


| The World Factbook | ||


|
Iraq |

|
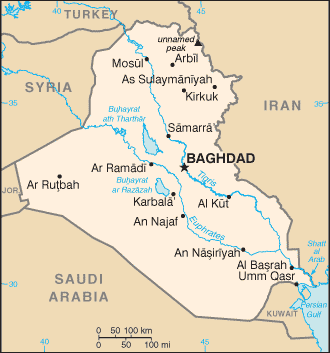
|
| Introduction | Iraq |
|
Background:
|
Formerly part of the Ottoman Empire, Iraq was occupied by Britain during the course of World War I; in 1920, it was declared a League of Nations mandate under UK administration. In stages over the next dozen years, Iraq attained its independence as a kingdom in 1932. A "republic" was proclaimed in 1958, but in actuality a series of military strongmen ruled the country, the latest was SADDAM Husayn. Territorial disputes with Iran led to an inconclusive and costly eight-year war (1980-88). In August 1990, Iraq seized Kuwait, but was expelled by US-led, UN coalition forces during the Gulf War of January-February 1991. Following Kuwait's liberation, the UN Security Council (UNSC) required Iraq to scrap all weapons of mass destruction and long-range missiles and to allow UN verification inspections. Continued Iraqi noncompliance with UNSC resolutions over a period of 12 years resulted in the US-led invasion of Iraq in March 2003 and the ouster of the SADDAM Husayn regime. Coalition forces remain in Iraq, helping to restore degraded infrastructure and facilitating the establishment of a freely elected government, while simultaneously dealing with a robust insurgency. The Coalition Provisional Authority transferred sovereignty to the Iraqi Interim Government (IG) on 28 June 2004. |
| Geography | Iraq |
|
Location:
|
Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iran and Kuwait |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
33 00 N, 44 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Middle East |
|
Area:
|
total: 437,072 sq km
water: 4,910 sq km land: 432,162 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly more than twice the size of Idaho |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 3,650 km
border countries: Iran 1,458 km, Jordan 181 km, Kuwait 240 km, Saudi Arabia 814 km, Syria 605 km, Turkey 352 km |
|
Coastline:
|
58 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
continental shelf: not specified |
|
Climate:
|
mostly desert; mild to cool winters with dry, hot, cloudless summers; northern mountainous regions along Iranian and Turkish borders experience cold winters with occasionally heavy snows that melt in early spring, sometimes causing extensive flooding in central and southern Iraq |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly broad plains; reedy marshes along Iranian border in south with large flooded areas; mountains along borders with Iran and Turkey |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point: unamed peak 3,611 m; note - this peak is not Gundah Zhur 3,607 m or Kuh-e Hajji-Ebrahim 3,595 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
petroleum, natural gas, phosphates, sulfur |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 13.15%
permanent crops: 0.78% other: 86.07% (2001) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
35,250 sq km (1998 est.) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
dust storms, sandstorms, floods |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
government water control projects have drained most of the inhabited marsh areas east of An Nasiriyah by drying up or diverting the feeder streams and rivers; a once sizable population of Marsh Arabs, who inhabited these areas for thousands of years, has been displaced; furthermore, the destruction of the natural habitat poses serious threats to the area's wildlife populations; inadequate supplies of potable water; development of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers system contingent upon agreements with upstream riparian Turkey; air and water pollution; soil degradation (salination) and erosion; desertification |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Law of the Sea
signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification |
|
Geography - note:
|
strategic location on Shatt al Arab waterway and at the head of the Persian Gulf |
| People | Iraq |
|
Population:
|
25,374,691 (July 2004 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 40.3% (male 5,198,966; female 5,039,173)
15-64 years: 56.7% (male 7,280,167; female 7,094,688) 65 years and over: 3% (male 357,651; female 404,046) (2004 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 19.2 years
male: 19.1 years female: 19.3 years (2004 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
2.74% (2004 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
33.09 births/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
5.66 deaths/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.03 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.89 male(s)/female total population: 1.02 male(s)/female (2004 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 52.71 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 46.55 deaths/1,000 live births (2004 est.) male: 58.58 deaths/1,000 live births |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 68.26 years
