|
Links |
|
Links |
||||||||
| - Project: We Are What We Do |
|
|||||||||
| - Project: Class & False Consciousness |
|
|||||||||
| - Project: Principles of Marxism & Money, Power, & Status |
|
|||||||||
|
|
- Major Works & Biography of Marx | |||||||||
|
|
- Biography of Engels | |||||||||
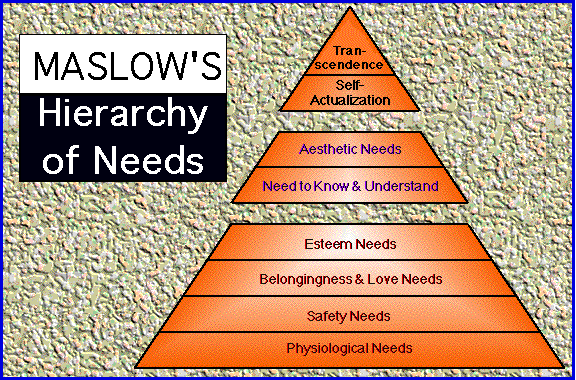
| Summary: There are FIFTEEN of Marx's fundamental concepts
1. Our human nature is that we are laboring/creating beings 2. Society consists of two fundamental components: the base & the superstructure 3. The forces of production & relations of production determine economic relationships & thus the Base & thus society 4. Individuals have conflicting self interests 5. There are "contradictions" in society 6. There is class conflict: proletariat & bourgeoisie 7. Conflict is the energy of social change-- of historical development 8. There is social evolution in the form of historical development of material life 9. Society is in a state of constant change & struggle 10. Conflict does not always mean violence 11. Capitalism is destructive of humanity 12. Capitalism is alienating 13. The upper class controls the economy 14. Culture is shaped by the economic Base of society 15. We have either class or false consciousness |
||||||||||
| SCHOLARS DIVIDE MARX'S WORK INTO "EARLY" & "LATE" MARX BECAUSE
IN HIS EARLY PERIOD
HE WAS MORE PHILOSOPHICAL & IN HIS LATE PERIOD HE WAS MORE ECONOMICS ORIENTED |
||||||||||
| There is much debate over the differences & the significance of the differences of Marx's early & late works | ||||||||||
| Early Marx is generally more global & philosophical in scope & offers a more complex & humanist view of human kind | ||||||||||
| Late Marx is generally more focused on the mechanisms of economic systems & is considered to present a more deterministic view of human nature | ||||||||||
| A major debate w/in Marxism is whether Marx's system was a deterministic system or not, & which sector of society had the greatest power over human nature, the economy or culture? | ||||||||||
| See Also: Economic v. Cultural Determinism | ||||||||||
| There is much debate over various interpretations of Marx's work | ||||||||||
| Early Marx is seen as a humanist w/ a social focus, & a dynamic view of human nature & social life | ||||||||||
| Late Marx has an economics focus & a deterministic view of human nature & social life | ||||||||||
| Many theorists debate whether Marxism is a deterministic system or not | ||||||||||
|
|
Preface: A Contribution to the Critique of Political Economy | |||||||||
| See Also: Entire preface | ||||||||||
| There are FIFTEEN of Marx's fundamental concepts | ||||||||||
|
|
1. OUR HUMAN NATURE IS THAT WE ARE LABORING / CREATING BEINGS | |||||||||
| There are many other bases of human nature | ||||||||||
| Marx used the term species being for human nature | ||||||||||
| Marx believed our species being is undeveloped |
|
|||||||||
| Marx believed in the perfectibility of the individual | ||||||||||
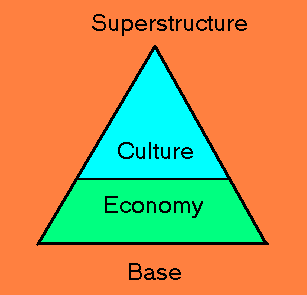
| 2. SOCIETY CONSISTS OF 2 FUNDAMENTAL COMPONENTS: THE BASE & THE SUPERSTRUCTURE | ||||||||||
| Economic relations make up the base or foundation of society | ||||||||||
| All other relationships make up the superstructure & are determined by the Base | ||||||||||
|
|
Did the so called communist countries actually change the economic foundation of their society? | |||||||||
| 3. THE FORCES & RELATIONS OF PRODUCTION
DETERMINE THE
NATURE OF THE ECONOMY & THUS THE BASE & THUS SOCIETY |
||||||||||
| See Also: Forces of Production | ||||||||||
| See Also: Relations of Production | ||||||||||
| 4. PEOPLE, GROUPS, ETC. HAVE CONFLICTING SELF INTERESTS | ||||||||||
| Conflict is linked to, or over the material / economic struggle
Groups (classes) conflict because of competition over scarce resources The major split of self interests was seen as being btwn owners & workers |
||||||||||
| 5. THERE ARE "CONTRADICTIONS" IN SOCIETY | ||||||||||
| Contradictions are social relations that cause conflict, which may or may not be seen as unjust or simply as "the way things are" | ||||||||||
