Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on Work
in the 21st Century
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
- Supplement: NPR. World
Renowned Economist John Maynard Keynes Predicted the 15 Work Week in 1930.
2015 |
Link
|
| |
- Supplement: NYT.
Bush Recession, 2007. 2010 |
Link
|
| |
TECH, GLOBAL COMPETITION, A MORE DIVERSE WKPLACE, & MORE
MIGRATION
OF WKRS WILL BE IMPORTANT FACTORS IN THE FUTURE WKPLACE |
|
| |
Tech change, increased world mkt competition, & the increased proportion
of women, minority, immigrant wkrs in the labor force are major changes
that will determine the nature of wk in the future |
|
| |
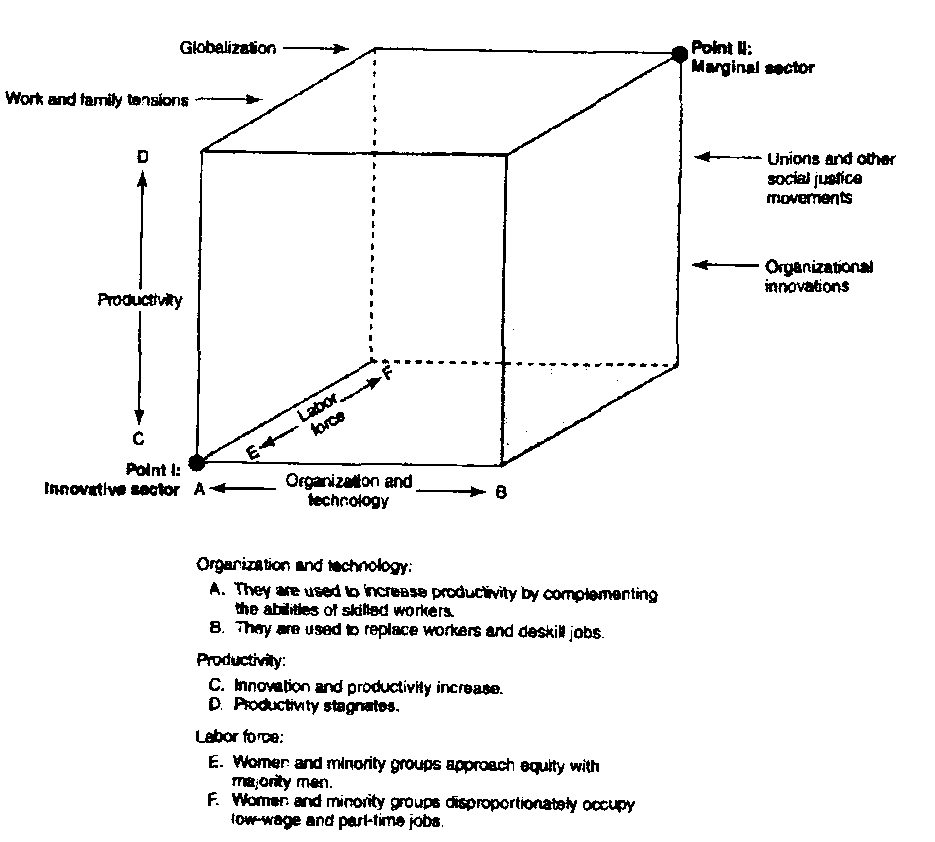
It is likely that the econ will be characterized by 2 different employment
sectors, one which is the innovative sector, the other which is the marginal
sector |
|
| |
SOME SEE THE 'END OF WORK' BUT OTHERS
SEE A LONG PERIOD PRIOR TO THAT WHICH MAY BE STRUCTURED AROUND INNOVATIVE
& MARGINAL OCCUPATIONS |
|
| |
While some social scientists such as Rifkin, 2004, believe
that work will disappear in the hi tech future, others such as Hodson,
do not |
|
| |
What is certain is that the nature of work appears to be diverging
btwn 2 increasingly distinct sectors of employment |
|
| |
The major factors that will impact the wkplace in the future include
tech change, orgl change, & the competitive climate |
|
| |
THE INNOVATIVE SECTOR OF OCCUPATIONS WILL BE
CRITICAL FOR A FUNCTIONAL FUTURE WKPLACE |
|
| |
In the innovative sector wkrs respond to heightened intl
competition & tech change will be the development of tech & orgl
innovations leading to increased productivity |
|
| |
In the innovative sector, tech & orgl innovation will be continuous,
jobs will be reasonably secure, pay will be adequate, job conditions will
be more or less pleasant, & wkrs will have an increased say in determining
the conditions of their work |
|
| |
THE MARGINAL SECTOR OF OCCUPATIONS WILL CONTINUE
TO GROW & WILL BE DIFFICULT TO REDUCE IN THE FUTURE WKPLACE |
|
| |
In the marginal sector, wkrs respond to intl competition
& tech change by constantly pressing down on labor costs through reducing
wages & benefits |
|
| |
In the marginal sector, innovation will be slow, jobs will be unpleasant
& even hazardous |
|
| |
The organizing principle of the marginal sector will be to achieve
econ viability by driving down wages rather than by promoting tech &
orgl innovation |
|
| |
Wkrs will have little say in determining the conditions of their employment
or the polices of their orgs |
|
| |
Female & minority wkrs are likely to be disproportionately employed
in the marginal sector |
|
|
|
THE RENOWNED ECONOMIST JOHN MAYNARD KEYNES PREDICTED
DRASTIC REDUCTIONS IN THE NEED TO WORK |
|
|
|
In the 1930s, the economist John Maynard Keynes predicted
that his grand kids would work just 15 hours a week |
|
|
|
Keynes' argument for the 15 hr work week was that over time, thanks
to machines & tech & new ideas, people get more productive, &
thus less labor is needed to produce the goods & services we need |
|
|
|
Keynes believed that as tech & orgl structuring creates more productivity,
an hour of labor produces more & more stuff, theoretically necessitating
less labor |
|
|
|
Keynes figured we'd just decide to work less |
|
|
|
In some nations, the number of hrs wked has dropped some |
|
|
|
But take the US, in 1950, people wked, on average, about 38 hrs a week |
|
|
|
Today, 6 decades after Keynes wrote we would be wking 15 hrs a week,
those people who are working work over 40 hrs a week, but there are more
people out of the wkforce today |
|
|
|
The full time work week is still 40 hrs, & the ave fully employed
wkr works about 46 hrs a week, not including the 'home labor' necessary
to prepare for work |
|
|
|
Richard Freeman, a Harvard economist, says one of the things Keynes