male: 67.09 years female: 69.48 years (2004 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
4.4 children born/woman (2004 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
less than 0.1% (2001 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
less than 1,000 |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
NA |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Iraqi(s)
adjective: Iraqi |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Arab 75%-80%, Kurdish 15%-20%, Turkoman, Assyrian or other 5% |
|
Religions:
|
Muslim 97% (Shi'a 60%-65%, Sunni 32%-37%), Christian or other 3% |
|
Languages:
|
Arabic, Kurdish (official in Kurdish regions), Assyrian, Armenian |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 40.4% male: 55.9% female: 24.4% (2003 est.) |
| Government | Iraq |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Iraq
conventional short form: Iraq local short form: Al Iraq local long form: Al Jumhuriyah al Iraqiyah |
|
Government type:
|
none; note - the Iraqi Interim Government (IG) was appointed on 1 June 2004 |
|
Capital:
|
Baghdad |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
18 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazah); Al Anbar, Al Basrah, Al Muthanna, Al Qadisiyah, An Najaf, Arbil, As Sulaymaniyah, At Ta'mim, Babil, Baghdad, Dahuk, Dhi Qar, Diyala, Karbala', Maysan, Ninawa, Salah ad Din, Wasit |
|
Independence:
|
3 October 1932 (from League of Nations mandate under British administration); note - on 28 June 2004 the Coalition Provisional Authority transferred sovereignty to the Iraqi Interim Government |
|
National holiday:
|
Revolution Day, 17 July (1968); note - this holiday was celebrated under the SADDAM Husayn regime but the Iraqi Interim Government has yet to declare a new national holiday |
|
Constitution:
|
interim constitution signed 8 March 2004; note - the Transitional Administrative Law (TAL) was enacted 8 March 2004 to govern the country until an elected Iraqi Transitional Government can draft and ratify a new constitution in 2005 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on civil and Islamic law under the Iraqi Interim Government (IG) and Transitional Administrative Law (TAL) |
|
Suffrage:
|
formerly 18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: Interim Iraqi Government (IG) President Ghazi al-YAWR (since 1 June 2004); Deputy Presidents Ibrahim al-JAFARI and Rowsch SHAWAYS (since 1 June 2004); note - the President and Deputy Presidents comprise the Presidency Council head of government: Interim Iraqi Government (IG) Prime Minister Ayad ALLAWI (since 28 June 2004) cabinet: 31 ministers appointed by the Presidency Council, plus a Deputy Prime Minister, Barham SALIH elections: scheduled to be held January 2005 |
|
Legislative branch:
|
Iraqi Interim National Council formed in July 2004 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court appointed by the Prime Minister, confirmed by the Presidency Council |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Iraq has over 300 emergent political parties, with the largest and most organized being the Supreme Council for the Islamic Revolution in Iraq or SCIRI [Abd al-Aziz al-HAKIM]; Da'wa Party [Ibrahim al-JA'FARI]; the Patriotic Union of Kurdistan or PUK [Jalal TALABANI]; the Kurdistan Democratic Party or KDP [Masud BARZANI], and the Iraqi Islamic Party or IIP [Muhsin Abd al-HAMID] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
an insurgency against the Iraqi Interim Government and Coalition forces is primarily concentrated in Baghdad and in areas west and north of the capital; the diverse, multigroup insurgency is led principally by Sunni Arabs whose only common denominator is a shared desire to oust the Coalition and end US influence in Iraq |
|
International organization participation:
|
ABEDA, ACC, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ISO, ITU, LAS, NAM, OAPEC, OIC, OPEC, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant)
chancery: 1801 P Street, NW, Washington, D.C. 20036 FAX: [1] (202) 462-5066 telephone: [1] (202) 483-7500 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador John D. NEGROPONTE
embassy: Baghdad mailing address: APO AE 09316 telephone: 00-1-240-553-0584 ext. 4354; note - Consular Section FAX: NA |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), white, and black with three green five-pointed stars in a horizontal line centered in the white band; the phrase ALLAHU AKBAR (God is Great) in green Arabic script - Allahu to the right of the middle star and Akbar to the left of the middle star - was added in January 1991 during the Persian Gulf crisis; similar to the flag of Syria, which has two stars but no script, Yemen, which has a plain white band, and that of Egypt which has a gold Eagle of Saladin centered in the white band; design is based upon the Arab Liberation colors |
