Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on an
Introduction to Global Warming
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
- Supplement: UNIPCC |
Link
|
| |
- Supplement: EPA on Global
Warming |
Link
|
| |
- Supplement: Frontline:
Timeline of the Science & Politics of Global Warming |
Link
|
| |
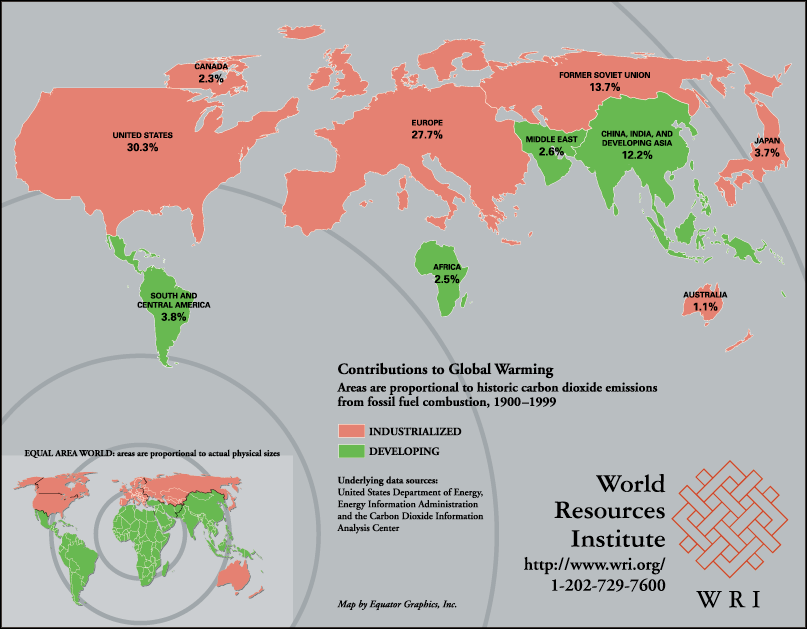
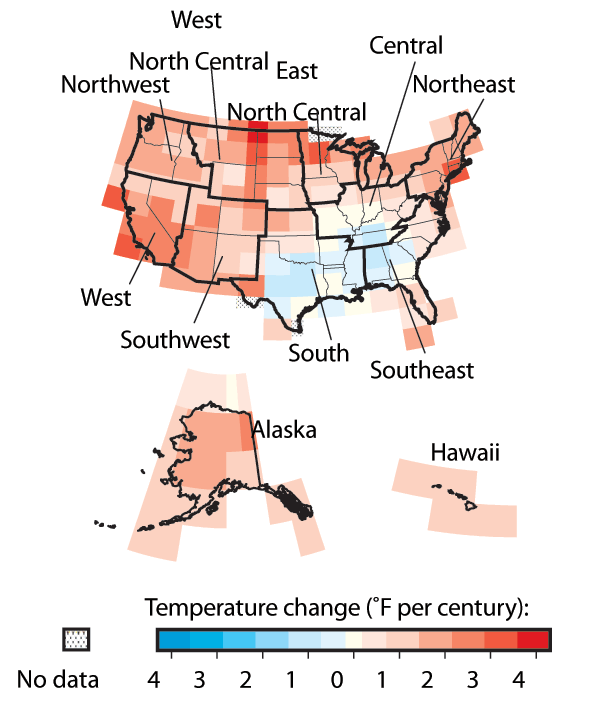
GLOBAL WARMING IS AN INCREASE IN THE AVERAGE TEMPERATURE OF THE
EARTH'S SURFACE |
|
| |
The term global warming, as used in most contexts today, refers to
human caused planetary warming, but in fact global warming & cooling
has occurred throughout history |
|
| |
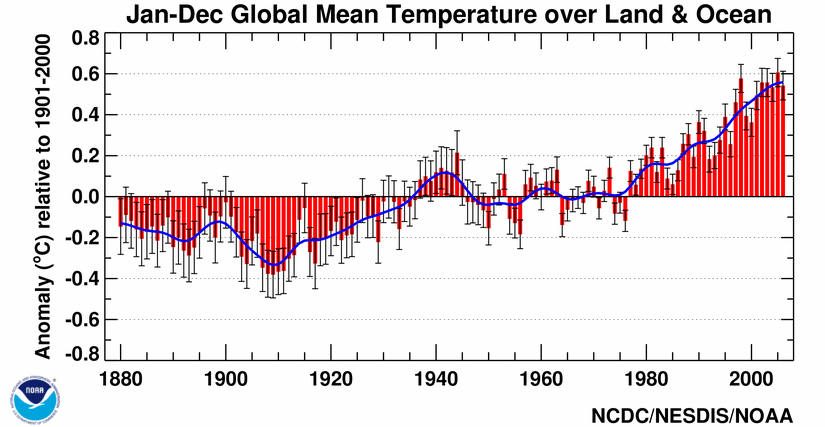
Since the late 1800s, the average temperature has increased about 0.9
to 1.6 Fahrenheit degrees (0.5 to 0.9 Celsius degree). . |
|
| |
Many experts estimate that the average temperature will rise btwn 3
& 8 additional Fahrenheit degrees (1.5 & 4.5 Celsius degrees) by
2100 |
|
| |
The current rate of increase of temp is several times faster than global
rates that typically occurred over long periods in the past |
|
| |
THE CAUSES OF GLOBAL WARMING ARE NATURAL & HUMAN &
NOT TOTALLY UNDERSTOOD, WHICH CREATES POLITICAL BICKERING |
|
|
|
Scientists disagree about the importance of various causes & potential
impacts of the warming trend |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: The Factors Contributing to Global Warming |
|
|
|
In general, it is believed that the greenhouse effect is responsible
for global warming & human's burning fossil fuels is on the the major
contributors to increasing the greenhouse effect |
|
| |
The atmosphere acts like a layer of blankets around the earth, trapping
solar radiation, which keeps the planet warm |
|
|
|
The Earth would be as cold as the moon w/o the greenhouse effect |
|
| |
CO2 is one of those blankets, traps heat |
|
| |
The primary greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide (
CO2 ), methane ( CH4 ), nitrous oxide ( NO ), & others |
|
| |
Human activity adds to all of these gases in the atmosphere |
|
| |
But if we release too much CO2 the blanket is too thick & we get
hot |
|
| |
Human activity, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, releases carbon,
& creates CO2 |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: The Greenhouse Effect |
|
|
|
THE ANALYSIS OF GLOBAL WARMING IS THE MOST COMPLEX SCIENCE QUESTION
OF ALL TIME
SET IN A TUMULTUOUS GEOPOLITICAL CONTEXT |
|
|
|
To understand the any env problem, but esp the global warming, one
needs to understand social construction of science |
|
|
|
Because global warming is a truly global problem, & because there
are both natural & social / human causes, the science, physical &
social, of the issue is perhaps one of the most complicated issues facing
humankind |
|
|
|
The social / poltical construction of science masks the real dilemmas
found in any attempt to develop policy from science |
|
| |
The envl / global warming debate swings from alarmism to pacifism because
envl science, like any issue, can become politicized when uncertainties
are emphasized, overlooked, focused on one pt of view, etc. |
|
|
|
Global warming & any global issues exist in the socio hist context
that is a combination of post cold war relations, post 9-11 relations &
the war on terrorism, post indlism, & the growing econ dev of semi
peripheral & peripheral nations such as China, India, Brazil, &
the Democratic Republic of Congo, & Bolivia, respectively |
|
|
|
THE SOLUTIONS TO GLOBAL WARMING OCCUR ON THE PERSONAL LEVEL &
THE SOCIAL / POLITICAL LEVEL |
|
|
|
People can make choices that make a real difference such as switching
to energy efficient light bulbs, recycling, using reusable shopping bags,
etc. |
|
| |
Govt & world instits are considering policies that encouraging
instit such as businesses to reduce energy use, limit CO2 production, save
forests, etc. |
|
| |
Two major lines of action are currently being pursued to limit global
warming & improve the env: global warming conferences & the
modification of the ops of global development instit |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: Global Warming Conferences |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: Global Development Orgs & the Env |
|
| |
The debate on global warming & the env in general often reflects
rich nations' interests, & ignores the semi peripheral & peripheral
nations' interests |
|
| |
In the media & the public consciousness, the debate on global warming
goes back & fourth btwn alarmism to pacifism, & what is needed
is reasonable debate & action |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
THE COMMONS IS PROPERTY THAT IS HELD BY THE PUBLIC |
|
| |
The commons is any resources held in common by the people |
|
| |
Today we often, but not always, call the commons public property |
|
|
|
The commons is the opposite of private property or land which has a
designated national sovereign |
|
| |
The commons includes resources that are not private property or public
property, in that the commons includes resources for which no person, nation,
etc. has ownership, & yet it has not been designated as public property |
|
| |
THE NATURE OF PUBLIC PROPERTY HAS CHANGED DRAMATICALLY OVER TIME |
|
|
|
Our notion of private property is greatly expanded as compared to that
of the middle ages |
|
| |
In the Mid Ages, peasants, i.e. the commoners had private property
in the sense of their homes & personal possessions, but in another
sense their sovereign, King, actually owned that property |
|
| |
All material property, & the people belonged to the sovereign,
but in another sense it belonged to the Kingdom in that the ruler only
had limited rights of bequeathal in that in most cases he could only bequeath
to the eldest son |
|
| |
The term commons originally referred to the common people as distinguished
from their rulers or a ruling class |
|
| |
The commons indicated the body of people not ennobled, as represented
in England by the lower house of Parliament House of Commons |
|
| |
Later the term commons came to denote the food provided at a common
table |
|
| |
The commons as the food provided by ruler represented the expanded
obligation of the ruler to the people, & the right of the people to
require the ruler to provide particular goods & services to them |
|
| |
The obligation of the ruler / right of the people finally expanded
to include access to land held in common, i.e. the commons |
|
| |
THE 'TRAGEDY OF THE COMMONS' IS THAT EVERYONE TRIES TO EXPLOIT IT
AS MUCH AS THEY CAN |
|
|
|
The dilemma of the commons is that if I exploit the env, I benefit
but everyone else loses; if I don't exploit, I lose & everyone else
wins |
|
| |
Today the public property has relatively clearly defined protections
that generally prevent individualistic exploitation |
|
| |
However, there is still large amts of resources that are not private
or public property & therefore are 'the commons of modernity' |
|
| |
Examples of the commons of modernity include the public property, &
the oceans, Antarctica, the Arctic, space, moon, the EM - spectrum, &
parts of the env which cannot be made into private property such as the
air, some bodies of water, many wild species of flora & fauna, etc. |
|
| |
The tragedy of the commons is seen in that commons areas are
often 1st area threatened by misuse |
|
| |
Everyone can use the commons, but no one is responsible for it |
|
| |
It is to an individual's advantage to use the commons as much as possible
since it is free |
|
| |
Others may use the commons up if I don't get it first |
|
| |
Grazing on public land encourages individuals, including corps, to
graze as many cattle as possible w/o concern for the land |
|
| |
Wood cutting on public land encourages individuals, including corps,
to log as much as possible w/o concern for the land |
|
| |
Agriculture industry grows as much as possible to max profits in the
short term, w/o a long term concern for the land |
|
| |
Note that these relationships do not necessarily change even w/ private
property because capitalism has created an ethic of max profits today,
w/o concern for the next gen, even if they are your own family |
|
| |
W/ private land there is a greater chance for responsible use because
a limited number of people may use the resource, & one person / grp
is responsible |
|
|
|
THE COMMONS IS AN 'INDICATOR SPECIES' IN THAT IT'S HEALTH IS REPRESENTATIVE
OF ENVL HEALTH IN GENERAL |
|
|
|
Healthy societies have had healthy commons policies |
|
| |
This develops a sense of cooperation & common responsibility |
|
| |
Commons areas are often the first to be threatened by misuse |