| Conflict, at the abstract level, is btwn classes while at the everyday or concrete level, conflict is when workers/unionists & particular capitalist firms engage in struggle | ||||||||||
Examples of Contradictions:
|
||||||||||
| Marx respected Hegel because, through the dialectic, he discussed an affirmative view of a phenomenon as well as its negation; i.e., its inevitable breaking up which takes account of the transient nature of things | ||||||||||
|
|
6. THERE IS CLASS CONFLICT IN SOCIETY | |||||||||
| The form of society is shaped by conflict btwn groups in society, as well as by the economic base | ||||||||||
| Marxists will see society in conflict whereas functionalists will see society as interdependent/cooperative | ||||||||||
| There were only two classes in Marx's day: the bourgeoisie & the proletariat | ||||||||||
| The bourgeoisie, aka the owners, are those who own the means
of production
The proletariat, aka the workers, are those who work with the means of production |
||||||||||
| Stratification is the study of class structure today | ||||||||||
| A typical formulation of classes today includes the upper class, UMC, MC, LMC, LC | ||||||||||
| See Also: Class Structure | ||||||||||
| Today, we see all classes in a struggle w/ each other
Example: how does more pay for coal miners affect the other groups? |
||||||||||
| 7. CONFLICT IS THE ENERGY OF SOCIAL CHANGE, OF HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT | ||||||||||
| Conflict brings social change | ||||||||||
| 8. SOCIAL EVOLUTION IS THE HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF MATERIAL LIFE | ||||||||||
| Marx sees all history as the history of class struggle | ||||||||||
| Each historical epoch has its own contradictions & classes | ||||||||||
| Humanity has developed through FOUR historical phases, which will be followed by TWO more | ||||||||||
| - Asiatic Egypt, China
- Ancient Greece, Roman Empire - Feudal W Europe - Capitalist last antagonistic system - Socialist Marx would maintain that socialism was never estb in Russia, China, etc. - Communist |
||||||||||
| While capitalism is last antagonistic system in that there is class conflict, there will always be individual struggle & conflict | ||||||||||
| See Also: An Overview of Marxist History | ||||||||||
| 9. SOCIETY IS IN A STATE OF CONTINUAL CHANGE & STRUGGLE | ||||||||||
| Equilibrium does not exist for Marx & other conflict theorists because the inherent tendency of society is toward conflict, not consensus | ||||||||||
| Conflict is natural, normal & useful to society | ||||||||||
| 10. CONFLICT DOES NOT ALWAYS MEAN VIOLENCE | ||||||||||
| Conflict is institutionalized so that differences can be worked out through society's channels such as unions, courts, etc. | ||||||||||
| Collective bargaining & civil rights panels are examples of the institutionalization of conflict | ||||||||||
| Violence occurs when groups become frustrated w/ society's channels to redress differences | ||||||||||
| Conflict eliminates social arrangements that harm society as a whole | ||||||||||
| Conflict offers disadvantaged groups the opportunity to improve their position in society | ||||||||||
|
|
11. CAPITALISM IS DESTRUCTIVE OF HUMANITY |
|
||||||||
|
|
The existing system of capitalism was not only preventing fulfillment of our potential, it was even depriving us of our animal needs: food, shelter, sex, fresh air, & so on |
|
||||||||
|
|
Hunger is a condition of deprivation imposed by people |
|
||||||||
|
|
During Marx's time, capitalism had reduced humanity to animal laborers where the worker's needs were at the barest & most miserable level &, in fact, people were becoming less than animals |
|
||||||||
|
|
See Also: Economic and Philosophic Manuscripts of 1844 | |||||||||
|
|
Market relations destroy society through TWO processes |
|
||||||||
| a. creativity is destroyed because we are not creating for ourselves, but instead we are creating for the market | ||||||||||
| b. the mkt concentrates wealth which creates monopoly | ||||||||||
| See Also: Pac Man economics & Mkt Concentration | ||||||||||
|
|
12. CAPITALISM IS ALIENATING, I.E. CAUSES SEPARATION OF INDIVIDUALS & SOCIAL GROUPS | |||||||||