| Economy | Iraq |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Iraq's economy is dominated by the oil sector, which has traditionally provided about 95% of foreign exchange earnings. In the 1980s financial problems caused by massive expenditures in the eight-year war with Iran and damage to oil export facilities by Iran led the government to implement austerity measures, borrow heavily, and later reschedule foreign debt payments; Iraq suffered economic losses from that war of at least $100 billion. After hostilities ended in 1988, oil exports gradually increased with the construction of new pipelines and restoration of damaged facilities. Iraq's seizure of Kuwait in August 1990, subsequent international economic sanctions, and damage from military action by an international coalition beginning in January 1991 drastically reduced economic activity. Although government policies supporting large military and internal security forces and allocating resources to key supporters of the regime have hurt the economy, implementation of the UN's oil-for-food program beginning in December 1996 helped improve conditions for the average Iraqi citizen. Iraq was allowed to export limited amounts of oil in exchange for food, medicine, and some infrastructure spare parts. In December 1999, the UN Security Council authorized Iraq to export under the program as much oil as required to meet humanitarian needs. The drop in GDP in 2001-02 was largely the result of the global economic slowdown and lower oil prices. Per capita food imports increased significantly, while medical supplies and health care services steadily improved. Per capita output and living standards were still well below the pre-1991 level, but any estimates have a wide range of error. The military victory of the US-led coalition in March-April 2003 resulted in the shutdown of much of the central economic administrative structure, but with the loss of a comparatively small amount of capital plant. The rebuilding of oil, electricity, and other production is proceeding steadily at the start of 2004 with foreign support and despite the continuation of severe internal strife. A joint UN and World Bank report released in the fall of 2003 estimated that Iraq's key reconstruction needs through 2007 would cost $55 billion. In October 2003, international donors pledged assistance worth more than $33 billion toward this rebuilding effort. |
|
GDP:
|
purchasing power parity - $37.92 billion (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
-21.8% (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita:
|
purchasing power parity - $1,500 (2003 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 6%
industry: 13% services: 81% (1993 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
NA |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA
highest 10%: NA |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
29.3% (2003 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
7.8 million (2004 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture NA, industry NA, services NA |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
NA (2003 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $12.8 billion NA
expenditures: $13.4 billion NA, including capital expenditures of NA (2004 budget) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
wheat, barley, rice, vegetables, dates, cotton; cattle, sheep |
|
Industries:
|
petroleum, chemicals, textiles, construction materials, food processing |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
NA |
|
Electricity - production:
|
36.01 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
33.49 billion kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
2.2 million bbl/day; note - prewar production was 2.8 million bbl/day (January 2004 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
460,000 bbl/day (2001 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
1.7 million bbl/day (January 2004) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
NA (2001) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
113.8 billion bbl (1 January 2002) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
2.76 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
2.76 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2001 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
3.149 trillion cu m (1 January 2002) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$1.136 billion (2003) |
|
Exports:
|
$7.542 billion f.o.b. (2003 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
crude oil |
|
Exports - partners:
|
US 48.8%, Jordan 8.4%, Canada 8%, Italy 7.9%, Morocco 5.3% (2003) |
|
Imports:
|
$6.521 billion f.o.b. (2003 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
food, medicine, manufactures |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Turkey 18.1%, Jordan 13.4%, Vietnam 10.7%, US 6.9%, Germany 5%, UK 4.7% (2003) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$93.95 billion (2003 est.) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
more than $33 billion in foreign aid pledged for 2004-07 (2004) |
|
Currency:
|
New Iraqi dinar (NID) as of 22 January 2004 |
|
Currency code:
|
NID, IQD prior to 22 January 2004 |
|
Exchange rates:
|