|
|
|
NATIONS ARE GAINING SOVEREIGNTY OVER SOME COMMON AREAS & DESIGNATING
OTHER AREAS AS 'COMMONS' |
|
| |
Intl bodies such as UN & EC see envl issues as a way to build their
orgs: this is their legit territory |
|
| |
It is hard for nations to argue against the commons w/o appearing to
be self interested |
|
|
|
The envl mvmt is a creator of the modern commons |
|
| |
The envl mvmt has a greater vision for alt society than other soc mvmts
as seen in it's critique of capitalism, alt value sys, alt soc, common
property, etc. |
|
|
|
LANDLORD - TENANT PROBLEM IS SIMILAR TO TRAGEDY OF COMMONS IN THAT
USERS HAVE INCENTIVES TO EXPLOIT |
|
|
|
Landlords pay capital investment costs |
|
|
|
Tenants pay operating costs |
|
|
|
Both tenants & landlords will tend to forego these costs, i.e.
investments & operating costs, unless they have long term reasons not
to |
|
| |
Landlords often have the long term interest of the value of bldg is
going up |
|
| |
The tenant may have the long term interest of intending to stay as
tenant for a long term |
|
| |
With the long term nature of the env, landlords do not see the value
of, e.g., forest land as increasing after it is logged |
|
| |
Natural resource harvesters operate as tenants who are not going to
stay |
|
|
|
Landlords will not pay for good insulation unless property is increasing
in value, & it benefits tenants so they can raise rents |
|
| |
SOLUTIONS TO THE COMMONS, LANDLORD - TENANT PROBLEMS INCLUDE PRIVATIZATION
& REGULATION |
|
| |
The classic economists' solution to the commons landlord - tenant problem
is to privatize everything |
|
| |
Modern economists advocate privatizing all resources, even those that
are indivisible such as air, water, etc., via a stock mkt, share system |
|
| |
The classic liberals' solution to the commons landlord - tenant problem
is public stewardship, i.e. govt ownership, mgt, & regulation of public
property |
|
| |
Modern liberals advocate quasi public ownership by, for example, the
Nature Conservancy, the people & the town of Boulder, CO, etc. |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on the
Causes of Climate Change
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
INTRO: CLIMATE MAY BE THOUGHT OF AS 'MACRO LEVEL WEATHER' |
|
| |
Climate is the weather of a place averaged over a length of time |
|
| |
The earth's climate varies from place to place, creating a variety
of environments |
|
| |
Thus, in various parts of the earth, we find deserts; tropical rain
forests; tundras (frozen, treeless plains); conifer forests, which consist
of cone bearing trees & bushes; prairies; & coverings of glacial
ice |
|
| |
THE EARTH HAS EXPERIENCED MANY TYPES OF CLIMATES IN IT'S 6 BILLION
YR EXISTENCE |
|
| |
Climate also changes w/ time |
|
| |
For example, a thousand yrs ago, northern latitudes were milder than
they are today |
|
| |
The warmer climate enabled Vikings from Iceland to settle on the southern
coast of Greenland |
|
| |
But the colder climate that developed over the following centuries
wiped out the settlements |
|
| |
GLOBAL WARMING IS ONE TYPE OF CLIMATE CHANGE |
|
| |
One major envl concern is that human activity may be changing the global
climate |
|
| |
The burning of fossil fuels, coal, oil, & natural gas, to power
motor vehicles, heat bldgs, generate electric energy, & perform various
industrial tasks is increasing the amount of carbon dioxide ( CO2 ) gas
released into the atmosphere |
|
| |
Fossil fuels contain carbon, & burning them produces CO2 |
|
| |
This gas slows the escape of heat released by the Earth into space |
|
| |
Thus, an increase in atmospheric CO2 may cause global warming, a rise
in the temperature of the air next to the earth's surface |
|
| |
Global warming could change rainfall patterns, leading to shifts in
plant & animal populations |
|
| |
It could also melt enough polar ice to raise the sea level, & it
could increase the frequency & severity of tropical storms |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: The Effects of Global Warming |
|
|
|
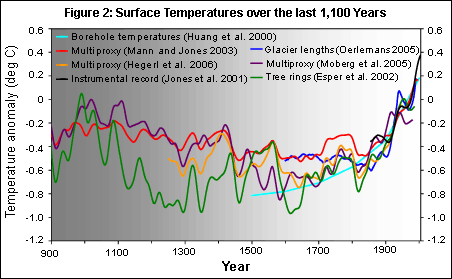
THROUGHOUT HISTORY, EARTH'S CLIMATE HAS BEEN RELATIVELY MILD &
STABLE |
|
| |
While the climate changes over time, since the last ice age, Earth's
climate has been relatively mild & stable |
|
| |
Within the past 1200 yrs, the period btwn about AD 950 & 1250 was
mild |
|
| |
The yrs from about 1400 to 1850 were cool |
|
| |
Since then, global average temperatures generally have risen |
|
| |
About 18,000 yrs ago, a sheet of glacial ice up to 10,000 ft thick
covered much of what is now Greenland, Canada, & the northern US |
|
| |
A warming trend gradually melted almost all the glaciers, except in
Greenland |
|
| |
In Canada & the US, the last large fields of ice had disappeared
by about 11,500 yrs ago |
|
| |
The warming trend ended after a mild period from 7,000 to 5,000 yrs
ago, when the global average temperature was higher than it is today |
|
| |
Within the past 1,200 yrs, the period btwn about A.D. 950 & 1250
was mild |
|
| |
The yrs from about 1400 to 1850 were cool & since then, global
average temperatures generally have risen |
|
| |
Past climate changes have been more dramatic, resulting in many much
hotter eras than today, as well as many ice ages |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: Past Climate Changes |
|
| |
THE CAUSES OF CLIMATE CHANGE ARE NATURAL & HUMAN |
|
| |
NATURAL IMPACTS ON CLIMATE CHANGE CONTINUE TODAY |
|
| |
Many natural processes influence a region's climate |
|
| |
Some of these processes, such as volcanic eruptions, are short lived
& cause short term changes |
|
| |
Other processes, such as mountain building, occur over long periods
& cause long term changes in climate |
|
| |
Human activity also may affect climate |
|
| |
Volcanic eruptions can cause short term cooling over large portions
of the planet, especially if the eruptions throw large amounts of sulfur
gases high into the atmosphere |
|
| |
The sulfur gases combine w/ moisture to produce droplets of sulfuric
acid & tiny sulfate particles |
|
| |
The sulfur droplets & particles created by major volcanic eruptions
absorb some solar radiation & reflect some back to space |
|
| |
As a result, less solar radiation reaches the earth's surface, &
so air temperatures fall |
|
| |
Because the droplets & particles are so small, they can remain
suspended in the atmosphere for months or yrs |
|
| |
Meanwhile, winds carry them around the globe |
|
| |
Scientists believe that volcanic eruptions can cause a maximum global
cooling of about 2 Fahrenheit degrees (1 Celsius degree) |
|
| |
In 1991, the eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines threw large
amounts of sulfur gases high into the atmosphere |
|
| |
This eruption likely caused a drop of 1.1 Fahrenheit degree in the
global average temperature during the following few yrs |
|
| |
Changes in ocean circulation can alter the climate |
|
| |
For example, changes in ocean currents that occur during El Nino can
affect the climate for a yr or two |
|
| |
El Nino is a large scale interaction btwn the tropical atmosphere &
tropical oceans that happens about every two to seven yrs |
|
| |
Changes in the air pressure over the tropical Pacific Ocean cause the
trade winds there to weaken or even reverse direction |
|
| |
This change enables the warm waters of the ocean surface to drift from
the western tropical Pacific to the eastern tropical Pacific |
|
| |
This flow makes sea surface temperatures lower than usual over the
western tropical Pacific & higher than usual over the eastern tropical
Pacific |
|
| |
The sea surface temperature changes, in turn, alter the circulation
of the atmosphere in tropical & middle latitudes |
|
| |
These alterations cause weather extremes in various parts of the world |
|
| |
Heavy rains drench the normally arid coastal plain of western So America,
drought is more likely in Hawaii & eastern Australia, & winters
are wetter than normal along the Gulf of Mexico coast |
|
|
Link
|
Activity on the sun's surface may affect the earth's climate
for short periods |
|
| |
Changes in carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere
may cause short term & long term variations in the climate |
|
| |
Atmospheric CO2 slows the flow of heat from the earth to space |
|
| |
This gas absorbs heat that radiates from the earth's surface &
radiates heat back to the surface |
|
| |
Human activity is currently increasing the level of atmospheric CO2,
but this level has varied significantly throughout the history of the earth |
|
| |
With past variations in atmospheric CO2, the global climate has warmed
or cooled |
|
| |
