounts w/ the lenders of the target corp
to pressure corps to come to terms w/ their wkrs (Peterson, Lee, and Finnegan,
1992) |
|
| |
Public boycotts of lenders can be encouraged |
|
| |
Negative publicity can have a strong effect on the target corps |
|
| |
The inside game is a bargaining tactic whereby union members
utilize informal shop floor activities to demonstrate workers' resolve,
power, & issues |
|
| |
The inside game may use the old tactic of "work to rule" where workers
follow procedures to the letter of the standard operating procedures |
|
| |
Working to rule slows down production dramatically |
|
| |
Workers may stop work & collectively discuss grievances w/ supervisors,
especially grievances about safety issues |
|
| |
The inside game operates in the gray area btwn appropriate procedures
& sanctionable offenses |
|
| |
For the inside game, workers may wear union buttons or a single color
of style of clothing to build solidarity & bolster courage |
|
|
|
The advantage of the inside game is much like the sit down strike,
the wkrs gets to stay on the job & draw pay while pressuring the corp |
|
| |
A union tries to get all the wkrs in a plant or industry to join the
union |
|
| |
In some establishments, the union & the employer agree to set up
a union shop |
|
| |
In a union shop, the employer can hire anyone but they must
eventually join the union |
|
| |
But new employees must join the union w/in a certain period or pay
the equivalent of union dues |
|
| |
The arrangement of joining or paying dues spreads the cost of union
representation evenly among the employees, who also share any benefits
the union wins |
|
| |
But individuals who oppose the union must contribute to it against
their wishes |
|
| |
Twenty one states, most of them in the South, have laws banning
union shops |
|
| |
Laws banning union shops are called right to work laws because
they guarantee a person's right to obtain employment without joining or
supporting a union |
|
| |
A business that employs both union & nonunion wkrs is called an
open
shop |
|
| |
Union dues are higher in most open shops than in union shops
because fewer people share the cost of union representation |
|
| |
In a closed shop, which is now generally illegal, the employer
could hire only union members |
|
| |
During the 1800s & early 1900s, many employers insisted that their
wkrs sign a promise not to join a union |
|
| |
An agreement promising not to join a union was called a yellow dog
contract |
|
| |
The Norris LaGuardia Act of 1932 said that an employee could
not be sued in fed court for breaking a yellow dog contract |
|
| |
As a result of the inability to sue to enforce yellow dog contracts,
such agreements became unenforceable and gradually disappeared |
|