New Iraqi dinars per US dollar - 1,890 (second half, 2003) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year |
| Communications | Iraq |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
675,000; note - an unknown number of telephone lines were damaged or destroyed during the March-April 2003 war (2003) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
20,000 (2002) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: the 2003 war severely disrupted telecommunications throughout Iraq including international connections; USAID is overseeing the repair of switching capability and the construction of mobile and satellite communications facilities
domestic: repairs to switches and lines destroyed in the recent fighting continue but sabotage remains a problem; cellular service is expected to be in place within two years international: country code - 964; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean and 1 Indian Ocean), 1 Intersputnik (Atlantic Ocean region), and 1 Arabsat (inoperative); coaxial cable and microwave radio relay to Jordan, Kuwait, Syria, and Turkey; Kuwait line is probably nonoperational |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
after 17 months of unregulated media growth, there are approximately 80 radio stations on the air inside Iraq (2004) |
|
Radios:
|
4.85 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
21 (2004) |
|
Televisions:
|
1.75 million (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.iq |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
1 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
25,000 (2002) |
| Transportation | Iraq |
|
Railways:
|
total: 1,963 km
standard gauge: 1,963 km 1.435-m gauge (2003) |
|
Highways:
|
total: 45,550 km
paved: 38,399 km unpaved: 7,151 km (2000 est.) |
|
Waterways:
|
5,275 km (not all navigable)
note: Euphrates River (2,815 km), Tigris River (1,895 km), and Third River (565 km) are principal waterways (2004) |
|
Pipelines:
|
gas 1,739 km; oil 5,418 km; refined products 1,343 km (2004) |
|
Ports and harbors:
|
Umm Qasr, Khawr az Zubayr, and Al Basrah have limited functionality |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 13 ships (1,000 GRT or over) 83,221 GRT/125,255 DWT
by type: cargo 6, passenger/cargo 1, petroleum tanker 5, roll on/roll off 1 registered in other countries: 3 (2003 est.) |
|
Airports:
|
111; note - unknown number were damaged during the March-April 2003 war (2003 est.) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 79
over 3,047 m: 21 2,438 to 3,047 m: 36 914 to 1,523 m: 7 under 914 m: 10 (2004 est.) 1,524 to 2,437 m: 5 |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 32
under 914 m: 9 (2004 est.) over 3,047 m: 2 2,438 to 3,047 m: 4 914 to 1,523 m: 12 1,524 to 2,437 m: 5 |
|
Heliports:
|
6 (2003 est.) |
| Military | Iraq |
|
Military branches:
|
note: in the summer of 2003 the Coalition Provisional Authority (CPA) began recruiting and training a New Iraqi Army (NIA) that would have a purely defensive mission and capability; in March 2004, the Iraqi Interim Government established a Ministry of Defense to create an Iraqi Armed Force; at that time the NIA was renamed the Iraqi Armed Force - Army (IAF-A); plans also were put into effect to reconstitute an Iraqi Army Air Corps (IAAC) and Coastal Defense Force (navy), but there are no plans to reconstitute an Iraqi Air Force; the Army's primary new focus will be domestic counterinsurgency, which is a change of direction from the CPA's intent to create an army not involved in domestic politics; in mid-2004 the Iraqi Civil Defense Corps (ICDC) was designated the Iraqi National Guard (ING) and subordinated to the Defense Ministry and the Iraqi Armed Forces Pre-war Iraqi military equipment was largely destroyed by Coalition forces during combat operations in early 2003 or subsequently looted or scrapped (September 2004) |
|
Military manpower - military age and obligation:
|
18 years of age; the Iraqi Interim Government is creating a new professional Iraqi military force of men aged 18 to 40 to defend Iraqi territory from external threats (September 2004) |
|
Military manpower - availability:
|
males age 15-49: 6,547,762 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - fit for military service:
|
males age 15-49: 3,654,947 (2004 est.) |
|
Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
|
males: 304,527 (2004 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$1.3 billion (FY00) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
NA |
| Transnational Issues | Iraq |
|
Disputes - international:
|
coalition forces assist Iraqis in monitoring boundary security, but resolution of disputes and creation of maritime boundaries with neighboring states will remain in hiatus until full sovereignty is restored in Iraq; Turkey has expressed concern over the status of Kurds in Iraq |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
refugees (country of origin): 150,000 (Palestinian Territories)
IDPs: 1,340,280 (ongoing US-led war and Kurds' subsequent return) (2004) |
|
This page was last updated on 27 January, 2005 |