For example, about 100 mm yrs ago, volcanic activity on the floor of
the Pacific Ocean released enough CO2 to cause global warming of perhaps
18 Fahrenheit degrees |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: The Greenhouse Effect |
|
|
Link
|
Changes in the Earth's orbit about the sun may cause climate changes
over tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of yrs |
|
|
Link
|
Continental drift is an extremely slow process that influences the
climate over periods of tens of millions of yrs |
|
|
Link
|
Mountain building, another extremely slow process, likely helped set
the stage for the ice ages during the Pleistocene Epoch. |
|
|
|
HUMAN IMPACTS ON CLIMATE CHANGE ARE INCREASING & CONTINUE TODAY |
|
|
|
Human activity also affects the climate |
|
|
|
The building of cities, the clearing of forests, & the burning
of oil, coal, & natural gas can all cause climatic changes |
|
|
|
Climatologists disagree, however, about the impact that human activity
has had on climate, particularly on the recent global warming trend |
|
| |
The burning of fossil fuels has contributed to recent increases in
the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere |
|
| |
See Also: Fossil Fuels & Global Warming |
|
| |
Economic development & urbanization have been shown to have a direct
impact on the climate, creating 'heat sinks' in the env |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: Urbanization & the Env |
|
|
|
Deforestation & other forestry practices have been shown to have
a direct impact on the climate because deforested areas result in hotter,
dryer ecozones, deforestation releases CO2, etc. |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: Deforestation |
|
| |
One of the best ways to gain understanding of climate is by exploring
climate change throughout the Earth's history |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: Past Climate Change |
|
|
Solar changing
conditions affect the Earth's climate
Sunspots are dark, relatively cool blotches that appear on the surface
of the sun
Faculae are relatively bright, hot areas on the solar surface
The number of sunspots & faculae increases & decreases over
a cycle of about 11 yrs
The ave amt of energy given off by the sun is slightly higher during
a sunspot maximum, when the # of sunspots & faculae is hi
The average amount is slightly lower during a sunspot minimum, when
the number is lo
Climatologists are not sure about the relationship btwn changes on
the sun's surface & variations in the Earth's climate
During the period from 1645 to 1715, the number of sunspots was unusually
low.
This episode corresponds to a portion of the Little Ice Age, a time
of relatively cool conditions.
Climatologists have not proved, however, that the reductions in the
number of sunspots caused the cooling
|
|
Earth's changing
orbit affects the Earth's climate
Milutin Milankovitch, a Serbian mathematician, proposed in the 1940's
that three orbital variations change how sunlight is distributed seasonally
& geographically over the planet:
(1) a precession (wobble) of the earth's axis,
(2) a variation in the tilt of the axis, &
(3) a variation in the path of the orbit.
The precession of the axis varies over a period of 23,000 yrs
This cycle alters the times of the yr when Earth is closest to the
sun & farthest from the sun
The tilt of the axis changes from 22.1° to 24.5° over a period
of 41,000 yrs
This cycle affects the contrast btwn winter & summer temperatures
The path of the orbit varies over a period of 100,000 yrs
The orbit is always elliptical, that is, shaped like a flattened circle
But during the 100,000 yr cycle, the amount of flatness changes from
a max to a min, then back to the max
This variation changes the distance btwn the earth & sun over the
course of a yr
These three orbital cycles probably have altered global temperatures
at regular intervals throughout the Earth's history
Climatologists believe that the cycles may have governed the major
fluctuations in Earth's glacial ice cover during the Pleistocene Epoch,
the period from about 2 mm yrs ago to 11,500 yrs ago
The three cycles probably produced temperature changes that caused
the ice cover to expand & contract at regular intervals
|
|
Continental drift
affects the Earth's climate
Earth's solid outer shell, which is typically 60 mi thick, is divided
into about 30 large plates that move slowly over the surface of the globe
The continents are embedded in these plates & slowly drift w/ them,
a process known as continental drift
About 200 million yrs ago, there was just one huge continent, called
Pangaea
Pangaea split into fragments that drifted apart & eventually reached
their present locations as the continents we know today
Continental drift helps explain the presence of coral reef fossils
in Wisconsin & of tropical plant fossils in areas north of the Arctic
Circle
When the coral & plants were alive, Wisconsin & the arctic
regions were at much lower latitudes than they are today
|
|
Mountain building
affects the Earth's climate
Mountain building, another extremely slow process, likely helped set
the stage for the ice ages during the Pleistocene Epoch
About 30 mm to 40 mm yrs ago, the Himalaya & the adjacent Tibetan
plateau began to rise in southern Asia
At about the same time, mountain building began in the western part
of the US
Half the total uplift of the Himalaya & the Colorado Plateau may
have occurred w/in the past 10 mm yrs
The rise of these massive landforms likely altered the wind belts that
encircle the planet
As a result, the earth's climate became more diverse, wetter, &
colder
|
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on the Greenhouse
Effect
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
- Project: The Greenhouse
Effect & Your Carbon Footprint |
Link
|
|
|
THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT OCCURS BECAUSE THE ATMOSPHERE TRAPS HEAT |
|
|
|
Greenhouse effect is a warming of the lower atmosphere & surface
of a planet by a complex process involving sunlight, gases, & particles
in the atmosphere |
|
|
|
On the earth, the greenhouse effect began long before human beings
existed |
|
|
|
However, recent human activity may have added to the effect |
|
|
|
The amounts of heat trapping atmospheric gases, called greenhouse gases,
have greatly increased since the mid 1800s, when modern industry became
widespread |
|
|
|
Since the late 1800s, the temperature of the earth's surface has also
risen |
|
|
|
The greenhouse effect is so named because the atmosphere acts much
like the glass roof & walls of a greenhouse, trapping heat from the
sun |
|
| |
The greenhouse effect is like a car w/ the windows rolled up; it get
much hotter than the surrounding air |
|
| |
Short wave length light enters the car & when it is reflected off
the interior, it becomes longer wave length… short wave length high energy |
|
| |
The long wavelength. longer waves cannot escape through the glass |
|
|
|
THE NATURAL GREENHOUSE EFFECT MODERATES THE EARTH'S CLIMATE |
|
|
|
The atmosphere reflects toward space about 30 % of the energy in incoming
sunlight |
|
|
|
The atmosphere absorbs about another 30 %, & the remaining 40 %
or so reaches the earth's surface |
|
|
|
The earth's surface reflects about 15 % of the solar energy that reaches
it back toward space |
|
|
|
The remaining 25 % of energy from the sun heats the lands & seas |
|
|
|
The Images of the Greenhouse Effect
shows that, in a delicate balance, some of the Sun's energy is kept on
Earth, & that some is reflected back into space, & that any changes
in this process can heat or cool the Earth |
Link
|
|
|
The warmed lands & seas then send most of the heat back into the
atmosphere, chiefly as infrared rays & in evaporated water |
|
|
|
Infrared rays are much like light waves but are invisible to the human
eye |
|
|
|
When the rays from the lands & seas strike certain substances in
the atmosphere, such as greenhouse gases % particles, those substances
absorb the rays |
|
|
|
As a result of being exposed to the reflected infrared light, the gases
& particles are heated |
|
|
|
They then are cooled by sending out infrared rays of their own |
|
|
|
Some of the rays go into space |
|
|
|
The remainder radiate back toward the earth's surface, adding to the
warming of the surface layer of air |
|
| |
Without the natural greenhouse effect, the average temperature of the
earth's surface would be about 59 Fahrenheit degrees (33 Celsius degrees)
colder than it is now |
|
| |
The chief greenhouse gases are made up of atoms of carbon (C), hydrogen
(H), & oxygen (O) |
|
| |
The chief greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane,
