Internal
Links
Top
|
|
Outline on an Intro
to the Future of the Labor Movement
|
|
External
Links
|
| |
ANTICIPATING THE EVOLUTION OF LABOR RELATIONS HELPS ONE PREPARE
FOR THE CHALLENGES THAT INEVITABLY ACCOMPANY CHANGE |
|
| |
Predicting specific direction of union mgt relationships will be difficult |
|
| |
Forecasts depend on decisions that are made by wkrs, firms, unions,
the public, the govt, & other actors in the situation |
|
| |
Many actors will affect the labor mgt relations sphere into the future |
|
| |
The possible relationships btwn external influences, mgt, &
union officials' negotiation of wk rule change as the very process of wk
changes |
|
| |
In trying to understand the unfolding of the future, one must consider
all factors, external & internal, that may impact labor relations future
direction |
|
|
Link
|
The Figure: A Model of the Labor
Relations Process demonstrates the relationships among internal participants
of wkrs, unions, firms, the govt, & more, & external factors &
participants such as tech, the econ, globalization, the mkt, the community
& wider culture, the labor mkt, & more |
|
| |
In the future, at this time it is neither anticipated that the fundamental
participants, nor the fundamental forces or trends, nor the relationships
among them will drastically change |
|
| |
In the future it is anticipated that the direction & impact of
the forces will change & some of the relationships among participants
& forces will change |
|
| |
Understanding the future of labor relations necessitates understanding
how & to what degree participants & structural forces will change |
|
Figure:
A Model of the Labor Relations Process
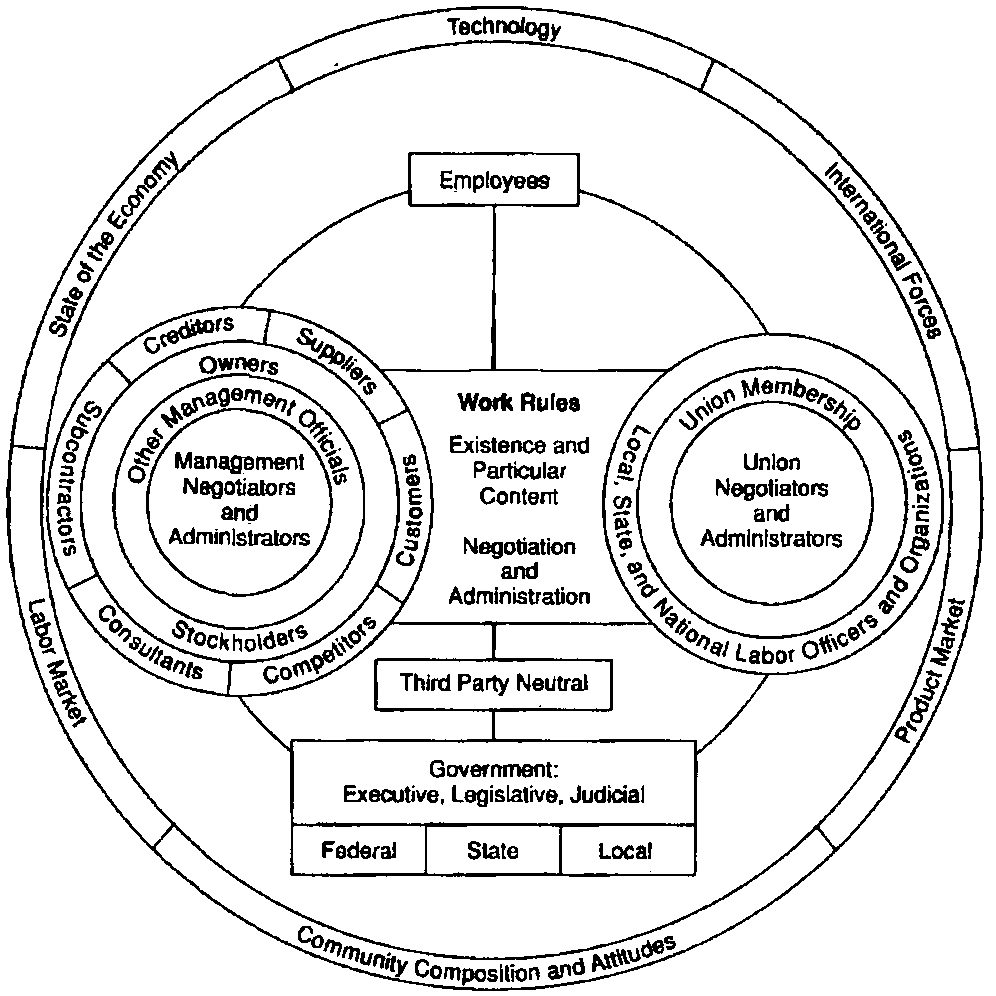
|
| The Figure:
A Model of the Labor Relations Process demonstrates the relationships
among internal participants of wkrs, unions, firms, the govt, & more,
& external factors & participants such as tech, the econ, globalization,
the mkt, the community & wider culture, the labor mkt, & more |
| |
EXTERNAL INFLUENCES WILL EXERT DIRECT & SIGNIFICANT
PRESSURE ON THE LABOR RELATIONS PROCESS |
|
| |
These influences, which are largely interrelated, will constrain &
limit negotiations of wages, econ benefits, wk rules, & other non econ
subjects |
|
| |
The realization of the global econ, coupled w/ the continuing trade
deficit problems, high cap costs for investments in new tech, the state
of the econ, & a wk force that is unprepared for a modern wkplace creates
challenges as well as opportunities for all the participants in the labor
relations process |
|
| |
A trade deficit occurs where foreign imports are greater than
exports |
|
| |
The Bush recession which began in 2007 which took the Obama admin several
yrs to deal w/, resulted in the decline of GDP, an increase in unemployment,
the collapse of the stock mkt, the collapse of the housing mkt, the closing
of plants, & more |
|
| |
The Bush recession of 2007-09 was a 'reality check' on unions, mgrs,
& wkrs; & resulted in re negotiations of many labor agreements |
|
| |
Since 2015 there has been over 5 yrs of job increases, stk mkt growth,
increase in the GDP, econ expansion, & more |
|
| |
The prosperity of the 2010 meant that unions were able to negotiate
some wage increases, but b/c of the low level of unionization in the econ,
wages overall in the econ, have only grown slowly |
|
| |
SOME OF THE MOST IMPORTANT EXT INFLUENCES FOR UNIONS
TO ATTEND TO ARE PUBLIC OPINION & THE MEDIA |
|
| |
Public opinion generate through the media will continue
to influence wkr attitudes toward unions & their subsequent decisions
to unionize &/or participate in various col barg activities such as
strikes |
|
| |
The extent of external influence on union & mgt participants has
not been accurately measured & is: generally small, always there,
always shifting, & variable in its significance |
|
| |
A shift in media portrayal Of unions & col barg appears to be taking
place |
|
| |