underestimated was the human desire to compete |
|
|
|
In the innovative employment sector, earning more money can make it
harder to take time off. b/c if someone is paid $200 an hr they do not
really want to leave early & go to the beach & miss all that money |
|
|
|
B/c of the competitive culture & the perceived need for security,
for the fully employed wkr, foregoing wk & reading a novel is not worth
the lost income |
|
|
|
The better you are at your job, the harder it can be to not do it |
|
|
|
At the marginal end of the jobs spectrum, many people do not work less
b/c the job(s) they have do not pay enough to allow them to work less |
|
|
|
In the marginal employment sector, wkrs are often 'underemployed,'
meaning that either they do not work full time, or they are employed in
a job that does not match their ed & skills |
|
|
|
Underemployed wkrs typically want more hrs or a different job
that utilizes their ed & skills |
|
|
|
While machine & orgl tech would allow us as a society to wk close
to Keynes' estm 15 hrs a week & still make a mid class living, the
factors that prevent this are many:
a. the 40 hrs work week is still standard & necessary
to earn retirement & benefits
b. in the innovative sector people do not want to forgo
income for competitive reasons
c. in the marginal sector people simply cannot survive
w/o wking 40 or more hrs a week
d. it is not socially acceptable in our culture, our values
often result in socially evaluating people who do choose to forgo income
for a leisurely lifestyle as misfits, lazy, moochers, wasteful, & so
on |
|
| |
MAJOR CHANGES IN THE WKPLACE ARE OFTEN NOT SEEN UNTIL
THEY ARRIVE |
|
| |
10 yrs ago, Facebook didn't exist; 10 yrs before that,
the internet did not exist; both are now major job sectors |
|
| |
In the future as both Facebook & other firms on the internet demonstrate,
the wkplace & work itself will be more flexible, for freelance, more
collaborative, & less secure than it is toddy |
|
| |
The future wkplace will be run by a generation w/ new values, women
& minorities will increasingly be at the controls |
|
|
|
THE RECOVERY AFTER THE BUSH RECESSION DEMONSTRATES THAT
THE
EXPECTATION OF FULL TIME WORK IS CHANGING AS IS THE TYPES OF OCCUPATIONS
AVAILABLE FOR EMPLOYMENT |
|
|
|
The Bush financial recession of 2007 to having begun in
December 2007, lasted 18 months, officially ended in June of 2009 when
GDP began to stop falling, but it was still far below where it had begun |
|
|
|
Some analysts declare that the recession didn't end until Dec 2015
when the Fed Res Bank raised the interest rate for the 1st time from zero
to .25% |
|
|
|
Until now the longest postwar recessions were those of 1973-5 &
1981-2, which each lasted 16 mos |
|
|
|
The end date to the recession also confirms what many had suspected:
the 2007-9 recession was the deepest on record since the 1929 Great Depression,
at least in terms of job losses |
|
|
|
The Bush recession, 2007, is shaping the wkplace of the future in that
it is forcing people to look harder at what they really want to do instead
of following a standard path |
|
|
|
The path that led many of America's elites to Wall Str is today a less
appealing destination, but it hasn't disappeared |
|
|
|
Financial centers like Charlotte, NC will flourish driven by the new
banking boom |
|
| |
The fall of finance has the upside that top grads will look to other
sectors that prize tech & analytical skills |
|
| |
According to consulting giant McKinsey & Co, about 85% of new jobs
created btwn 1998 & 2006 involved complex 'knowledge work' |
|
| |
Jobs in math & across the sciences are expected to expand |
|
| |
The Dept of Labor predicts the sectors of network systems & data
communication to grow rapidly |
|
| |
Info tech jobs will grow at twice the overall job growth rate from
2016 to 2023 |
|
|
|
Other job sectors expected to grow at an above average rate include:
health care, education, providing for seniors, the non fossil fuel energy
sector |
|
|
|
The contracting job sectors include Uber, Air B & B, Zip Car, Travelocity,
Temps Inc, & many more |
|
| |
WKRS ACT MORE LIKE INDEPENDENT CONTRACTORS EVEN
THOUGH THEY ARE EMPLOYEES IN THAT THEY ARE BECOMING MORE RESPONSIBLE FOR
THEIR OWN HEALTH CARE, RETIREMENT, & SO ON |
|
| |
One major change coming in the wkplace is that wkrs are
increasingly on their own when it comes to retirement savings & health
care |
|
| |
Firms don't typically eliminate an important wkr benefit, but they
are shifting more of these costs onto wkrs who feel it in terms of higher
health care premiums, rising co pmts, & 401k retirement plans replacing
tradl fixed income retirement plans, less or no paid leave, & others |
|
| |
As more wkrs & entrepreneurs move to the 'sharing economy' like
Uber & Air B & B, these sectors of the econ offer no benefits &
have no job security |
|
| |
MORE WKRS TODAY, & IN THE FUTURE, WILL EMBRACE THE
YOLO
PHILOSOPHY & REFUSE TO BE A WORKAHOLIC |
|
| |
In the innovative sector more wkrs are refusing to 'climb
the ladder,' that is, instead of giving it all to work to climb up the
wkplace hierarchy, they are choosing to wk less, or differently, to have
more qual of living |
|
| |
An example of refusing the ladder is the tax accountant who restructured
her job to include more telecommunting & less hours |
|
| |
In the past, this was only done by women on the 'mommy track,' but
today more male & female wkrs are refusing the ladder to improve their
qual of life as exemplified by the YOLO lifestyle |
|
| |
Firms in the innovative sector are supporting more natural growth,
letting wkrs wend their way upward like climbing vine instead of forcing
the structure of the corporate ladder w/ one way up, or nothing |
|
| |
Old school mgrs often resist or even punish YOLO wkrs by scheduling
meetings when a wkrs are out, favoring tradl 'the job 1st' wkrs, etc |
|
| |
BOOMERS MAY HANG ONTO THEIR JOBS UNTIL THE BITTER
END |
|
| |
Even before the 2007 Bush recession, Boomers had not saved
enough for retirement, & this non saving trend continues for today's
younger wkrs |
|
| |
Investment firm T Rowe Price estm that the oldest boomers will delay
retirement by 9 yrs, & it is now estm that all wkrs will push back
retirement |
|
| |
Wkrs will have to wk longer |
|
| |
As boomers continue to wk, economists estm that they will squeeze out
younger wkrs pushing 'normal' unemployment to over 10% b/c the normal retirement
cycle has been disrupted |
|
| |
A rise in the % of older wkrs has the advantage of a greater utilization
of the entire wkforce & a decrease or brake on inflation b/c older
wkrs have topped out in their earnings, thus resulting in less raises |
|
| |
WOMEN WILL HEAD MORE BUSINESSES |
|
| |
Women are more likely to support the work life balance
demanded by the YOLO wkr of youth today |
|
| |
Female mgt style is not soft; it's lucrative; the wkplace research
grp Catalyst studied 353 Fortune 500 firms & found those w/ the most
women in senior mgt had a higher rate of return by more than 1/3 rd |
|
| |
Women are more cautious, focus on the long term while men take risk,
esp when surrounded by other men |
|
| |
Women are consensus builders, conciliators & collaborators &
they employ transformational leadership style: heavily engaged, motivational,
extremely well suited for the emerging, less hierarchical wkplace |
|
| |
The Employment Policy Foundation estm there will be a 6 mm person shortage
of college ed wkrs, & b/c women are far outpacing men in college ed,
women will take more positions of power in the future wkplace |
|
| |
Women & the wkplace of the future are tending to give wkrs more
freedom & firms like Capital One have found productivity shoots
up |
|
| |
Women are getting rid of the 'crunchy' criticism of work life balance,