& ozone |
|
| |
The greenhouse particles include cloud droplets, soot, & dust |
|
| |
INCREASES IN GREENHOUSE GASES HAVE OCCURRED BECAUSE OF HUMAN ACTIVITY |
|
| |
Human activity has caused small but important changes in the composition
of the air |
|
| |
The amounts of many gases in the air, such as carbon dioxide, are increasing
at significant rates |
|
| |
Since the early to mid 1800s, the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere has
increased by about 25 % & the methane concentration has risen by about
150 % |
|
| |
Levels of methane & nitrous oxide have more than doubled, &
there were no chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) in the atmosphere before 1930 |
|
| |
CFCs are synthetic substances that were formerly used widely as refrigerants
in air conditioners & refrigerators & as propellants in aerosol
spray products |
|
| |
Most of the increase has been due to human activities, chiefly the
burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, & natural gas & the
clearing of land |
|
| |
Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere whenever coal, oil, or other fuels
containing carbon are burned |
|
| |
Fossil fuels contain carbon, & burning them creates carbon dioxide |
|
| |
Trees & other plants absorb the gas through the process of photosynthesis |
|
| |
As land is cleared & forests are cut down, carbon dioxide levels
rise |
|
| |
The average temp of the earth's surface has increased by about 0.9
to 1.6 Fahrenheit degrees (0.5 to 0.9 Celsius degree) since the late 1800s |
|
| |
Scientists have not yet proved that an increase in atmospheric carbon
dioxide has raised the surface temperature |
|
| |
But in the likely event that the relationship btwn CO2 & temp does
exist, the eventual results could be severe |
|
| |
Many scientists estimate that by about 2050, the amount of carbon dioxide
in the atmosphere will have doubled from the pre industrial level |
|
| |
If this increase were to add to the natural greenhouse effect, the
earth's surface temperature might rise btwn 3 & 8 Fahrenheit degrees
(1.5 & 4.5 Celsius degrees) by 2100 |
|
| |
Many scientists believe that the increases in the gases & the introduction
of CFCs has strengthened the greenhouse effect |
|
| |
A strengthening of the greenhouse effect would produce global warming,
an increase in the average temperature of the earth's surface |
|
| |
CFCs ARE HUMAN MADE CHEMICALS WHICH BOTH CONTRIBUTE TO THE GREENHOUSE
EFFECT & DESTROY ATMOSPHERIC OZONE WHICH PROTECTS US FROM UV
RAYS |
|
| |
CFCs are also involved in the weakening of the protective layer of
ozone in the stratosphere & troposphere |
|
| |
CFCs are harmless near the ground, but cause damage when they drift
up into the stratosphere & troposphere |
|
| |
There, CFCs break apart & release chlorine atoms |
|
| |
The chlorine reacts w/ the ozone, converting it into ordinary oxygen
molecules |
|
| |
This conversion enables an increased amount of harmful ultraviolet
radiation to reach the earth's surface |
|
| |
In 1990, the US & most other industrialized countries agreed to
stop production of most CFCs |
|
| |
But the core nations continue to produce CFCs in semi peripheral &
peripheral nations & sell them there |
|
| |
STUDYING THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT SHOWS A HIGH LIKELIHOOD THAT
HUMANS HAVE INCREASED IT & THAT IT LEADS TO GLOBAL WARMING |
|
| |
Researchers use high speed computers to study how carbon dioxide concentration
may affect surface temperature |
|
| |
The computers manipulate mathematical models, sets of equations that
describe relationships btwn changeable factors |
|
| |
Scientists do not have enough data to prove that variations in carbon
dioxide & other human caused changes to atmospheric composition cause
shifts in surface temperature |
|
| |
They may need until the 2010s to gather enough data, but certain models
suggest that the 2010's may be too late to avoid some damage from global
warming |
|
| |
Scientists have also examined evidence from the distant past to determine
whether changes in carbon dioxide concentration cause temperature changes |
|
| |
Cores of ice drilled from great depths in Greenland & Antarctica
provide a record for the past 160,000 years |
|
| |
During the past 160,000 years, the climate warmed & cooled several
times |
|
| |
Researchers analyzed the gases & other substances that were trapped
in the ice when it formed |
|
| |
During the cooler periods, the atm contained about 30 % less carbon
& 50 % less methane than during the warmer periods |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on the
Carbon Footprint
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
- Project: The Greenhouse
Effect & Your Carbon Footprint |
Link
|
|
|
A CARBON FOOTPRINT IS THE REPRESENTATION OF THE NET AMOUNT
OF CARBON BASED GREENHOUSE GASES THAT ONE RELEASES INTO THE ENV |
|
|
|
A carbon footprint is the amount of C02 & other carbon compounds
emitted due to the consumption of fossil fuels by a particular person,
group, etc. either directly or indirectly |
|
| |
A carbon footprint includes the direct consumption of a fuel such as
gasoline which releases C02, or indirectly through the consumption of a
product such as a pair of shoes which used energy to make & therefore
consumed some fuel & released some C02 |
|
| |
When talking about climate change, a carbon footprint is a metaphor
for the total impact that something has on the climate |
|
| |
A carbon footprint would include everything one does to create greenhouse
gases as well as what one does to eliminate greenhouse gases |
|
| |
One creates greenhouse gases when one burns gasoline & one reduces
greenhouse gases when one plants a tree |
|
|
Carbon footprint is a shorthand for sum total of all the different
greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming that one is responsible
for creating in the env |
|
| |
The total carbon footprint is difficult to calculate b/c of the large
amt of data required & the fact that carbon dioxide can be produced
by natural occurrences |
|
| |
Wright, Kemp, & Williams, writing in the journal Carbon Mgt, suggest
a narrower definition where carbon footprint is measure of the total
amt of CO2 & methane (CH4) emissions of a defined population, system
or activity, considering all relevant sources, sinks & storage w/in
the spatial & temporal boundary of the population, system or activity
of interest |
|
| |
The term carbon footprint is a shorthand to describe the best est that
we can get of the full climate change impact of something including an
activity, an item, a lifestyle, a company, a country or even the whole
world |
|
| |
Carbon footprint is the result of direct & indirect emissions &
absorption of C02 & methane, which are the two most common greenhouse
gases |
|
| |
The true carbon footprint of a plastic toy, for example, includes not
only direct emissions resulting from the manufacturing process & the
transportation of the toy to the shop: it also includes a whole host of
indirect emissions, such as those caused by the extraction & processing
of the oil used to make the plastic in the first place. |
|
| |
The true carbon footprint of driving a car includes not only the emissions
that come out of the exhaust pipe, but also all the emissions that take
place when oil is extracted, shipped, refined into fuel & transported
to the gas station, not to mention the substantial emissions caused by
producing & maintaining the car |
|
| |
Most of the carbon footprint emissions for the average US household
come from 'indirect' sources, ie fuel burned to produce goods far away
from the final consumer |
|
| |
THE CONCEPT OF THE CARBON FOOTPRINT GREW OUT OF THE ECOLOGY PT
OF VIEW THAT EMPHASIZES THE INTERCONNECTEDNESS OF ALL LIFE PROCESSES,
FOCUSING ON HOW HUMAN PROCESSES INTERACT W/ ALL PHYSICAL & BIOLOGICAL
PROCESSES |
|
| |
The concept name of the carbon footprint originates from ecological
footprint, discussion, which was developed by Rees & Wackernagel in
the 1990s which est the number of 'earths' that would theoretically be
required if everyone on the planet consumed resources at the same level
as the person calculating their ecological footprint |
|
| |
Carbon footprints are much more specific than ecological footprints
since they measure direct emissions of gases that cause climate change
into the atmosphere |
|
| |
A carbon footprint has historically been defined by Championne as 'the
total sets of greenhouse gas emissions caused by an organization, event,
product or person' |
|
| |
THERE ARE MANY CARBON CALCULATORS AVAILABLE, VARYING IN THEIR DETAIL
& COMPLEXITY |
|
| |