Unions involved in Easter Airlines & Pittston coal miners' strikes
in the 90s were portrayed as underdogs fighting for a principle against
financially questionable mgt practices, & this has become more the
norm
than the exception |
|
| |
During some stages of the 1990 prof baseball players' strike, mgt was
portrayed as being more greedy & unreasonable than players |
|
| |
However as is the case w/ many prof sports labor mgt conflicts, one
reason the public often sides w/ mgt is b/c of the upper class level of
the salaries the players receive, which are highly publicized |
|
| |
It is important to note that the owners & their corps are much
less well know, & people have little understanding that they receive
even higher income from prof sports |
|
| |
And any violence that occurs during any strike, eg the Pittston &
Greyhound strikes, as well as allegations of corruption, only hurts the
union image |
|
| |
MGT'S RESPONSE TO EXT INFLUENCES WILL BE TO PURSUE GREATER
CONTROL
VIA 'HARD & SOFT' TACTICS |
|
| |
In the future, mgt will seek labor agreements that increase
its freedom to direct floor operations such as fewer job classifications,
contain or reduce costs, & directly related compensation to the org's
financial results |
|
| |
Some firms will use tactics which increase pressure on the unions &
their members prior to negotiations |
|
| |
Some firms advertise for replacement wkrs & have new applicants
line up outside the employment office w/in viewing distance of the wkplace
so the present wkrs are aware of intentions to replace strikers |
|
| |
LABOR'S RESPONSE TO EXT & INT INFLUENCES WILL BE
TO MIN STRIKES & FOCUS ON COOPERATION, CAMPAIGNS,
PUBLICITY,
& LEGAL REMEDIES |
|
| |
Unions will focus on external influences impacts on job
security |
|
| |
Labor agreement provisions for employment guarantees, advance notice
of layoffs & tech change, restrictions on subcontracting, & job
retraining & relocation services, & more |
|
| |
Unions will be reluctant to use strikes to obtain their bargaining
objectives |
|
| |
The number of wkr days lost due to this barg alt has decreased in every
decade since the 80s |
|
| |
In response to 'hard ball' tactics of mgrs, unions will increasingly
resort to corp campaigns as an alt to strikes |
|
| |
Unions will wage campaigns on many fronts, making it difficult for
mgt to plan a response as is possible in preparation for a strike |
|
| |
Corp campaign tactics will include adverse publicity about the firm,
consumer boycotts, targeting financial instits that do business w/
the firm, pol lobbying, & putting pressure on shareholders |
|
| |
Unions will increase their use of info picketing & tele picketing
to advise shoppers to avoid patronizing non union retail estb |
|
| |
Unions will play an ever increasing role in the financial arena |
|
| |
Unions are learning to use their financial clout by purchasing stock
or participating in corp takeovers |
|
| |
There will also be a greater focus by unions on ESOPs |
|
| |
The AFL CIO has estb the Employee Partnership Fun (EPF) for which it
hopes to raise funds for small & medium size financial deals |
|
|
|
THE INTERNAL INFLUENCES THAT ARE EXPECTED TO CHANGE
FOR LABOR INCLUDE BARG APPROACHES, & A DEVELOPMENT OF COOPERATIVE
RELATIONS |
|
| |
The barg approaches that will be used by mgt & unions are difficult
to predict |
|
| |
It would appear that external influences will generate parallel goals
for the participants; namely, the firms survival that is necessary for
revenues, returns to shareholders, & wkrs' jobs |
|
| |
This situation could result in more integrative, problem solving contract
negotiations & admin |
|
| |
The approach of problem solving contract negotiations advanced by the
Bureau of Labor Mgt Relations & Cooperative Programs of the US DOL
as a 'win win' approach to col barg |
|
| |
The win win approach of the DOL included principles barg, collaborative
barg, integrative bar, & mutual gain among its advocated practices |
|
| |