| While both Hegel & Feuerbach discussed the nature of alienation, Marx built upon these to develop his own dialectical- material view of alienation | ||||||||||
| See Also: Alienation | ||||||||||
|
|
13. THE UPPER CLASS CONTROL THE ECONOMY ( 50% of income ) |
|
||||||||
|
|
See Also: Introduction on the Economic Power of the Upper Class | |||||||||
| The UC controls the economy & thus the culture | ||||||||||
| Bill Gates controls more wealth, over $100 bb in 2000, more than the lower 20% of the population | ||||||||||
| In 2000, there were over 1000 billionaires in the world | ||||||||||
| American income distribution demonstrates that the richest 20% has more income as all the rest | ||||||||||
| The top 5% of the population controls more than the lower 40% of the population | ||||||||||
|
|
American income distribution demonstrates that the richest 20% has more income as all the rest | |||||||||
|
|
Groups w/ advantage will attempt to preserve the status quo: i.e. existing set of arrangements |
|
||||||||
|
|
While society experiences conflict, in the long run, society is relatively stable, & income distribution has changed little in the last 100 yrs. |
|
| Link | 14. CULTURE IS SHAPED BY THE ECONOMIC BASE |
|
|
|
By controlling the base, the upper class ( UC ) controls the superstructure & thus we have conflicting values & ideologies |
|
|
|
Marx believed that the powerful promote a belief in their ideology, i.e., ideology of the UC |
|
| Most Am have the ideology of the rich which may be thought of as a morbid belief that they also can be rich when the cold reality is that class structure has changed only minutely in last 100 yrs. |
|
|
|
|
The media holds success stories up for workers to see |
|
|
|
15. WE HAVE EITHER CLASS OR FALSE CONSCIOUSNESS |
|
|
|
For Marx, we have class consciousness if we support policies that advance our interests |
|
| An example of class consciousness is when the working class supports policies in its own interest such as lower taxes for the non upper classes, the advancement of unions, universal health care, etc. | ||
|
|
For Marx, we have false consciousness if we support policies that harm or reverse our interests |
|
| An example of class consciousness is when the upper class supports policies that are not in its own interest such as the advancement of unions, capital gains taxes, inheritance taxes w/ a high deductible rate | ||
|
|
An ideology or world view is a mental system of beliefs about reality, which may be real or ideal |
|
|
|
See Also: Ideology | |
|
|
See Also: Class & False Consciousness |
|
|
|
Conflicting ideologies often appear as a conflict of values |
|
|
|
For Marx, most workers support the status quo, i.e., the ideology of the upper class, & thus, they have false consciousness |
|
|
|
Marx viewed the development of the modern era as fraught w/ both immense problems & immense potentials |
|
|
|
Modernity was defined by the capitalist economy |
|
|
|
Modernity had developed as a result of the transition from earlier forms of society | |
|
|
Marx restricted himself mostly to a critique of the economic system & its deformities such as alienation, exploitation, econ collapse, monopolization, etc. |

Karl Marx 1818 - 1883 Born in the German Rhineland, Marx spent most of his adult life in political
exile
|
 |
||||
Economic and Philosophic Manuscripts of 1844 The Communist Manifesto Das Kapital Thesis on Feuerbach A Contribution to the Critique of Political Economy 1859 |
|||||
Though Engels was also born in the Rhineland, his father was a textile mfr. w/ interests in England Engels moved to England to 1st work at, then manage, then own, a cotton mill in Manchester Marx & Engels met briefly in 1842, again in 1844 From that time on they worked closely together From 1850 Engels provided financial support for Marx, & Marx's family after Marx died |
z 0515 Hist Mx
|
Society & Nature, Dickens, Chap
2
|
Russia, China: did they change the economic foundation?
And what was the effect on the superstructure?
|
Labor v. mgt Wkrs v. mgt Environmentalism
|
Pretty Woman: prostitute succeeds: marries millionaire Cinderella Who wants to be a millionaire? Lottery Beauty Queen marries a multi-millionaire |