One of the most well researched & accept carbon footprint calculators
is done by the University of CA Berkeley Cool Climate Network Research
Consortium |
|
| |
http://coolclimate.berkeley.edu/about |
Link
|
| |
THE MOST COMMON WAY TO REDUCE A CARBON FOOTPRINT IS
TO REDUCE, REUSE, & RECYCLE |
|
| |
Reduction in the amount of energy, products, food, land,
etc that one consumes reduces ones carbon footprint |
|
| |
Reduction in the amount of garbage, pollution, haz mat, water, etc
that one discards reduces ones carbon footprint |
|
| |
Using reusable items such as thermoses for daily coffee or plastic
containers for water & other cold beverages rather than disposable
ones |
|
| |
If a reusable option is not available, it is best to use items that
can be properly recycled after the disposable items is used |
|
| |
When one household recycles at least half of their household waste,
they can save 1.2 tons of carbon dioxide annually |
|
| |
An easy option based on reduction is to drive less; by walking or biking
to the destination rather than driving, not only is a person going to save
money on gas, but they will be burning less fuel & releasing fewer
emissions into the atmosphere |
|
| |
If walking is not an option, one can look into simply catching a ride
w/ a friend, carpooling, or mass transportation |
|
| |
Reducing the carbon footprint can be done by using less air conditioning
& heating in the home & mostly importantly, at work |
|
| |
Insulation to the walls & attic of one's home, & installing
weather stripping or caulking around doors & windows one can lower
their heating costs more than 25 % |
|
| |
Very inexpensively upgrading the clothing or 'insulation' worn by residents
of the home or wkplace can allows a person to remain warm w/ the thermostat
lowered by about 10° F, which reduces carbon emissions by almost 10
% |
|
| |
Choice of diet is a major influence on a person's carbon footprint
b/c some foods have a much higher carbon footprint in production than do
others |
|
| |
The consumption of meat has a large carbon footprint that eating fish
or a vegetarian diet b/c it takes a large amt of animal feed to produce
a relatively small amt of meat |
|
| |
In the developed nations, modern industrial agricultural methods have
a larger carbon footprint than do traditional ag methods |
|
| |
While modern industrial agricultural methods are more efficient by
Western standards, when judged by ecological standards, they are less efficient
& unsustainable in the long run |
|
| |
modern industrial agricultural farmers & ag engineers are seeking
methods which have smaller carbon footprints & are sustainable in the
long run |
|
| |
Rice has a large carbon footprint b/c it is typically produced in high
methane emitting paddies |
|
| |
Foods that is transported long distance &/or via fuel inefficient
transport, such as highly perishable produce flown long distance has a
large carbon footprint |
|
| |
Heavily processed & packaged foods typically have a large carbon
footprint both b/c they are produced through mechanized erg techniques
which have a large carbon footprint & b/c highly processing & packaging
food for convenience is also a carbon intensive process |
|
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
A FOREST IS TREES & MUCH, MUCH MORE & THE WHOLE IS GREATER
THAN THE SUM OF THE PARTS |
|
| |
Forest is a large area of land covered w/ trees, but a forest is much
more than just trees |
|
| |
It also includes smaller plants, such as mosses, shrubs, & wild
flowers |
|
| |
In addition, many kinds of birds, insects, & other animals make
their home in the forest |
|
| |
Millions upon millions of living things that can only be seen under
a microscope also live in the forest |
|
| |
Climate, soil, & water determine the kinds of plants & animals
that can live in a forest |
|
| |
ECOSYSTEMS ARE CYCLES OF LIFE & OTHER NATURAL PROCESSES |
|
| |
The living things & their env together make up the forest ecosystem |
|
| |
An ecosystem consists of all the living & nonliving things in a
particular area & the relationships among them |
|
| |
The forest ecosystem is highly complicated |
|
| |
The trees & other green plants use sunlight to make their own food
from the air & from water & minerals in the soil |
|
| |
The plants themselves serve as food for certain animals. These
animals, in turn, are eaten by other animals |
|
| |
After plants & animals die, their remains are broken down by bacteria
& other organisms, such as protozoans & fungi |
|
| |
This process returns minerals to the soil, where they can again be
used by plants to make food |
|
| |
Although individual members of the ecosystem die, the forest itself
lives on |
|
| |
If the forest is wisely managed, it provides us w/ a continuous source
of wood & many other products |
|
| |
THE CARBON CYCLE IS ONE OF THE NATURAL CYCLES IN THE FORESTS &
ALL ECOSYSTEMS |
|
| |
The balance carbon cycle in the forest is critical to the balance of
the carbon cycle on the Earth |
|
| |
One step in the arboreal carbon cycle occurs when trees & other
plants take carbon from the air by breathing in CO2 |
|
| |
The carbon is contained, or sequestered in the living plants, such
as the wood of the trees themselves |
|
| |
As the plants die, some of the carbon is released back into the atm
by burning, or natural decomposition |
|
| |
Some carbon becomes part of the soil & is available as soil for
other plants to use, or simply remains sequestered in the soil |
|
| |
THERE IS HALF THE AMT FORESTED LAND TODAY AS COMPARED TO 12 K YRS
AGO |
|
| |
Before people began to clear the forests for farms & cities, great
stretches of forest land covered about 60 % of the earth's land area |
|
| |
Today, forests occupy about 30 % of the land |
|
| |
The forests differ greatly from one part of the world to another |
|
| |
For example, the steamy, vine choked rain forests of central Africa
are far different from the cool, towering spruce & fir forests of northern
Canada |
|
|
|
FORESTS ARE A KEY FEATURE IN THE CYCLICAL FLOW OF GLOBAL ECOSYSTEMS |
|
|
|
Forests help conserve & enrich the env in several ways |
|
| |
WATER |
|
| |
For example, forest soil soaks up large amounts of rainfall |
|
| |
It thus prevents the rapid runoff of water that can cause erosion &
flooding |
|
| |
In addition, rain is filtered as it passes through the soil & becomes
ground water |
|
| |
This ground water flows through the ground & provides a clean,
fresh source of water for streams, lakes, & wells |
|
| |
AIR |
|
| |
Forest plants, like all green plants, help renew the atmosphere |
|
| |
As the trees & other green plants make food, they give off oxygen |
|
| |
They also remove carbon dioxide from the air |
|
| |
People & nearly all other living things require oxygen |
|
| |
If green plants did not continuously renew the oxygen supply, almost
all life would soon stop |
|
| |
CARBON |
|
| |
If carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere, it could severely alter
the earth's climate |
|
| |
Forests are a carbon sink or reservoir in that it stores very large
amts of carbon |
|
| |
Besides the direct heating that affects the climate from deforested
areas, deforestation removes stored carbon from the forest & transfers
it to the atm in the form of CO2 |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: Deforestation |
|
|
|
FORESTS ARE OUR SOURCES & RESERVES OF TYPICAL & RARE FLORA
& FAUNA |
|
|
|
Forests also provide a home for many plants & animals that can
live nowhere else |
|
|
|
Without the forest, many kinds of wildlife could not exist |
|
|
|
FORESTS HAVE AN AESTHETIC VALUE WHICH ONLY NATURE CAN PROVIDE |
|
|
|
The natural beauty & peace of the forest offer a special source
of enjoyment |
|
| |
In the US, Canada, & many other countries, huge forest lands have
been set aside for people's enjoyment |
|
| |
Many people use these forests for such activities as camping, hiking,
& hunting |
|
| |
Others visit them simply to enjoy the scenery & relax in the quiet
beauty |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
DEFORESTATION BEGAN WHEN CIVILIZATION BEGAN, ABOUT 11,000 YRS AGO |
|
|
|
Human activities have had tremendous impact on modern forests |
|
|
|
Since ag began about 11,000 yrs ago, large forest areas have been cleared
for farms & cities |
|
|
|
Beginning in the 1800s, great expanses of forest have also been eliminated
because of logging & indl pollution |
|
|
|
The destruction & degrading of forests is called deforestation |
|
|
|
DEFORESTATION HAS AFFECTED MOST OF THE EARTH'S FORESTS |
|
|
|
Severe deforestation now occurs around the world, even in the most
remote rain forests & boreal forests |
|
|
|