Several conditions are necessary for labor mgt coop to occur on a wide
range basis |
|
| |
Mgt, union officials, & wkrs must clearly recognize a payoff for
their efforts |
|
| |
Unions might find it difficult to cooperate if their efforts resulted
in higher productivity & fewer jobs |
|
| |
Labor & mgt tend to forget their motivation for & related maintenance
of cooperation in good times |
|
| |
NEW MECHANISMS FOR COOPERATIVE LABOR RELATIONS WILL
BE DEVELOPED |
|
| |
Adequate mechanisms for cooperative efforts need to be
estb |
|
| |
In various wkr input programs, a 2 way commo mechanism needs to be
estb so wkrs can voice opinions w/o fear of mgl retaliation & union
officials do not have to worry about their org & positions being subverted
by the process |
|
| |
Problem solving relies on the sharing of sufficient, even confidential
info such as financial & production data, sales, &/or revenue projections
btwn mgt & unions so both may be informed participants |
|
| |
Info exchange related to another cooperation prerequisite:
sound interpersonal relationships |
|
| |
Some research has indicated that this condition will be more important
than econ pressures of the past in implementing successful cooperative
programs |
|
| |
Unions & mgt will need to trust each other & cooperation will
be more likely to occur insinuations where at least some mgrs experience
'shared hardship' of reduced wages & benefits &/or layoffs |
|
| |
ANTAGONISM WILL CONTINUE BTWN UNIONS & FIRMS
B/C OF THE PRESENT LEGAL PROCEDURES OR ESTBING REP RTS FOR UNIONS |
|
| |
There are reasons labor finds it difficult to trust mgt |
|
| |
Wkrs find it difficult to accept mgt's requests to control wage demands
&/or accept wage reductions when they read about exec pay levels &
raises |
|
| |
After adjusting or inflation, factory wkr pay rates have remained approximately
constant |
|
| |
Representation rts are essentially designed to lead to an adversarial
relationship, esp in the 1st negotiation |
|
| |
The organizing campaign typically includes unpleasant, perhaps degrading,
statements & brochures about the opposite party |
|
| |
If the union is successful, some negative sentiments are carried over
to the negotiation table |
|
| |
Both parties spend sizable amts of time, money, & resources in
organizing campaigns, all of which could be spent on ways to make the org
more productive & competitive |
|
| |
Other nations have a less adversarial approach to the steps for organizing |
|
| |
The Canadian procedure relies on card signing by wkrs to certify the
union & 3rd party arbitration of the 1st contract if the 2 parties
are unable to negotiate it on their own. |
|
| |
Current law allows for extensive delays & minor penalties for violating
the laws |
|
| |
The extensive delays allowed by present law not only frustrate wkrs
who want representation rts but provide the means by which firms may forestall
unionization & wkr representation at the barg table |
|
| |
W/ such small penalties, some firms build legal violation into their
labor relations strats |
|
| |
UNIONS WILL FOCUS ON CHANGES TO THE LAW &
LEGAL
REMEDIES TO ADDRESS 'FREE RIDERS' IN RT TO WK STATES, TO ORGANIZE
SUPERVISORS, & TO CREATE CARD CHECK OFF REPRESENTATION |
|
| |
In the future there will be a closer examination of some of the legal
concepts that have been basic to the labor relations process |
|
| |
Our public policy should examine labor rel processes in other nations
& consider those concepts that work |
|
| |
In the US, supervisory wkrs are excluded from union representation
rts & after buyouts or plant closings, these jobholders were frequently
the 1st ones to be laid off or fired |
|
| |
In the changing nature of the wkplace, the line btwn supervisor &
wkr is becoming ever more narrow |
|
|
|
Another concept to examine is the union obligation to represent
barg unit wkrs who do not financially support the union |
|
| |
It is not fair for union members to bay barg rep & contract admin