the YOLO wkplace, the mommy track, demonstrating that it makes good business
sense to institute the flexible wkplace w/ wkrs free to make money as they
see fit |
|
| |
IN THE FUTURE THERE WILL BE MORE GREEN JOBS |
|
| |
A number os environmentalists & economists believe
that by implementing a comprehensive energy program, we can not only avert
climate change, but also create a generational boost to the econ like those
created by the institutionalization of the railroad, the interstate highway
system, the airlines, the internet, & other sectors |
|
| |
Green jobs represent the green way of doing everything we do now including:
raising & dist food, wind mills & solar panels, green buildings,
mass transit, electric cars, zero waste production, space flight, &
more |
|
| |
The Mayors' Report predicts that for the next 3 decades, green jobs
will provide 10% of all new jobs |
|
| |
W/ the emergence of new sectors of the econ, the challenge in the wkplace,
esp for the wkrs, is the process of how to shift from one econ sector to
another |
|
| |
GEN X WILL BRING A NEW SET OF VALUES TO THE WKPLACE |
|
| |
Gen X, born btwn 65 & 78 will spend 2 decades running
into the 'gray ceiling' of the Boomers until 2019 when Gen X will finally
be in charge |
|
| |
Gen Y, born btwn 1979 & 2000, is unlikely to follow their parents'
lead: paying your dues, moving up slowly is going away |
|
| |
Success will be defined will be defined not by rank or seniority, but
by getting what maters to you personally |
|
| |
Firms already want more short term independent contractors & consultants,
& fewer tradl wkrs b/c contractors are cheaper |
|
| |
One new challenge for Gen X mgrs is to estb collaborative dec
mking involving team members who are scattered around the world |
|
| |
Leaders will have to be culturally dexterous on a global scale |
|
| |
MFR WILL RETURN / REMAIN IN THE FUTURE WKPLACE |
|
| |
The death of Am mfring has been greatly exaggerated |
|
| |
THe US remains by far the world's largest mfr, producing nearly 2X
that as No 2, China |
|
| |
Since 1990, US mfr output has grown by nearly $800 bb |
|
| |
But growth does not mean jobs; Am wkrs doubled their productivity which
eliminated many jobs in mfr |
|
| |
Mfr is requiring more highly skilled wkrs who produce high value products
in high stakes industries |
|
| |
Firms now make a distinction btwn exportable jobs & jobs that should
stay home |
|
| |
Corner cutting scandals in China, such as lead paint tainted children's
toys, or melamine laced milk, have underlined the advantages of mgr at
home |
|
| |
Innovative firms also stay home b/c of the US's superior network of
universities & its relatively stringent intellectual property laws |
|
| |
WE WILL SEE THE LAST DAYS OF CUBICLE LIFE IN
THE WKPLACE OF THE FUTURE |
|
| |
Today & in the future, firms will no longer expect
wkrs to drive to a blding to sit & work |
|
| |
When work gets auctioned off to the lowest bidder, the job gets a lot
more stressful |
|
| |
Jobs of the future will have little to do w/ processing words or numbers
b/c the internet can do that; nor will people act as place holders, errand
runners or receptionists |
|
| |
The focus will be on finding the essential people & outsourcing
the rest |
|
| |
Many jobs will be for people who manage customers, organize fans, who
do digital community mgt |
|
|
|
Rather than show up at the office & taking your place in your cubicle,
rather you will be sent a file or take place in a teleconference |
|
| |
Everything at work will be measured, when you log in, what you type,
what you access; & all this info will be available not only to the
boss, but also to the team |
|
| |
Wkrs will go from a few days alone at home, maintaining the status
quo, to remote wk being the norm, punctuated by urgent team sessions, sometimes
in person, often online |
|
|