Until the late 1940s, rain forests covered about 8.7 million sq mi
of the Earth's land |
|
|
|
Today, they cover less than half that area |
|
|
|
Millions of acres or hectares of rain forests are destroyed each year |
|
|
|
Since 1800, huge areas of temperate forests have also been cleared |
|
|
|
Many parts of eastern North America, for example, have less than 2
% of even degraded forests remaining |
|
| |
LOGGING FOR TIMBER & TO CLEAR LAND FOR AG HAS DEFORESTED MANY
AREAS |
|
| |
Commercial logging & the expansion of agriculture have damaged
or wiped out extensive areas of rain forest |
|
| |
Huge mining projects, the construction of hydroelectric dams, &
govt resettlement programs have also taken their toll |
|
| |
In the last 50 years half of tropical rain forest have been cut for
timber or to make farmland |
|
| |
A complex mix of social, political, & econ factors has triggered
these destructive activities |
|
| |
Rapid population growth & poverty often intensify the pressure
to clear rain forest for short term econ benefits |
|
| |
Brazil, Indonesia, & other nations have cut down huge expanses
of rain forest to create new settlements that allow people to move out
of overcrowded cities |
|
| |
Moreover, the govts of many tropical countries are deeply in debt |
|
| |
This debt provides a strong motivation to gather as much as possible
from the rain forest as quickly as possible |
|
| |
After clearing the forest to harvest wood & other products, people
then commonly use the land to grow crops |
|
| |
LOGGING OCCURS NOT ONLY IN RAIN FORESTS, BUT ALSO IN TEMPERATE FORESTS |
|
| |
The developed nations continue to log both their own forests, &
fund the deforestation around the world |
|
| |
Many temperate forests have been cleared for farms & cities, &
many others have been cut down for fuel & lumber |
|
| |
Many Canadian forests have been heavily logged |
|
| |
The scale of Canadian deforestation now compares to that in the US |
|
| |
Many people in British Columbia & other provinces are greatly concerned
about the destruction of original forests & the common practice of
clear cutting (removing all trees) over large areas |
|
| |
ACID RAIN ALSO DEFORESTS LARGE AREAS |
|
| |
Industrial pollution is a chief cause of deforestation |
|
| |
Factories often release poisonous gases into the air & dangerous
wastes into lakes & rivers |
|
| |
Air pollutants may combine w/ rain or other precipitation & fall
to earth as acid rain |
|
| |
Acid rain & polluted bodies of water can restrict plant growth
or even kill most plants in a forest |
|
| |
LOGGING & SCAVENGING DEFORESTS LARGE AREAS AS PEOPLE GATHER
WOOD FOR FUEL FOR COOKING & FOR HEAT |
|
| |
Most of the population of the world cooks & heats w/ wood |
|
| |
Heating & cooking w/ wood is often done in very inefficient stoves
which also create large amts of air pollution & CO2 |
|
| |
Many of the areas of the cradles of civilization & of ancient society
from England to Italy to Greece to Judea to China & more were deforested
as early people logged & scavenged for wood for construction,
heat, & cooking |
|
| |
Many of the ancient areas which experienced ancient deforestation have
had their climate / weather changed to such an extent that they are still
impacted & remain largely w/o forests, esp Israel, the Sahara, &
even the UK & Italy |
|
| |
DEFORESTATION FRAGMENTS FORESTS INTO MERE ISLANDS OF TREES
UNABLE TO SUSTAIN THEIR NATURAL FLORA & FAUNA |
|
| |
Massive deforestation has made many remaining forest tracts small,
isolated islands |
|
| |
As forests become smaller, their ability to sustain the full variety
of plant species decreases |
|
| |
Many forests are so seriously degraded by logging activities that they
fail to regenerate replacement forests |
|
| |
The destruction of forest ecosystems also destroys the habitats of
many living creatures |
|
| |
Countless species of animals & plants have been wiped out by deforestation,
& more are killed each year at an increasing rate |
|
| |
This deforestation places woodland animals in danger |
|
| |
Extensive logging in the Pacific Northwest of the US, for example,
has destroyed much of the habitat of the spotted owl, threatening the existence
of that species |
|
| |
DEFORESTATION HARMS PEOPLE TOO |
|
| |
Deforestation usually displaces forest peoples |
|
| |
When denied access to the forest, these peoples often lose important
knowledge about rain forest species & their uses |
|
| |
Loss of such knowledge further threatens the survival of the forests |
|
| |
DEFORESTATION CAUSES FLOODS & LESS O2 PRODUCTION |
|
| |
Loss of forests has helped create many ecological problems |
|
| |
For example, rain water normally absorbed by the forests is causing
more floods around the world |
|
| |
In addition, as forest areas decrease or degrade, the production of
oxygen from photosynthesis also decreases |
|
|
|
Oxygen renewal is vital to the survival of oxygen breathing organisms |
|
|
|
DEFORESTATION CREATES MORE GREENHOUSE GAS, ESP CO2 |
|
|
|
At the same time, as less carbon dioxide is taken up by photosynthesis,
the amounts of carbon dioxide released into the air increases |
|
| |
The clearing of forests also contributes to the buildup of atmospheric
CO2 by reducing the rate at which the gas is removed from the air |
|
| |
Trees & other green plants remove CO2 from the air during photosynthesis
the process they use to produce food |
|
| |
Thus more heat from the sun is trapped near the earth's surface instead
of being reflected back into space |
|
| |
Many scientists believe that this greenhouse effect is causing a steady
warming that could lead to threatening climatic conditions |
|
| |
Rain forest destruction accounts for 15% of greenhouse gas problems,
which is small compared to the total amt of greenhouse gases produced by
the developed world |
|
| |
PEOPLE ARE FIGHTING DEFORESTATION BUT IT IS UNCLEAR WHETHER THE
PROBLEM IS DECREASING OR NOT |
|
| |
To combat these problems, people & govts have been seeking out
& protecting old growth forests that remain undisturbed by humans |
|
| |
Such protection enables scientists to conduct long term research on
how old growth forests sustain the variety of plants & animals that
live there |
|
| |
It has been estimated that as much as 75% of the Haitian population
is living in absolute poverty& wood has become the most valuable resource
in Haiti where it is relied upon for heating, cooking, & construction |
|
| |
The result of this reliance on wood has lead to only 3% of Haiti’s
forest being untouched & the subsequent deforestation has lead to the
rich topsoil run off choking the reefs & marine life |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Urbanization
& the Environment
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
URBAN AREAS BOTH HEAT & DRY THE CLIMATE OF A REGION |
|
| |
The construction of cities creates areas that are warmer & drier
than the surrounding countryside |
|
| |
Cities are drier because they have storm sewer systems that quickly
carry off rainwater & snowmelt |
|
| |
Cities are warmer for several reasons |
|
| |
The use of storm drainage systems means that less solar radiation is
used to evaporate water & more is used to heat the city surfaces &
air |
|
| |
The brick, asphalt, & concrete surfaces readily radiate the heat
they absorb & so raise urban air temperatures even more |
|
| |
In addition, cities themselves generate heat from a number of sources,
including motor vehicles & heating & air conditioning systems |
|
| |
URBAN AREAS ALSO AFFECT THE CLIMATE IN THE SURROUNDING REGION |
|
| |
Large urban areas also affect the climate in the areas downwind of
them |
|
| |
Smokestacks & automobile tailpipes in cities emit water vapor &
tiny particles that stimulate the formation of clouds |
|
| |
Heat from a city also spurs the growth of clouds |
|
| |
Thus, the climate downwind from many large urban areas is cloudier
& wetter than the climate upwind from those same areas |
|
| |
CITIES ARE PRIMARY SOURCES OF POLLUTION |
|
| |
Many cities have a serious pollution problem |
|
| |
Motor vehicles, factories, & other sources create so much air pollution
that it may hang in the air like dirty fog |
|
| |
Air pollution threatens the health of the people who live in cities |
|
| |
City wastes cause water pollution when they are poured into waterways |
|
|
|
These wastes kill fish & make some areas unfit for swimming |
|
|
|
In addition, many large cities have difficulty disposing of their refuse |
|
|
|
The amount of refuse grows each year, but places to put it are quickly
filling up |
|
| |
Motor vehicles, factories, & other sources pollute the air fumes
that endanger the health of the people in cities |