expenses for the non paying wkrs |
|
| |
In cases where the wkrs want union rep but are unable to achieve a
majority, there should be some mechanism, called card check off, by which
these wkrs can be represented or obtain some form of recognition rts for
assoc members |
|
| |
MANY BELIEVE THAT UNIONS ARE AN IMPORTANT BULWARK
TO THE POWER OF CORPS |
|
| |
The US cannot afford to allow the number of unions to shrink
to such a small % that they no longer serve effectively as a balancing
force to the corp coalition & govt |
|
| |
Non unions wkrs should be educated to realize the 'spill overs' they
receive from the labor agreements |
|
| |
The future will not see an end of adversarial relationships & thus
it will be difficult when corps hold out a handshake w/ one hand while
trying to clobber unions w/ the other |
|
| |
There is little reason to expect that govt at any level will substantially
change the content & direction of existing labor legislation, except
that Republican states are attacking unions at that level |
|
| |
GENDER, RACE, IMMIGRATION, LGBT
RTS, & MORE ARE ISSUES WHICH UNIONS ARE NOW ADDRESSING AS IMPORTANT
WKPLACE & SOCIETAL ISSUES B/C THE PURSUIT OF JUSTICE REQUIRES
IT |
|
| |
In the future, as women become increasingly committed to
the labor force, they may become less satisfied w/ their traditional jobs
& so more prone to struggle for comparable worth & unionism |
|
| |
As the South becomes increasingly industrialized, both racial tensions
& anti union sentiments may decline |
|
| |
Unions may win converts among college trained members of Baby Boomers,
Gen X & the Millennial b/c only a fraction of these grps can be accommodated
in the prof & mgrl jobs creating frustration which may incline them
towards unions |
|
| |
Immigration & the rts of immigrant wkrs as well as LGBT rts have
been in the undergrd econ for too long, & thus have not been addressed
by unions, corps, govt, wider society or others |
|
| |
Unions are now developing mechanisms & policies to bring immigrant
wkrs into the mainstream econ, recognizing them as green card wkrs, &
eventually citizens |
|
| |
Unions have supported the efforts of the LGBT community to receive
fair treatment in the wkplace, including spousal benefits, freedom from
discrim in hiring, firing, & promotions |
|
| |
UNIONS WILL FOCUS ON JUSTICE & VOICE FOR
WKRS,
& EXPAND THEIR EFFORTS TO ESTB JUSTICE & VOICE FOR
ALL CITIZENS,
UNION MEMBERSHIP NOTWITHSTANDING |
|
| |
Unions must move beyond just focusing on more wages &
benefits & wkplace rules to consider the welfare of society as a whole |
|
| |
As Samuel Gompers stated,
We want more school houses & less jails, more books & less
arsenals;...
More learning & less vice, more constant work & less crime,
more leisure
& less greed, more justice & less revenge
In fact more of the opportunities to cultivate our better natures,
to make personhood
more noble & beautiful, & childhood more happy & bright |
|
|
| |
There will continue to be internal struggles w/in unions on strat |
|
| |
Strats can focus on one or two wkr preference categories, including:
first, short run, measurable & material improvements in the wkplace
conditions, & second, long run broad improvements affecting wkrs off
the job life |
|
| |
In the past unions have primarily focuses on short run material goals
for wkrs on the job, but unions must, & are beginning to focus on long
run improvement for all society |
|
| |
Unions in the future will, & are focusing on both short run benefits
for wkrs & long run benefits for all of society |
|
| |
Other schisms are inevitable w/in the labor mvmt, such as that btwn
younger & older wkrs |
|
| |
In some cases the trad benefits of seniority have been weakened by
large layoffs & mgrl barg pressures for fewer job classifications |
|
| |
Addl barg over benefit cost containment such as insurance & pension
will exacerbate the differences btwn younger & older wkrs, & a
fair way forward must be found |
|
|