|
| |
Urban wastes pollute waterways |
|
| |
City residents & industries produce extraordinary amounts of refuse |
|
| |
LOCAL GOVTS ARE MOVING AHEAD OF THE FED GOVT TO ADDRESS ENVL PROBLEMS |
|
| |
Many cities & counties have established the 'green city' designation
to indicate cities that are reducing pollution, energy use, CO2 production,
sprawl, etc. |
|
| |
A govt might want to end pollution by eliminating sources of contamination |
|
| |
Many people believe that the only option for the govt to control global
warming is to close factories & prohibit almost all automobiles to
do so, thus crippling the econ & inconveniencing the people, but this
is mistaken |
|
| |
Instead, citizens, govts, industry, scientists, & business people
must work together to gradually reduce pollution, energy consumption, heat
producing urban sprawl, transportation gridlock, etc. |
|
| |
For example, most cities have introduced recycling programs, which
cut down on refuse & the space needed to store it |
|
| |
Residents separate recyclable products from garbage, & city govts
provide drop off sites or pick up the products from homes |
|
| |
Cambridge MA has estb an energy conservation building program which
they believe will drastically reduce energy consumption & thus the
production of greenhouse gases |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Global
Pollution
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
TODAY, ALL ENVL PROBLEMS HAVE BECOME GLOBAL PROBLEMS |
|
| |
ALL envl problems must be seen as global problems |
|
| |
People often view envl problems as someone else's problem |
|
| |
Only a few envl probs are seen as global |
|
| |
ENVL PROBLEMS WHICH OCCUR LOCALLY ARE SO COMMON THAT THEY ARE HAVING
A GLOBAL IMPACT |
|
| |
Almost all pollution moves from area to area |
|
| |
An example of the global effect of a locally used pollutant is DDT |
|
| |
DDT is sprayed on fields to kill bugs; migratory birds ate the bugs;
this killed birds over large areas |
|
| |
Today DDT is sprayed on Mex fruits & veggies so US citizens still
ingest it & it is building up |
|
| |
While DDT is no longer produced or used in the US, western corps produce
it & use it in semi peripheral & peripheral nations |
|
|
|
AIR POLLUTION IS ONE OF THE MOST RAPIDLY MOVING GLOBAL POLLUTANTS |
|
|
|
The US west coast now suffers the effects of air pollution from Asia
Canada & Euro suffer the effects of US air pollution
Asia suffers the effects of Euro pollution |
|
| |
Similar patterns of shifting air pollution are developing in the southern
hemisphere |
|
| |
WATER POLLUTION IS A RELATIVELY FAST MOVING GLOBAL POLLUTANT |
|
|
|
Water that is polluted by herbicide & fertilizer run off in So
Dak travels down the Missouri River, down the Mississippi River to the
Gulf of Mexico where there are large "dead zones" & algae blooms |
|
| |
The Rhine & Danube Rivers are intll rivers in that they border
& flow through many Euro nations, & very polluted |
|
| |
Ocean dumping killing many fish; it is estimated that there are 40
k pieces of plastic, alone, per sq mi in the ocean, as well as chem pollution
& more |
|
| |
GLOBAL WARMING IS THE FIRST WIDELY RECOGNIZED GLOBAL ENVL PROBLEM |
|
| |
While envlists have recognized the fact that many envl problems are
global in nature, leaders & the people are less likely to 'connect
the dots' |
|
|
|
Burning fossil fuels, wherever it is done, causes global warming |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: Global Warming |
|
|
|
POLLUTION MOVES AT DIFFERENT RATES & THUS BECOMES GLOBAL AT
DIFFERENT RATES |
|
|
|
Air pollution moves very quickly |
|
| |
Water pollution moves relatively quickly |
|
|
|
Ground water pollution moves slowly over decades |
|
|
|
Hazardous wastes pollution moves over centuries |
|
|
|
Many people mistakenly view some types of pollution as stationary |
|
|
|
GOVTS & CORPS INTENTIONALLY & UNINTENTIONALLY SHIFT ENVL
BURDENS TO OTHER NATIONS |
|
|
|
As understood via concepts of envl racism / imperialism / classism,
the strong often transfer envl & other burdens to the weak |
|
|
|
Govts pass laws that shift the burden of pollution to econ & pol
weak nations |
|
|
|
And as seen in air pollution, pollution travels around the globe |
|
|
|
Govts allow the export & import of haz waste |
|
| |
Govts allow the semi peripheral & peripheral nations to produce
in hazardous & envlly unsound manners that they do not allow in core
nations |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Changes
in the Environment
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
PUBLIC LANDS GIVE 'EARLY WARNINGS' OF ENVL THREATS |
|
| |
One of the factors that makes understanding global warming & other
human induced changes to the env so difficult is that changes to the env
occur as a result of both human & natural forces |
|
| |
Public lands & land held in common, i.e. the commons, are in many
senses, indicator species in that they react to / are sensitive to changes
in the env |
|
|
Link
|
See Also: The Commons |
|
| |
Public lands & the commons are the "canaries in the coal mine"
that can give us early warning as to the effects of global warming &
other envl changes |
|
| |
MANY US PARKS ARE THREATENED BY POLLUTION & SPRAWL |
|
| |
Today, many changes in the env endanger parks worldwide |
|
| |
Various forms of pollution, esp air & water pollution, present
major threats because they easily cross park boundaries |
|
| |
For example, the scenic views of Grand Canyon National Park in the
US are often reduced due to air pollution from LA, which lies about 300
mi away |
|
| |
In addition, the park's env has suffered from the construction of dams
upstream on the Colorado River, which flows through the Grand Canyon |
|
| |
Changes in the flow of water have harmed water birds & other wildlife
in the park |
|
| |
The Smoky Mtn NP in TN is renowned for it's 'smoky' landscape which
is the result of moisture in the air |
|
| |
The vistas in the Smoky Mtn NP have been reduced significantly by air
borne pollution & the Park reports that they have almost no natural
views left in that haze impacts the view every day |
|
| |
GLOBAL WARMING IS THREATENING THE SENSITIVE MICRO CLIMATES OF MANY
PARKS WORLDWIDE |
|
| |
Worldwide envl problems also threaten national parks |
|
| |
These problems include an increase in the so called greenhouse effect
& the rapid reduction of tropical rain forests |
|
| |
The greenhouse effect is a warming at the earth's surface that results
when the earth's atmosphere traps the sun's heat. |
|
| |
The heat is trapped when it is absorbed by carbon dioxide & other
gases in the atmosphere. |
|
| |
The amt of CO2 in the atm has grown because of the increased burning
of such fuels as coal, gas, & oil |
|
| |
Rain forests absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide |
|
| |
But the forests can handle less & less carbon dioxide because developers
& farmers continue to cut down or burn the trees. |
|
| |
Some scientists are concerned about the effect of higher temperatures
on the earth's surface |
|
| |
They warn that global warming may produce mass extinction of plants
& animals & other harmful effects |
|
| |
THE COMMONS IS PERHAPS EXPERIENCING THE MOST DEVASTATING EFFECTS
OF CLIMATE CHANGE |
|
| |
Whether scientists believe in human caused global warming or not, all
recognize that the arctic & antarctic & other climates in the higher
latitudes such as Greenland & Siberia are experiencing drastic changes
as a result of climate change |
|
| |
Permafrost is melting, which is decimating black spruce forests which
were adapted to such an env |
|
| |
Polar bears, seals, & walrus are threatened because of a lack of
ice in the summer |
|
| |
People are threatened as native villages are being lost to the encroaching
ocean |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Global
Warming Conferences
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
THE KYOTO PROTOCOL COMMITTED NATIONS TO VOLUNTARY 1990 LEVELS OF
CO2 PRODUCTION |
|
| |
Delegates from more than 160 countries met in December 1997 in Kyoto,
Japan to draft an agreement to limit global warming |
|
| |
The meeting, called the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate
Change, took place in Kyoto, Japan. |
|
| |
The resulting agreement, known as the Kyoto Protocol, calls for decreases
in the emission of greenhouse gases. |
|
| |
38 industrialized nations would have to cut their emissions of carbon
dioxide & five other gases |
|
| |
The cuts would occur during the years from 2008 through 2012 |
|
| |
The cuts would average from 6 % to 8 % of the 38 nations' 1990 emissions
levels |
|
| |
Developing countries would limit emissions voluntarily or by cooperating
w/ nations that would be subject to limitations |
|
| |
THE KYOTO PROTOCOL PERMITTED POLLUTION TRADING |
|
| |
In addition, the Kyoto Protocol would allow industrialized nations
to buy or sell emissions permits |
|
| |
If a nation cut its emissions more than required by the agreement,
that country could sell other industrialized nations permits allowing those
nations to emit the remaining amounts |
|
| |
THE KYOTO PROTOCOL ENCOURAGED DEVL & ENVL AID FROM THE CORE
TO PERIPHERAL NATIONS |
|
| |
An industrialized nation could also earn credit toward meeting its
requirement by helping a developing country reduce emissions |
|
| |
For example, the industrialized nation might help the developing country
replace fossil fuels in some applications |
|
|
|
One replacement might be solar energy devices that generate electric
power |
|
|
|
The protocol would took effect when 55 countries approved it &
the approving countries' emissions were equal to or greater than 55 % of
the 1990 emissions of the 38 industrialized nations |
|
| |
The developed nations finally hammered out a voluntary agreement to
reduce emissions, & the semi peripheral & peripheral nations demanded
exemptions to these reductions |
|
| |
The US Congress refused to sign the Kyoto agreement until the semi
peripheral & peripheral nations complies w/ some level of non voluntary
reduction |
|
| |
Many nations, but not the US, which is the largest producer of greenhouse
gases, have begun to operate under the Kyoto protocols & are moving
toward meeting their goals |
|
| |
Because the US dithered under the leadership of Bush, Jr, there was
no progress made in the US on reducing greenhouse gas production, now making
it much more difficult to achieve 1990 levels than it would have been had
we worked toward that goal beginning during the Clinton admin |
|
| |
AFTER KYOTO, LITTLE PROGRESS HAS BEEN MADE THROUGH GLOBAL AGREEMENTS,
BUT PROGRESS IS STILL BEING MADE BY GRPS OF NATIONS |
|
| |
Despite more global conferences aimed at reaching an agreement to limit
greenhouse gas production, no significant advances have been agreed to |
|
| |
The US still refuses to sign, but has made weak overtures toward the
reduction of greenhouse gases |
|
| |
Other dev nations, esp Euro & Japan, have moved toward significant
reductions of greenhouse gases |
|
| |
In 2008, China surpassed the US in total greenhouse emissions, but
both China & India have now agreed to greenhouse emission limitations |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Global
Development Orgs & the Environment
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
THE SUCCESS OF GLOBAL DEVELOPMENT ORGS IN ECON DEV OR ADDRESSING
GLOBAL WARMING IS CHECKERED |
|
| |
The internationalization of envlism is grafted on to a set of pre existing
geopolitical instits including the existing nation states, as well as global
instits such as the World Bank, IMF, GATT |
|
| |
The env mvmt has worked w/ World Bank, the IMF, & other global
instits on envlly correct development projects & other issues |
|
| |
THE 3RD WORLD DEBT CRISIS IS A THREAT IN THAT STRESSED NATIONS
CARE LESS FOR THE ENV,
& AN OPPORTUNITY IN THAT DEBT DEALS CAN BE USED TO LEVERAGE
ENV FRIENDLY PROJECTS |
|
| |
But in general the envl mvmt has not taken on the world debt crisis
as being a fundamental contributor to envl degradation |
|
| |
The World Bank's control of 3rd world debt is one of the primary determinants
of 3rd world development |
|
| |
Social justice oriented opposition, which became much stronger at the
end of Cold War, is still important, but adding the envl agenda to debt
deals has only complicated 3rd world development making it appear
that the social justice mvmts & the envl mvmt are resistant to econ
dev |
|
| |
Because of the perception of opposition to 3rd world dev, the social
justice & envl mvmts must clearly state that they are for econ dev,
& that envlly correct econ dev is superior to tradl dev |
|
| |
Indebted countries are subject to having envl agendas attached to debt
deals & unless envl agendas provide additional advantages, nations
will avoid them |
|
| |
POOR NATIONS RESIST BEING FORCED INTO ENVLY COSTLY PROGRAMS UNLESS
THERE IS ALSO A NET BENEFIT |
|
| |
Because they perceive that envlism limits their options, the 3rd world
reacts against they see as 'envl colonialism' |
|
| |
In the debate over greenhouse gas emission, the 3rd world produces
only a small proportion of the overall amt |
|
| |
The 3rd world wants the right to produce more greenhouse gases, which
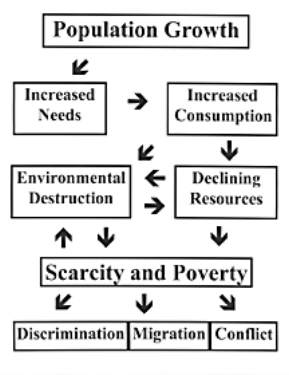
will still only be a small proportion as compared to the lions share produced
by the core nations |
|
| |
Greenhouse gases produced by developing nations are called 'survival
emissions' because these nations need this level just for their people
to survive & grow |
|
| |
Greenhouse gases produced by developed nations are called 'luxury
emissions' because these nations do not need them in the sense of basic
necessities as do the developing nations, & indeed many are produced
by luxuries unknown to developing nations' peoples such as SUVs, air conditioning,
lawn care, etc. |
|
| |
The 3rd world is demanding parity btwn 'survival emissions' of the
semi peripheral & peripheral nations & the 'luxury emissions' of
the core |
|
| |
REFORM CONTINUES ON 3 FRONTS: ON 3RD WORLD DEV, ON THE DEV
ORGS & BANKS, & ON ENVL DEV |
|
| |
The World Bank, GATT, state sovereignty, & end of Cold War have
had adverse consequences for the env because today the globalized system
degrades the env by forcing competition among countries over the exploitation
/ destruction of the env, i.e. it has exasperated the commons problem |
|
| |
The end of the Cold War provides little geopolitical reason to restore
foreign aid to 70s level |
|
| |
Efforts to reform the World Bank & other world development orgs
continue |
|
| |
Reformists of world development orgs want econ dev to be less on the
western model & more customized to the needs of each nation |
|
Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Saving
the Rain Forest
|
|
External
Links
|
|
|
SAVING THE RAIN FOREST WILL REDUCE GLOBAL WARMING BECAUSE IT STORES
CO2 & COOLS THE EARTH |
|
| |
Rain forests have a significant amt of biomass, more than any other
single entity except the ocean |
|
| |
In the rain forests' biomass is a significant amt of carbon |
|
| |
The rain forests also keep the equator region cooler by absorbing the
sun's rays |
|
| |
MANY GOVTS & ENVL ORGS ARE WORKING TO SAVE THE RAIN FOREST |
|
|
|
Many conservation orgs, including the World Wildlife Fund, Conservation
Intl, & the Nature Conservancy, are working w/ govts to conserve rain
forests |
|
|
|
Efforts to save the rain forest include:
a. establishing protected areas
b. promoting intelligent management of rain forests
c. increasing public awareness about the importance of
the forests |
|
| |
In the 1980s & 1990s, hundreds of protected areas were established
in tropical forests |
|
| |
These areas included nature reserves, wildlife sanctuaries, & national
parks |
|
| |
However, such efforts affected only a small percentage of the total
area of rain forest |
|
| |
Moreover, many conservation areas remain only "paper parks," w/ little
protection or enforcement on the ground |
|
| |
GOVTS & ENVL ORGS ARE DEVELOPING BEST MGT STANDARDS FOR
RAIN FORESTS TO EDUCATE & REGULATE RAIN FOREST USERS |
|
| |
Govts & conservation orgs also promote sound mgt of tropical forests
by the people who use them |
|
| |
For example, certain orgs certify timber from loggers that harvest
rain forest wood in a sustainable fashion |
|
| |
Lowes & Home Depot now carry certified lumber in their stores,
which is lumber that has been grown & harvested under more envlly sound
practices |
|
| |
Certified timbers may bring a higher price on the intl mkt |
|
| |
Areas of some rain forests have been set aside as extractive reserves |
|
| |
Local populations manage these reserves & practice sustainable
harvesting of many forest products |
|
| |
THE RAIN FOREST AFFECTS EVERYONE IN A GLOBAL ECON |
|
| |
In the core nations, we all use products that come from the rain forest,
most notably, fast food |
|
| |
Thus saving the rain forest saves people & their lifestyle in the
core nations & what people in the core nations do impacts what happens
in the rain forest |
|
| |
Increasing public awareness about the plight of rain forests may also
aid the struggle to conserve them |
|
| |
Awareness has grown due to greater exposure of rain forest issues in
the media, & to an increasing number of tourists who travel to rain
forests |
|